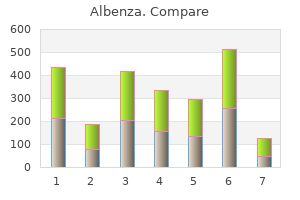
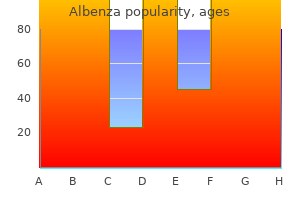
Amy C. Donihi, PharmD, BCPS, FCCP
 https://www.pharmacy.pitt.edu/directory/profile.php?profile=34 Common sites of traumatic injury in the orbitofrontal treatment quincke edema cheap albenza on line, temporopolar and lateral temporal areas of the brain are specifically included symptoms valley fever best purchase albenza. It is important to distinguish encephalomalacia from atrophy treatment xyy order albenza 400mg on line, the former resulting from a remote insult to the brain and the latter suggesting an ongoing process of neurodegeneration symptoms at 4 weeks pregnant purchase genuine albenza online. Encephalomalacia in a vascular territory suggests infarction rather than traumatic injury. This section of the report follows the current reporting standard, in which the interpreter is advised to discuss all relevant abnormalities seen on imaging, whether or not they may be associated with a dementing illness. Finally the option is included for the radiologist to recommend that the study be escalated for review by a subspecialty neuroradiologist with specific expertise in dementia. Choi, PhD 1-Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Emory School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia 2-Department of Biomedical Informatics, Emory School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia 3-Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia 4-Northside Radiology Associates, Atlanta, Georgia Corresponding Author: Falgun H. Accuracy, receiver operated curves, and area under the curve were calculated and tabulated. These rules based methods, however, were dependent on identifying specific words 1, 2 and phrases based on human references and annotations of training set reports and some 6, 7 were beholden to domain-specific medical lexicons and ontologies. Moreover, the performance of both non-neural and neural network models has yet to be demonstrated using radiology reports containing acute and communicable findings. As adapted from 3 Chokshi et al, each radiology report was classified for 5 categories: 1) study severity, 2) acute intracranial bleed, 3) mass effect, 4) acute stroke and 5) hydrocephalus using a scale of 0 Page 5 of 18 (normal) to 2 (new or worsening finding that would warrant a phone call to the ordering team). Next, to evaluate the performance of the three machine learning algorithms for classification of acute, communicable findings on the reports, all findings that were scored 0 or 1 were grouped together were grouped a negative for acute, communicable findings and those scored 2 as positive for acute communicable findings. This conversion to a binary outcome system allowed us to train the algorithms to be more accurate for clinically relevant findings. Word2Vec is open-source software that converts raw text into word vectors represented in Cartesian space. This allows contextual relationships between words and phrases to be geometrically evaluated and their strength can be quantified. The primary metric was accuracy, which was measured by dividing agreed finding on annotation by the total finding on annotation. The accuracies achieved by neural network models in the five classes for identification of acute and communicable findings range from 0. More sophisticated methods such as neural network based deep learning techniques. With increased mandates by federal regulators to Page 10 of 18 26 demonstrate quality, improve outcomes, and reduce costs, there is an increasing need to develop scalable and reliable methods of unstructured data mining. However, human annotation of such reports requires expertise in head imaging and can be laborious. The advent of multi institutional annotated reference sets will likely obviate these limitations. The information discovered by algorithms can be used for outcomes, quality improvement, cost analysis, and operations research. Natural Language Processing Technologies in Radiology Research and Clinical Applications. Tumor information extraction in radiology reports for hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Natural language processing of radiology reports for the detection of thromboembolic diseases and clinically relevant incidental findings. Extracting information on pneumonia in infants using natural language processing of radiology reports. Natural language processing: state of the art and prospects for significant progress, a workshop sponsored by the National Library of Medicine. Peeling away the black box label: clinical validation of a MaxEnt machine learning character n-gram feature set for acute lung injury. Convolutional neural networks for biomedical text classification: application in indexing biomedical articles. Scores Class Total 0 1 2 Severity of Study 58 940 402 1400 Acute Blood 653 546 201 1400 Mass Effect 751 443 206 1400 Acute Stroke 1113 173 114 1400 Hydrocephalus 1078 172 150 1400 Page 16 of 18 Tables continued Table 2. Pre hyperchloremic acidosis, hypokalemia, growth retardation (in children receiving ventionofrenalcalculicomposedofuricacidorcystine. Inhibition of renal carbonic anhydrase, resulting in self-limiting urinary ex cretionofsodium,potassium,bicarbonate,andwater. Alkaline diuresis Drug-Drug: Excretion of barbiturates, aspirin, and lithium isqand may lead prevents precipitation of uric acid or cystine in the urinary tract. Excretion of amphetamine, quinidine, procainamide, and fects: Lowering of intraocular pressure. Notify Patient/FamilyTeaching health care professional immediately if neurologic symptoms worsen or ifpatient Instruct patient to take as directed. Take missed doses as soon as possible unless becomesmoredyspneicandralesorcracklesdevelop. PotentialNursingDiagnoses Caution patient to use sunscreen and wear protective clothing to prevent photo Disturbedsensoryperception(visual)(Indications) sensitivityreactions. Evaluation/DesiredOutcomes Decrease in intraocular pressure when used for glaucoma. If therapy is not effec tive or patient is unable to tolerate one carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, using an othermaybeeffectiveandmoretolerable. Perlman is clinical Professor of neurology at the david geffen school of Medicine at ucla. Perlman has been the director of the ucla ataxia clinic since 1986, where she has engaged in clinical research and has published numerous articles on the inherited and sporadic ataxias. Perlman has been a tremendous asset to the national ataxia foundation and to those affected by ataxia. We are fortunate that in the past fve years, several pharmaceutical companies, partnering with research groups, have begun to add drugs to their pipelines that may have application to cerebellar ataxia in the near future. Even in a situation where there really appears to be nothing else to offer, sharing of information and seeking new information together can provide strength and encouragement to the patient and family, which is the true foundation of the therapeutic relationship. Muscles show decreased tone, resulting in defective posture maintenance and reduced ability to check excessive movement (rebound or sway). Vestibular ataxia has prominent vertigo (directional spinning sensations) and may cause past-pointing of limb movements, but spares speech. Sensory ataxia has no vertigo or dizziness, also spares speech, worsens when the eyes are closed (positive Romberg sign), and is accompanied by decreased vibration and joint position sense. Acquired ataxias may have more sudden or subacute onset and progression (weeks to months) and be asymmetrical or frankly focal in presentation. Presynaptic impairment of cerebellar inhibitory synapses by an autoantibody to glutamate decarboxylase. Gluten ataxia in perspective: epidemiology, genetic susceptibility and clinical characteristics. Additional laboratory studies can then be ordered (blood; urine; spinal fuid; biopsy of muscle, nerve, or brain). Table 3 is a list of laboratory studies that can be performed on any ataxic patient, with or without a family history of ataxia, to help defne the ataxia phenotype and to look for associated features and acquired causes. Pathogenetic classifcation would group scas 1-3, 6, 7, 12, 17, and drPla as polyglutamine (triplet repeat or cag repeat) disorders; scas 8, 10, 31, and 36 as other repeat types; scas 4, 5, 11-16, 23, 27, and gss as resulting from other mutation types; and scas 6, 13, 19, 22, and Ea-1, 2, and 5 as primary channelopathies. May reduce French (broader age of onset, cognitive impairment) expression of ataxin-1 in Purkinje cells, and mutant ataxin-1 may reduce expression families described.
They are made in the bone marrow and circulate in the blood for approximately 10 days medicine for stomach pain buy cheapest albenza, and are measured by thousands per microliter L symptoms of dehydration purchase albenza in india. When blood comes into contact with anything other than the smooth lining of the blood vessels symptoms 7 dpo bfp discount albenza 400 mg mastercard, platelets stick together to form a plug and release chemicals that further assist clot formation medicine university cheap albenza 400 mg mastercard. Thrombocytopenia, a platelet count below 50,000, can occur with bone marrow suppression from chemotherapy and/or radiation, leukemia, malignancies of the bone and autoimmune disorders. Medications that increase the production of white blood cells in the bone marrow. Thrombocytosis, an increase in the platelet count, can occur with dehydration, spleen dysfunction, or as a response to injury or inflammation. It is important to use age and pregnancy-specifc normal ranges for the white blood cell count. A repeat complete blood count with peripheral smear may provide helpful information, such as types and maturity of white blood cells, uniformity of white blood cells, and toxic granulations. The leukocyte differential may show eosinophilia in parasitic or allergic conditions, or it may reveal lymphocytosis in childhood viral illnesses. Leukocytosis is a common sign of infection, particularly bacterial, and should prompt physicians to identify other signs and symptoms of infection. The peripheral white blood cell count can double within hours after certain stimuli because of the large bone marrow stor age and intravascularly marginated pools of neutrophils. Stressors capable of causing an acute leukocytosis include surgery, exercise, trauma, and emotional stress. Other nonmalignant etiologies of leukocytosis include certain medi cations, asplenia, smoking, obesity, and chronic infammatory conditions. Symptoms suggestive of a hematologic malignancy include fever, weight loss, bruising, or fatigue. If malignancy cannot be excluded or another more likely cause is not suspected, referral to a hematologist/oncologist is indicated. It is important for clinicians to pregnancy, there is a gradual increase in the evant fnancial affliations. By two weeks of age, the life cycle of leukocytes includes devel this decreases to approximately 5,000 to opment and differentiation, storage in the 20,000 per mm3 (5. Stem reach adult levels of 4,500 to 11,000 per mm3 cells in the bone marrow produce cell lines 1004Downloaded from the American Family Physician website at Lym Leukocytosis is not a reliable indicator of C 6 phoblasts develop into various types of T postpartum bacterial infection. Myeloblasts further Patients with leukocytosis and no other signs of C 19 differentiate into monocytes and granulo systemic infammatory response syndrome do cytes, a designation that includes neutro not require blood cultures. A relatively small pool (2% to 3%) of leukocytes circulate freely in the peripheral blood1; the rest stay depos Table 1. White Blood Cell Count Variation with Age ited along the margins of blood vessel walls and Pregnancy or in the spleen. Once a leukocyte is Patient characteristic Normal total leukocyte count released into circulation and peripheral tis Newborn infant 13,000 to 38,000 per mm3 sues, its life span ranges from two to 16 days, 9 (13. To calculate the absolute cell count, the total leukocyte Stem cell count is multiplied by the differential per centage. The most common type of leukocytosis Platelets Erythrocyte Lymphocyte is neutrophilia (an increase in the absolute number of mature neutrophils to greater than 7,000 per mm3 [7. Normal White Blood Cell syphilis, viral infections, hypersensitivity Distribution reactions, and certain subtypes of leukemia or lymphoma. Lymphocytosis is more likely White blood Normal percentage of to be benign in children than in adults. Selected Conditions Associated with Elevations Isolated basophilia (number of basophils in Certain White Blood Cell Types greater than 100 per mm3 [0. Eosinophils Allergic conditions, dermatologic conditions, eosinophilic esophagitis, idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome, Nonmalignant Etiologies malignancies, medication reactions, parasitic infections A reactive leukocytosis, typically in the Lymphocytes Acute or chronic leukemia, hypersensitivity reaction, range of 11,000 to 30,000 per mm3 (11. Dur ing the recovery phase after hemorrhage or hemolysis, a rebound leukocytosis can occur. In the acute stage of many bacte rial infections, there are primarily mature and immature neutrophils (Figure 2); sometimes, as the infection progresses, there is a shift to lymphocyte predominance. An 18-year-old neutropenias, such as typhoid fever, rickett woman with distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy for benign sial infections, brucellosis, and dengue. Note neutrophils (arrows) with < 3 lobes but not defnitive, marker of the presence of to nuclei (band cells). Lymphocytosis in a 70-year-old woman with a history of tion, such as rheumatoid arthritis, infam chronic lymphocytic leukemia presenting to the emergency depart matory bowel disease, or a granulomatous ment with a fve-day history of subjective fevers, sore throat, and disease, may also exhibit leukocytosis. Note many mature lymphocytes (small nuclei near the size of a red blood cell with thin rim cytoplasm; black arrows) Malignant Etiologies and many smudge cells (white arrows). Leukocytosis may herald a malignant dis order, such as an acute or chronic leukemia (Figure 3), or a myeloproliferative disorder, such as polycythemia vera, myelofbrosis, or essential thrombocytosis. A previous article on leukemia in American Family Physician reviewed the features and differentiation of malignant hematopoietic disorders. Chronic leukemias are most com monly diagnosed after incidental fndings of leukocytosis on complete blood counts in asymptomatic patients. Patients with fea tures suggestive of hematologic malignancies require prompt referral to a hematologist/ oncologist (Table 5). Eosinophilia in malignancy in a 76-year-old man with a his kocytosis includes identifying historical tory signifcant for metastatic prostate cancer presenting for che clues that suggest potential causes (Figure 5). The peripheral smear should be Fatigue, weakness examined for toxic granulations (suggestive Fever > 100. On evaluation of a leukocytosis with Physical examination fndings lymphocyte predominance, a monomorphic Lymphadenopathy population is concerning for chronic lym Petechiae phocytic leukemia, whereas a pleomorphic Splenomegaly or hepatomegaly (varying sizes and shapes) lymphocytosis is Laboratory abnormalities suggestive of a reactive process. Predominantly immature cells on peripheral As indicated by the history and examina smear 3 tion fndings, physicians should consider White blood cell count > 30,000 per mm (30. Radiologic studies may include chest radiography (to identify infections, some malignancy. If hematologic stressful events, medication use, smoking malignancy is suspected, additional confr status, and history of splenectomy or sickle matory testing may include fow cytometry, cell anemia. Leukocy Data Sources: the primary literature search was tosis lasting hours to days has a different completed using Essential Evidence Plus and included differential diagnosis. In addition, PubMed searches were performed using the terms leu persists for weeks to months. No Yes No further workup necessary Obtain additional history and perform physical examination Leukocytosis explained by history or patient characteristics. No Yes No further workup necessary Patient presents with: Weight loss, fatigue, night sweats, fevers Abnormal red blood cell and platelet count Immature leukocyte forms (blasts) Chronic duration (weeks or years) History of or risk factors for malignancy, splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, bruising No Yes Consider nonmalignant etiologies Consider malignancy: Which cell line is affected Hematology/oncology consultation Consider additional testing to include fow cytometry, cytogenetic testing, or molecular testing of the bone marrow or peripheral blood Neutrophilia (> 7,000 per Monocytosis (> 880 per mm3 [0. Air Advance: eosinophil infltration of solid tumors is an Force Eglin Family Medicine Residency Program, Eglin early and persistent infammatory host response. Leukocytosis, leukopenia, and other reactive University of the Health Sciences School of Medicine, changes of myelopoiesis. Diagnostic value of laboratory tests in identifying seri ous infections in febrile children: systematic review. Comparison of the test characteristics of procalcitonin to C-reactive protein and 3. Surviving sepsis campaign: interna and differential leukocyte counts percentiles in normal tional guidelines for management of severe sepsis and pregnancy. Leukocyte blood this adult patient with suspected bacteremia require count during early puerperium and its relation to puer blood cultures Panic-attack-induced transient leukocytosis in a analysis of 1,004 consecutive patients. Buy discount albenza on line. Pulmonya: Sakit na Nakamamatay – ni Doc Mon Fernandez (Lung Doctor) #16. This alters the physico-chemical properties of the hemoglobin molecule substantially treatment integrity cheap albenza online mastercard, resulting in polymerization of hemoglobin when deoxygenated symptoms in dogs cheap albenza 400mg mastercard. As the HbS polymerizes medications over the counter generic 400mg albenza amex, it distorts and dehydrates the red cell treatment abbreviation buy albenza 400 mg visa, causing it to assume the sickle shape. HbS can resume its normal shape when it is reoxygenated, and so the sickling process is potentially reversible. However, with repeated sickling and unsickling, the cell accumulates enough membrane damage to become permanently sickled. These irreversibly sickled cells are apparent on the peripheral blood smear and have a short life span. HbF in a cell inhibits HbS polymerization, thus its quantity and its distribution in each cell will affect the likelihood of sickling. In general, patients who have more cells with relatively high HbF levels have less severe disease. Sickle cells interact with endothelium and other blood cells to cause vaso-occlusion, particularly in the microvasculature. Sickling is highly dependent on the sickle hemoglobin concentration in the red cell, and is thus ameliorated by the presence of higher levels of HbF or, in the heterozygous state, HbA. An adenine (A) to thymidine (T) transversion (A6T) at codon 6 in the hemoglobin gene on chromosome 11 leads to the substitution of a glutamic acid codon 6 S by a valine codon. HbS polymer injures the erythrocyte and leads to a heterogeneous population of sickle cells with damaged membrane cytoskeleton, reduced cation and water content, and altered distribution of membrane lipids. In the vasculature, sickle cells interact with endothelium and other blood cells to cause vaso-occlusion. The normal balance of vasoconstriction versus vasodilation is therefore skewed toward vasoconstriction, endothelial activation, and proliferation. Clinical Manifestations of Sickle Cell Disease: Manifestations of sickle cell disease begin at about 6 months of age, when beta globin chain production becomes dominant and the levels of fetal hemoglobin decline. Hemolytic Anemia and its consequences: Sickled red cells are very undeformable and are unable to negotiate the small vessels in the liver and spleen. They are phagocytized by macrophages in both organs causing a chronic extravascular hemolytic anemia. Most people with sickle cell anemia have hematocrits in the 25-30% range and sickle cells can be seen on peripheral smear (fig 5. They are also prone to the complications of chronic hemolysis discussed in Chapter 4, including aplastic crises due to parvovirus infection, folate deficiency, bilirubin gallstones, and iron overload. Life-threatening episodes of acute anemia may occur in children due to sequestration of red cells in a large spleen. After the spleen atrophies, the liver is the site of the ongoing chronic hemolysis. Vaso-occlusion the sickle cell patient is subject to a lifelong, body-wide destructive process caused by occlusion of the microvasculature with ischemic death (infarction) of tissue. Microinfarctions lead to acute pain crises as well as to extensive acute and chronic organ damage. The deformed sickled cells sequester in the microvasculature, injuring and activating endothelial cells. Sickle cell patients with the highest rate of hemolysis have the highest reticulocyte counts and the highest vaso occlusive risk. Neutrophils are elevated in most patients with sickle cell disease, an indicator of a chronic inflammatory state. Patients with higher neutrophil counts at baseline are at highest risk for serious vaso-occlusive complications such as stroke, acute chest syndrome, and priapism. The first manifestation may be painful swelling of the hands and feet called dactylitis. This syndrome can be life-threatening and is treated with supplemental oxygen, transfusion or exchange transfusion, nitric oxide, bronchodilators, and antibiotics. The finding of increased blood turbulence on a cranial Doppler study identifies a child as being at high risk for stroke. Such individuals then undergo chronic transfusion therapy, which decreases the concentration of sickle cells and improves outcome. Leg ulcers, osteonecrosis of the femoral head, pulmonary hypertension, chronic kidney disease, heart failure, retinal disease, and increased fetal loss during pregnancy are among the more common manifestations. Infection Because of recurrent micro-occlusive events, the spleen atrophies in most sickle cell patients. This results in significant susceptibility to encapsulated organisms, especially the pneumococcus. Children are usually treated with penicillin prophylaxis from infancy until at least age 6. Infarcted tissue is particularly vulnerable to infection; this is a particular problem in bone, where Salmonella and Staphylococcal infections predominate. Prevention and Treatment Early diagnosis and care through a comprehensive sickle cell clinic is very helpful. A major therapeutic breakthrough in sickle cell disease has been the use of hydroxyurea. This agent can increase HbF production, decrease inflammation, affect cell-cell interactions, and improve the hydration status of the red cell. Children treated with hydroxyurea prior to autosplenectomy retain splenic function longer, show better growth curves, fewer vaso occlusive events, and a slightly higher baseline Hb. In the adult population, hydoxyurea treatment has dramatically improved the quality of life for many patients. Treatment with iron chelating agents (deferoxamine, given intravenously, or deferasirox, given orally) may decrease the incidence of end organ failure due to iron overload. The only curative treatment for sickle cell anemia is allogeneic bone marrow transplant. This is not commonly performed due to a shortage of suitable donors and the potential morbidity associated with bone marrow transplant, which must be weighed against the somewhat unpredictable clinical course of sickle cell disease in an individual patient. Sickle Trait A S Sickle trait (HbA/S: ) found in 10% of African-Americans, is basically asymptomatic and should not be considered a disease. In special situations, such as severe dehydration or travel to very high altitudes, sickling may occur. Denial of employment or of life or health insurance because of sickle trait is not justified and is illegal in many states. Some abnormal hemoglobins may: crystallize (hemoglobin C) cause decreased production of the globin chain (hemoglobin E) denature (hemoglobin Koln) cause methemoglobinemia (hemoglobin M). About 3% of African-Americans are A/C heterozygotes and one in 10,000 is a C/C homozygote. The C trait (A/C) is asymptomatic with a normal hemoglobin and a normal blood smear. The peripheral smear shows almost 100% target cells and rare hemoglobin crystals within the red cells. The shortened red cell life span is due to the crystals, which increase red cell rigidity and lead to phagocytosis by splenic macrophages. S C Red cells with compound heterozygosity do sickle but S/C disease is generally milder than S/S disease. It is due to a single th amino acid substitution of lysine for glutamic acid at the 27 position of the beta globin chain. Instead of polymerizing like sickle hemoglobin or crystallizing like hemoglobin C, this amino acid substitution decreases production of an otherwise normally functioning beta globin chain, i. Like other hemoglobinopathies and thalassemias, it is thought to offer some protection against malaria. With increasing immigration from Southeast Asia, HbE is emerging as a significant concern in the United States. HgE becomes very clinically significant when in the compound heterozygous state with beta thalassemia. Unstable hemoglobins (Prototype: Hb Koln) Unstable hemoglobins (those that denature) are a rare cause of congenital hemolytic anemia. Mutations and deletions occur in the vicinity of the heme pocket, which disrupts the stability of the heme-globin linkage. Precipitation of the hemoglobin into 1-2 micron particles called Heinz bodies then occurs.
Akinetic mutism may be the nal state common to the end-stages of a number of neurodegenerative pathologies medications 2 times a day purchase genuine albenza line. Akinetic mutism from hypothalamic damage: successful treatment with dopamine agonists medicine administration order albenza 400 mg without a prescription. Cross References Aphasia; Aphemia Alexia Alexia is an acquired disorder of reading medicine cabinet purchase albenza 400mg with amex. Patients lose the ability to recognize written words quickly and easily; they seem unable to process all the elements of a written word in parallel medicine go down buy 400mg albenza otc. Alexia without agraphia often coexists with a right homonymous hemianopia, and colour anomia or impaired colour perception (achromatopsia); this latter may be restricted to one hemield, classically right-sided (hemiachromatopsia). Patients tend to be slower with text than single words as they cannot plan rightward reading saccades. The various forms of peripheral alexia may coexist; following a stroke, patients may present with global alexia which evolves to a pure alexia over the following weeks. Pure alexia is caused by damage to the left occipitotemporal junction, its afferents from early mesial visual areas, or its efferents to the medial temporal lobe. Global alexia usually occurs when there is additional damage to the splenium or white matter above the occipital horn of the lateral ventricle. Hemianopic alexia is usually associated with infarction in the territory of the posterior cerebral artery damaging geniculostriate bres or area V1 itself, but can be caused by any lesion outside the occipital lobe that causes a macular splitting homonymous eld defect. Visual agnosia: disorders of object recognition and what they tell us about normal vision. There is evidence from functional imag ing studies that alexithymics process facial expressions differently from normals, leading to the suggestion that this contributes to disordered affect regulation. Alexithymia: an experi mental study of cerebral commissurotomy patients and normal control subjects. These phenomena were associated with an intrinsic tumour of the right (non-dominant) frontal lobe. These phenomena are often associated with a prominent grasp reex, forced groping, intermanual conict, and magnetic move ments of the hand. Frontal type: shows features of environmental dependency, such as forced grasping and groping, and utilization behaviour. A paroxysmal alien hand has been described, probably related to seizures of frontomedial origin. The mechanism of alloaesthesia is uncertain: some 20 Allodynia A consider it a disturbance within sensory pathways, others consider that it is a sensory response to neglect. Cross References Allochiria; Allokinesia, Allokinesis; Neglect Allochiria Allochiria is the mislocation of sensory stimuli to the corresponding half of the body or space, a term coined by Obersteiner in 1882. There is overlap with alloaesthesia, originally used by Stewart (1894) to describe stimuli displaced to a different point on the same extremity. The treatment of neuropathic pain is typically with agents such as carba mazepine, amitriptyline, gabapentin, and pregabalin. Interruption of sympa thetic outow, for example with regional guanethidine blocks, may sometimes help, but relapse may occur. Cross References Hyperalgesia; Hyperpathia -21 A Allographia Allographia this term has been used to describe a peripheral agraphia syndrome character ized by problems spelling both words and non-words, with case change errors such that upper and lower case letters are mixed when writing, with upper and lower case versions of the same letter sometimes superimposed on one another. These defects have been interpreted as a disturbance in selection of allographic forms in response to graphemic information outputted from the graphemic response buffer. Central vision may be preserved (macula sparing) because the blood supply of the macula often comes from the cilioretinal arteries. Cross References Hemianopia; Macula sparing, Macula splitting; Quadrantanopia; Visual eld defects Amaurosis Amaurosis is visual loss, with the implication that this is not due to refractive error or intrinsic ocular disease. The term is most often used in the context of amaurosis fugax, a transient monocular blindness, which is most often due to embolism from a stenotic ipsilateral internal carotid artery (ocular transient ischaemic attack). Giant cell arteritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome are also recognized causes. Amblyopia may not become apparent until adulthood, when the patient sud denly becomes aware of unilateral poor vision. The nding of a latent strabismus (heterophoria) may be a clue to the fact that such visual loss is long-standing. This is a component of long-term (as opposed to working) memory which is distinct from memory for facts (semantic memory), in that episodic memory is unique to the individual whereas semantic memory encompasses knowledge held in common by members of a cultural or linguistic group. A precise clinical denition for amnesia has not been demarcated, perhaps reecting the heterogeneity of the syndrome. Amnesia may be retrograde (for events already experienced) or anterograde (for newly experienced events). Retrograde amnesia may show a temporal gradi ent, with distant events being better recalled than more recent ones, relating to the duration of anterograde amnesia. Plasma exchange or intravenous immunoglobulin therapy may be helpful in non-paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis associated with autoantibodies directed against voltage-gated potassium channels. Functional or psychogenic amnesia may involve failure to recall basic auto biographical details such as name and address. Reversal of the usual temporal gradient of memory loss may be observed (but this may also be the case in the syndrome of focal retrograde amnesia). |