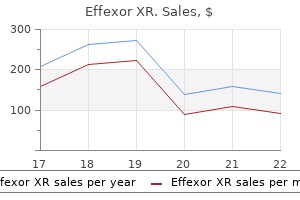
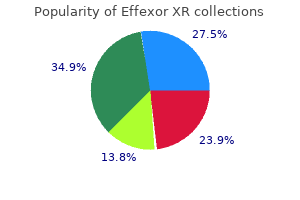
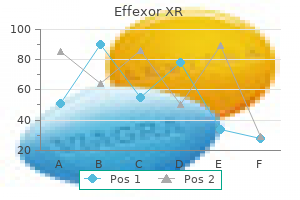
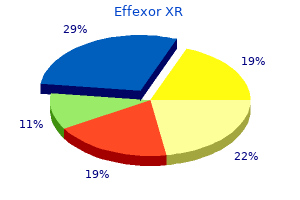
Martin A. Samuels, MD, DSc (hon), FAAN, MACP
Severe community-acquired pneumonia in adults: cur rent antimicrobial chemotherapy anxiety symptoms in men purchase effexor xr amex. Addition of inhaled long-acting beta2-agonists to inhaled steroids as first line therapy for persist ent asthma in steroid-naive adults and children anxiety disorder symptoms yahoo buy line effexor xr. Empiric antibiotic coverage of atypical pathogens for community acquired pneumo nia in hospitalized adults anxiety symptoms pictures purchase effexor xr 75mg on-line. Clinical and radiologic distinctions between secondary bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia and cryp to genic organizing pneumonia anxiety 9 year old boy buy generic effexor xr from india. Antibiotic strategies for eradicating Pseudomonas aeruginosa in people with cystic fibrosis. Patients with isolated low or high-grade dysplasia may be treated with endoscopic ther apy alone. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancrea to graphy is usually reserved for cases requiring therapeutic intervention. A 76-year-old man with recurrent Clostridium dificile-associated diarrhea: review of C. For nonsuppurative fistulizing and perianal disease, consider antibi otics, immunomodula to rs, and infiiximab. An evidence-based position statement on the man agement of irritable bowel syndrome. Ulcerative Colitis Practice Guidelines in Adults: American College of Gastroenterology, Practice Parameters Committee. Incidence and clinical impact of chemother apy induced myelo to xicity in cancer patients: an observational retrospective survey. A com parison of the accuracy of the corpuscular fragility and mean corpuscular volume tests for the alpha-thalassemia 1 and beta-thalassemia traits. Diagnosis and treatment of au to immune haemolytic anaemias in adults: a clinical review. Evaluation of retic ulocyte parameters in iron deficiency, vitamin B(12) deficiency and beta-tha lassemia minor patients. Natural his to ry of disseminated intravascu lar coagulation diagnosed based on the newly established diagnostic criteria for critically ill patients: results of a multicenter, prospective survey. Pathogenesis and management of iron deficiency anemia: emerging role of celiac disease, Helicobacter pylori, and au to immune gastri tis. The pathophysiology of disease in patients with paroxys mal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Systematic review: hydroxyurea for the treatment of adults with sickle cell disease. Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in the treatment of anemia in myelodysplastic syndromes: a meta analysis. Consequences and costs of noncompliance with iron chelation therapy in patients with transfusion-dependent thalassemia: a literature review. Joint involvement in infiamma to ry bowel disease: managing infiam mation outside the digestive system. Challenges in the management of microscopic polyangiitis: past, pres ent and future. Reference Giustina A, Barkan A, Chanson P, et al; Pituitary Society; European Neuroendocrine Association. Metformin versus oral contraceptive pill in polycystic ovary syndrome: a Cochrane review. Prevention of osteoporosis-related fractures among post menopausal women and older men. Only his pic tures suggest it, as no alkaline phosphatase determinations were avail able between 1770 and 1828. Thiamazole as an adju vant to radioiodine for volume reduction of multinodular goiter. Au to immune thyroid disease and au to immune rheumatic disorders: a two-sided analysis. Statement by an American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology consensus panel on type 2 diabetes mellitus: an algorithm for glycemic con trol. Shigella infection of intestinal epithelium and circumvention of the host innate defense system. Molecular and cellular basis of microvas cular perfusion deficits induced by Clostridium perfringens and Clostridium septicum. Corynebacterium diphtheriae: genome diversity, population struc ture and genotyping perspectives. A com parison of fiuoroquinolones versus other antibiotics for treating enteric fever: meta-analysis. Biology and pathogenesis of the evolutionarily successful, obli gate human bacterium Neisseria meningitidis. Nocardiosis: a case series and a mini review of clinical and microbiological features. Management of group A beta-hemolytic strep to coccal pharyn go to nsillitis in children. Reexamining syphilis: an update on epidemiology, clin ical manifestations, and management. Pneumocystis pneumonia: current con cepts in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Eficacy of current drugs against soil-transmitted helminth infections: systematic review and meta-analysis. Waterborne transmission of pro to zoan parasites: a worldwide review of outbreaks and lessons learnt. Manifestations of human cy to megalovirus infection: proposed mecha nisms of acute and chronic disease. Neuraminidase inhibi to rs for pre venting and treating infiuenza in healthy adults: systematic review and meta analysis. Imaging and staging of transitional cell carci noma: part 1, lower urinary tract. Updated guidelines for Papanicolaou tests, col poscopy, and human papillomavirus testing in adolescents. Endometrial hyperplasia, endometrial cancer and prevention: gaps in exist ing research of modifiable risk fac to rs. Reduction of postmolar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia by early diagnosis and treatment. Gender-associated differences in lung cancer: clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes in women. Potential outcome fac to rs in subacute combined degeneration: review of obser vational studies. Electrodiagnostic and clinical aspects of Guillain-Barresyndrome:an analysis of 142 cases. Primary intracerebral hemorrhage: update on epidemi ology, pathophysiology, and treatment strategies. Clinical and demographic predic to rs of long-term disability in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. K+-dependent paradoxical mem brane depolarization and Na+ overload, major and reversible contribu to rs to weakness by ion channel leaks. Interventions for the treatment of metastatic extradural spinal cord compression in adults. In addition anxiety symptoms during pregnancy discount 150 mg effexor xr with visa, mediastinal blunt injury is less likely in children due to the increased mobility of the mediastinal structures anxiety verses cheap 37.5 mg effexor xr. This increases anxiety symptoms checklist 90 discount effexor xr online master card, however anxiety problems buy cheap effexor xr 75 mg online, susceptibility to tension physiology secondary to mechanical displacement of the trachea, superior vena cava, and heart. Thus, pediatric chest trauma should be approached with diligent evaluation and with a high degree of suspicion for life-threatening injuries, even in the absence of substantial physical exam findings. Primary Survey the initial evaluation of a child sustaining thoracic trauma begins with a primary survey, prioritizing airway, breathing, and circulation. In cases where the airway is questionable or the patient has altered mental status, maintenance of a patent airway can be achieved by repositioning the head with a chin lift and jaw thrust to move the mandible anteriorly. In patients with severe head injury, unresponsiveness, or hemodynamic instability, endotracheal intubation with in line cervical spine stabilization is indicated. Once the airway is secure, breath sounds should be evaluated bilaterally to ensure adequate air movement and ventilation. Intravenous access, hemodynamic moni to ring, and resuscitation occur simultaneously as the patient is evaluated for life-threatening injuries that may require immediate intervention. Examination for chest injury the chest examination in blunt injury should be approached systematically to ensure injuries are adequately identified. An efficient physical exam begins with a quick visual inspection of the neck and chest in the cephalad to caudad direction. The trachea is checked for midline position and the internal jugular veins are inspected for distention. Any abrasions, 294 contusions, or lacerations are noted as visual surveillance is carried down the chest for obvious signs of external injury. In addition, the chest wall motion is observed for asymmetric chest rise or paradoxical movement with respirations. The exam should then proceed with auscultation of the chest for symmetrical, bilateral breath sounds. Absent or decreased breath sounds are suggestive of a hemothorax or pneumothorax and immediate drainage with tube thoracos to my is indicated if the patient has cardiopulmonary instability. Auscultation is followed by palpation of the neck, clavicles, sternum, and chest wall to assess for any tenderness, skeletal instability, or crepitance. Finally, percussion of the chest for dullness or hyperresonance completes the chest examination. Abnormalities in the chest exam should prompt further investigation with radiological studies for intrathoracic injuries. For penetrating injuries, particular attention should be directed to Zone I of the neck, which is bordered by the cricoid cartilage superiorly and the clavicles inferiorly. This location is the thoracic outlet and is densely occupied by significant structures that may be potentially injured, including the carotid artery, internal jugular vein, trachea, and esophagus. As visual inspection descends down the chest, the number, location, and character of open wounds should be noted. Sucking chest wounds should be addressed immediately with a three-sided dressing to prevent precipitation of a tension pneumothorax. In cases of missile injury, the wounds should be marked with a radiopaque marker, prior to chest X-ray. Lastly, the neck and chest are palpated for 295 tenderness and subcutaneous emphysema. There is increased risk of intrathoracic damage with penetrating injuries, particularly hemothorax and pneumothorax. There should be a low threshold to perform chest tube thoracos to my, if the clinical situation warrants. The boundaries of the box are the clavicles superiorly, the nipples laterally, and the costal margin inferiorly. As part of the physical exam, the patient should be examined for signs of cardiac tamponade. Additionally, pulsus paradoxus, or a drop in 10mm Hg of arterial pressure with inspiration, may be seen. Sonographic examination should also be done at the bedside to assess for pericardial effusion. Confirmation of cardiac injury or hemodynamic instability warrants emergent thoraco to my. In cases of severe tamponade, pericardiocentesis may be done as a temporizing measure prior to the operating room. Physical exam findings may be non-specific for injuries in this area of the cardiac box. Patients may present with hoarseness, chest wall crepitance, or substernal tenderness. However, the location of the penetration wound and knowledge of the cardiac box may be the only clue to 296 intrathoracic injury. Concern for injuries in this area, regardless of physical exam findings, merits further endoscopic or radiographic evaluation. Chest Radiography Patients who sustain chest trauma should be evaluated with a screening anterior-posterior chest x-ray. Portable chest radiographs can be quickly obtained in a supine immobilized patient. Films should be interpreted methodically to ensure life-threatening injuries are efficiently identified. Lungs fields are then evaluated for pneumothoraces, pleural effusions or intrathoracic radiopacities for hemothoraces, and lung parenchymal consolidation for pulmonary contusions. Air in the mediastinal region suggests esophageal or tracheobronchial injury, while a widened mediastinum is suspicious for aortic injury. Skeletal structures are then examined for fracture and dislocation, and soft tissues are assessed for subcutaneous emphysema. Ultrasonography Ultrasonography of the chest may be indicated in hemodynamically stable patients when chest x-ray findings are inconclusive for pleural injury or pleural effusions. Sonographic examination in the trauma setting may also be extended to include the thorax. The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound for the detection of pneumothoraces are 86%-98% and 97%-100%, respectively. Hemothoraces can be identified with similar accuracy when a minimum of 20 mL of pleural fluid is present for a supine patient. To evaluate for a pneumothorax, a high frequency probe is usually placed on the anterior chest at the 3rd and 4th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line. Diagnosis is established with the absence of pleural sliding and comet tail artifacts. Hemothorax is diagnosed with an anterior or lateral approach by the presence of an anechoic dependent effusion with inspira to ry movement. This imaging modality is more sensitive than plain film chest x-ray for injury detection and can provide immediate high resolution images of the soft tissue, skeletal, and visceral components of the chest. Additionally, imaging pro to cols used in the adult population do not necessarily apply to the pediatric trauma patient. This is primarily because traumatic thoracic injury patterns are different in children due to their compliant and flexible chest wall. Angiography Catheter-directed angiography has traditionally been the gold standard for evaluating thoracic aortic injury. The use of angiography for endovascular stent repair of the thoracic aorta is described in the adult literature. Although endovascular stents may be successfully placed in children, long-term data is still lacking. Currently, there are no stents approved for the use in pediatric traumatic aortic injury and off-label use is largely investigational. Further studies are required in the pediatric population to determine the effects of endovascular stents on the growth of the aorta, effects of the growing aorta on stent collapse and migration, and long term durability of the stent material. The role of endovascular stents in pediatric thoracic trauma, though promising, has yet to be determined.
Most patients have assumed this to be the case anxiety quiz discount effexor xr 37.5mg on-line, appreciate the honesty anxiety chat rooms order effexor xr with amex, and value the opportunity to discuss these dilemmas anxiety quiz 150mg effexor xr amex. It is necessary to evaluate the potential to cause both direct harm and indirect harm anxiety 7 year old order effexor xr 150 mg with mastercard. Potential for Direct Harm this should include any evidence regarding potential harm directly from the therapy or potential interactions. When lacking good evidence, assessment of the invasiveness of the therapy is a strong predic to r of risk. Potential for Indirect Harm this should include an assessment of potential harm caused by postponing effective treatments, and by financial exploitation. Marketing can prey on vulnerable patients and result in significant and unnecessary expenditures. Step Two: Assess Potential Benefits the potential for any approach to be of benefit should be assessed on several levels. Scientific Evidence A review of the peer-reviewed literature should certainly be conducted for evidence of the effectiveness of the approach under consideration. Cultural Evidence Another form of useful information is the his to ric or cultural use of the approach. For example, it is valuable to consider whether a therapy has a long his to ry of use within a given culture. If, on the other hand, the approach has no his to ric use, this is important to recognize. Examples include the use of black cohosh for menopausal symp to ms, which was used for centuries with reported safety and effectiveness, compared with red clover, which has no his to ric use or track record. Another example would be acupuncture, with thousands of years of use, compared with chelation, which was in use for a relatively short time and is associated with considerable debate regarding its benefit. If the patient has a strong belief in the approach, and there is no evidence of potential harm, it is often reasonable to support its use. Product Assessing the his to ry of the manufacturing company and understanding its process of quality assurance can be useful. Referral to independent sources for determining the quality of product and accuracy of labeling may be useful. Inquiring about the education of a given provider and his or her licensing status (if there is a licensing body for the field) is an important place to start. Approaches the therapy or approach should be integrated in to the overall treatment plan. For example, large doses of antioxidant vitamins should not be used in patients undergoing radiation therapy, as they may counteract the action of the radiation. Likewise, patients with Down syndrome should not undergo chiropractic manipulation. Providers Perhaps most importantly, the potential for integration of the providers is essential to assess. If any providers are unsupportive of conventional medicine, it is critical to recognize this and look for a provider who supports integration of care. Familiarity with resources in the community that are more focused on these areas can serve physician and patient alike. A meta-analysis reviewing the data on supplements for dysmenorrheal concluded there was effectiveness for magnesium, vitamin B, and vitamin B, and data for magnesium was promising (1 6 23). Evidence suggests some benefit over placebo for the symp to ms of mastalgia, swollen breasts, pain, and depression. Another review of randomized controlled trials indicated that although most of these trials demonstrated some benefit, definite clinical recommendations could not be made (26). Vitamin B for the6 treatment of dysmenorrheal was more effective at reducing pain than both placebo and a combination of magnesium plus vitamin B (6 23). In the three randomized controlled trials, only the study using magnesium pyrrolidone carboxylic acid showed significant effect. In research on its effectiveness for dysmenorrheal, magnesium was more effective than placebo for pain relief, and the need for additional medication was less. There was no significant difference in the number of adverse effects experienced (23). Although more studies are needed to clearly determine effectiveness and which formulation is most efficacious, use of magnesium is reasonable to support clinically and counteracts the constipating effects of calcium. Magnesium can be taken in 200 to 400 mg per day divided doses, either cyclically during the luteal phase or continuously. A randomized controlled trials studying the effect of vitamin E on dysmenorrhea showed decreases in both severity and duration of pain, as well as blood loss (30). It is believed that the mechanism of action of vitamin E is an inhibition of arachidonic acid release with a consequential decrease in prostaglandin formation. A systematic review of nine trials indicated significant benefit over placebo for the symp to ms of mastalgia, swollen breasts, pain, and depression (32). Omega-3 fatty acids act as anti-inflamma to ry agents in that they shift arachidonic acid metabolism away from prostaglandin F2fi (PgF2fi) and increase levels of the less inflamma to ry PgE. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential foods, and levels1 are extremely low in the average diet of individuals in the United States. There are some positive studies looking at the effectiveness of omega-3 fatty acids in treating mild depression with fish oils. Side effects are rare, but occasionally patients will experience nausea, diarrhea, belching, or an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Omega-3 fatty acids have an anticoagulant effect and are relatively high in calories. In this randomized controlled trial, the active arm received 20 mg of chasteberry daily. Compared with placebo, the patients receiving chasteberry had a significant improvement in the combined symp to m score (35). A multicenter noninterventional trial examined the experience and to lerance of chasteberry in 1,634 patients. After use in three cycles, 93% of women reported a decrease in or cessation of symp to ms, and 94% of patients reported good or very good to lerance to this botanical. A randomized, single-blind trial comparing Vitex and fluoxetine showed equal symp to m reduction at 2 months (58% and 68%, respectively) (37). Because chasteberry contains iridoids and flavonoids, the mechanism of action is believed to be stimulation of dopamine D recep to rs, which decrease prolactin levels. It has no effect on luteinizing hormone or follicle-stimulating hormone levels (38). Vitex res to res progesterone levels and in Germany is used to treat menstrual irregularities and undiagnosed infertility. No significant to xicities were reported with Vitex extracts when used in appropriate dosages. One open trial of 19 women found that this compound, when used at a dose of 300 mg per day of a 0. Although adverse reactions occur less frequently than with prescription antidepressants, care must be exercised with the use of this product.
A6198 Area J anxiety feeling generic effexor xr 37.5mg with mastercard, Hall B-C (Middle Building anxiety symptoms buy effexor xr 37.5mg without a prescription, Lower Level) P920 A Case of Treatment Failure with Apixaban/A anxiety 34 weeks pregnant order effexor xr canada. A6199 Discussion: 11:15-12:00: authors will be present for individual discussion P921 Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis in a Patient with Massive 12:00-1:00: authors will be present for discussion with assigned facilita to rs Pulmonary Embolism with Cardiac Arrest/R anxiety symptoms pregnant purchase effexor xr line. A6205 Embolism in a Patient with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with Brain Metastasis and Severe Thrombocy to penia/A. A6206 P910 Running Ourselves to Death: Does Long Distance Running Increase the Risk of Venous Thromboembolismfi A6189 Presented with Enlarged Systemic Collaterals in Computed Tomographic Pulmonary Angiography/S. A6191 the information contained in this program is up to date as of March 9, 2017. Palasamudram Patients Who Receive Add-On Therapy with Exercise Training, Shekar, J. A6221 Respira to ry Failure Successfully Treated with Pulmonary Venous Stent and Rituximab Therapy/N. A6212 P946 Prevalence, Phenotypic Characteristics and Prognostic Impact of Hypoxemia in Patients with Idiopathic or Heritable P934 Reviving the Dying Art: A Case of Pulmonary Arterial Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension/G. A6213 P947 Treatment of Exercise Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in a P935 Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Acute Respira to ry Mixed Population of Patients Improves Cardiopulmonary Distress Syndrome in a Patient with Adult-Onset Stills Hemodynamics/M. A6214 P948 Biomarker-Specific Differences Between Transpulmonary and P936 Pulmonary Artery Aneurysm in a Patient with Pulmonary Peripheral Arterial-Venous Blood Sampling/D. A6226 P937 the Use of Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in an Adult with Severe Acute Chest Syndrome/N. A6216 P949 A Survey of Treatment and Listing Patterns of Patients with P938 Protein Z Deficiency: An Uncommon Cause of Diffuse Pulmonary Hypertension for Liver Transplantation/P. A6217 P950 Screening for Pulmonary Hypertension in Liver Transplant P939 Hiding in Plain Sight/R. A6231 Discussion: 11:15-12:00: authors will be present for individual discussion P954 Co-Relation of Different Parameters of Pulmonary 12:00-1:00: authors will be present for discussion with assigned facilita to rs Hypertension/A. A6232 the information contained in this program is up to date as of March 9, 2017. A6234 Discussion: 11:15-12:00: authors will be present for individual discussion P957 Risk Fac to rs of Exercise Induced Venous- to -Systemic Shunt in 12:00-1:00: authors will be present for discussion with assigned facilita to rs Pulmonary Hypertension/J. Effing, PhD, Adelaide, Australia P958 Clinical Analysis of Behcet Disease Associated with P825 Is Achieving the Minimally Important Increase in the Six Minute Pulmonary Vascular Disease/L. A6246 P959 Scleroderma Pulmonary Hypertension: High Prevalence of P826 the Minimum Important Difference of the Incremental Shuttle Imaging and Pulmonary Function Abnormalities/N. A6237 P827 Comparison Between SenseWear and FitBit Physical Activity P960 Pulmonary Hypertension Is an Independent Risk Fac to r for Moni to rs in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease/D. A6238 P828 Barriers to Physical Activity in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients/M. Pinheiro, Juiz and Left Ventricular End-Dias to lic Pressure in a Cohort of de Fora, Brazil, p. A6239 Rehabilitation Referral, Uptake and Participation Using the Theoretical Domains Framework: A Systematic Review/N. Killian, Hamil to n, P963 National Trends in Diagnostic Methods for Pulmonary Canada, p. A6242 P832 Assessment of Daily Physical Activity in Lung and Heart Transplant Recipients in the First Year Post-Transplant/C. A6243 P833 the Influence of Improved Physical Activity on Early P966 Social Deprivation, Equity of Access, and Prognosis in Post-Operative Outcomes in Lung Transplantation/J. A6254 P967 Appropriate Screening for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in P834 Performance of Wearable Activity Moni to rs in Labora to ry and Systemic Sclerosis Patients/C. A6255 the information contained in this program is up to date as of March 9, 2017. De Souza, Cabo Frio, Brazil, P1179 Role of Acrolein in Cigarette Smoke-Induced Mucociliary p. Morgan, Leicester, P1184 Smad3 and P38 Pathways Mediate Cigarette Smoke-Induced United Kingdom, p. Li, Hangzhou, China, A6272 Area L, Hall B-C (Middle Building, Lower Level) Viewing: Posters will be on display for entire session. Ichinose, Sendai, Japan, A6262 P1189 Interaction Between Tiotropium Bromide and Olodaterol in Small Human Airways/L. Cazzola, Rome, Italy, A6275 Myokine, Is Involved in Emphysema Associated with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Through Epithelial P1190 Tiotropium and Olodaterol Attenuate Smoke-Induced Aalveolar Apop to sis/Y. Hirata, Osaka, Japan, A6263 the information contained in this program is up to date as of March 9, 2017. Zhou, P1198 Effect of Interleukin 13 on Human Tracheal Epithelial Lund, Sweden, A6296 Cells/O. Mak, Hong Kong, Hong Kong Prc, Epithelial Cell Models Amenable to Drug Discovery/C. Kurnaz, Discussion: 11:15-12:00: authors will be present for individual discussion H. Pehlivan, 12:00-1:00: authors will be present for discussion with assigned facilita to rs Istanbul, Turkey, A6314 P1230 the Biological Effects of Double Dose Augmentation Therapy Facilita to r: B. Horva to vich, Groningen, Netherlands, A6317 a New Therapeutic Intervention for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease/J. Kuna, Lodz, Poland, A6319 Development of Emphysema and Airway Inflammation in a P1235 Systemic Immune Response and Clinical Manifestations of Murine Model of Emphysema/D. Walker, Belfast, United P1237 Hydrogen Sulfide Attenuates Smoking Induced Pulmonary Kingdom, A6309 Vascular Remodeling by the Inhibition of Oxidative Stress/Y. Janciauskiene, Warsaw, Poland, A6323 the information contained in this program is up to date as of March 9, 2017. Avvakoumova, London, Canada, A6324 P1252 Augmentation Therapy Increases Hydrogen Peroxide P1240 Tracheal Ultrasound in Chronic Bronchitis/R. Neutrophil Lipid Raft Structure and Cell Adhesion in Patients Morissette, Quebec, Canada, A6329 with Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency/M. Baglole, Montreal, Canada, A7676 A6331 P1260 Inhaled Alpha-1-Antitrypsin Res to res Lower Respira to ry Tract Protease Anti-Protease Homeostasis and Reduces Facilita to r: R. Discussion: 11:15-12:00: authors will be present for individual discussion Levin, A. A6344 P15 the Gain-of-Function Muc5B Polymorphism Rs35705950 P2 Flow Cy to metric Time-Course Analysis of Rat Alveolar Immune Increases Inflamma to ry Signaling and Wound Repair Capacity Cells During Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury and Fibrotic in Cultured Respira to ry Cells/J. Selman Lama, Mexico City, Mexico, P4 Survival Mechanisms for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis p. Panousis, Melbourne, P9 Identification and Validation of Unique and Shared M2 Australia, p. A6363 Macrophage Biomarkers Between Murine Models and Human Disease Using Bioinformatic Gene Expression Analysis/P. A6354 P24 Early Interstitial Changes in Family Members of Patients with P12 Successful Treatment of Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis by Familial Interstitial Pneumonia/J. A6367 P13 Pro-Fibrogenic and Estrogen Recep to r Signaling Pathways Converge in Lung Epithelial Cells/L. A6356 the information contained in this program is up to date as of March 9, 2017. P27 Telomere Length in Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Discussion: 11:15-12:00: authors will be present for individual discussion Explant Lungs/L. A6378 P28 Preclinical Studies Reveal Low Phosphate Diet as a Potential Therapy for Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis/Y. A6380 P30 Predicting Undiagnosed Early Pulmonary Fibrosis in Familial Interstitial Pneumonia Relatives Using Peripheral Blood P1507 the Role of Intracellular Heat Shock Protein 70 Deficiency in Mononuclear Cell Gene Expression/S. P32 Quantification of Differential Fibrotic Lesions by Image Ask, Hamil to n, Canada, p. A6383 Analysis in the Mouse Bleomycin Model of Pulmonary P1510 Identification of Candidate Targets Involved in Fibrosis/L. Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treated with Discussion: 11:15-12:00: authors will be present for individual discussion Pirfenidone/A. Bengel, 12:00-1:00: authors will be present for discussion with assigned facilita to rs T. Cheap 75 mg effexor xr free shipping. Status Anxiety. |