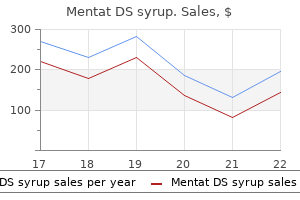
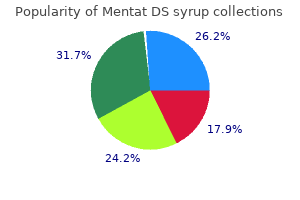
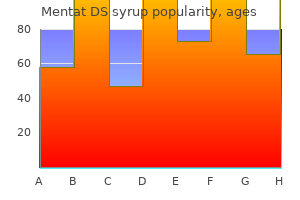
Clare E. Close, MD
Falsethe direct care staff member should always tie knots tightly and securely in order to prevent the resident from escaping medications list form generic mentat ds syrup 100 ml visa. Falsethe resident should be left alone and not interrupted until he or she calms down enough so the restraints can be removed hb treatment mentat ds syrup 100ml low cost. False It is okay to give a resident a medication so he or she falls asleep instead of wandering at night medicine nobel prize 2016 order mentat ds syrup 100ml overnight delivery. False It is not necessary to notify the residents responsible party when restraints are used medications enlarged prostate discount 100ml mentat ds syrup amex. The chapter will assist direct care staff in understanding difficult end of life decisions experienced by residents and family members. The chapter will provide information to assist direct care staff workers in supporting the family, resident, and direct care staff during the dying process. To understand end of life decisions such as Do Not Resuscitate orders, hospice care, etc. To be able to recognize the stages and awareness of death and dying to support the resident and family members during the process d. To understand the individualized process of bereavement, grief, and loss of a loved one. To be able to recognize the importance of person-centered care and support during the death, dying, and bereavement process 2. Take a moment to notice where you are, what you are doing, who is with you, how do you feel, what are the smells, sounds, and other specifics around you. Instruct the class to share only what they are comfortable sharing about this topic. The idea of dying may not have been a thought that a direct care staff member has thought about happening to them. It may be hard for a direct care staff member to connect with a person at the end of life. This exercise will give the direct care staff the opportunity to envision what it is like to be the person at the end of life and what it would mean to have the support and respect from the people surrounding them before death. When this question was asked during a study by Hallenbeck and associates some of the common themes of a good death involved: Home. Factors such as how, when and where death occurs for these individuals has change dramatically for older adults living today. The goal is for the power of attorney to make 702 decisions based on what the person would have originally wanted if he/she could communicate these wishes. Palliative care can be combined with hospice care or it can be used to lessen the symptoms of a disease or illness. Some older adults could be experiencing chronic illnesses or receiving hospice services. Elizabeth Kubler-Ross developed a five stage psychological response to help explain some of the emotions experienced at the end of life. Each person may respond by going through the stages backward, skipping steps, or never reaching the acceptance of their death. The job of a direct care staff worker is to meet the person at their point on their journey and support that individual. The grandson should respond in a supporting manner so that the resident does not become upset. Important: Each direct care staff member will have a different experience with the dying process. It is always ok to reach out to other staff members for support in handling the death or dying process of a resident. In the grieving process the body may react by causing headaches, stomach aches, and intestinal problems. The person may have a strong need to focus on the past and being with the deceased person. This fact can be an illusion based on the numbness felt from accomplishing the routine of preparing for the death arrangements. Once the arrangements have been planned and executed the bereaved may ultimately feel grief. The person may second guess decisions made because the deceased was the primary decision maker. In most cases, the direct care staff spend more time in the lives of their residents than they do with relationships outside of their workplace. It is important to recognize your own grief and be aware of your own needs during the process. Although it is important to recognize your feelings, it is important that you respect the residents decisions and provide support to them. It is important to accept and respect the fact that not all family members and loved ones will grieve in the same way as others. For example, having a community (the whole facility residents, staff, and families) meeting in which everyone can share stories of the person who died. Bibliography and Resources Death, Dying, and Bereavement Department of Social Services Curriculum Hallenbeck, J. Falsethe goal of hospice care is to provide a cure for the individuals chronic illness Describe one way that direct care staff can help when a person loses the ability to speak before death. What can be expected when a person is in the Bargaining stage of the Elizabeth Kubler-Ross Stage Model The person may ask their God or higher power to give them more time so that he or she will be able to see a significant event. Gerontologists specialize in the unique life stage of late life, special needs and issues that relate to older adults and to aging populations 724 in general. Geriatrics is a branch of medicine that looks at health and disease in later life. It is multidisciplinary, meaning it includes the study of physical, mental, and social changes in older people as they age. Mandated reporters are required to report suspected abuse, neglect, or exploitation of elders or incapacitated adults. These rights refer to treatment and care, privacy and confidentiality, personal choice, safety, and disclosure of information related to services and fees charged for accommodations, services, and care. Forgetting to do something for a resident happens to every worker once in a while. It includes threatening or humiliating with words, in a way that hurts or harms a persons emotional well-being, or makes them afraid. An individual diagnosed with autism may show signs of social impairment, communication difficulties, and repetitive behaviors. Many individuals with autism can work and live either independently or in a supervised environment. Clouding on the lens occurs and the pupil changes color from black to a cloudy white. A disease of the eye that results in the outside of the picture you normally see disappearing. This disorder is typically a result of prolonged used of antipsychotic medications. The alcohol prevents the proper breakdown of the Vitamin B1 in the body resulting in the deficiency. Chapter 6 Residents with Special Health Care Needs Angioplasty used to physically open a blocked coronary artery. There is a build-up of fatty deposits called plaque on the inside walls of arteries.
Immunologic studies reveal combine immunodeficiency consisting of selective IgA and IgG2 deficiency medications and mothers milk 2014 quality mentat ds syrup 100ml, cutaneous anergy and depression of in vitro T cell function study medicine zithromax order cheap mentat ds syrup online. Hyper-IgE syndrome is characterized by chronic pruritic dermatitis medicine lux purchase mentat ds syrup cheap online, recurrent staphylococcal infections (skin and respiratory tract) treatment 7th feb bournemouth cheap mentat ds syrup 100 ml free shipping, markedly elevated serum IgE, eosinophilia and coarse facial features. The diagnosis may be difficult since there is no clear definition of high IgE levels and IgE levels may fluctuate from time to time. In addition, a high IgE level with eosinophilia is commonly seen in severe atopic dermatitis. Therefore, recurrent staphylococcal infections involving the skin, lungs and joints with other features including a distinctive facial appearance, dental abnormalities and bone fractures are essential for the diagnosis. Treatment with good skin care and continuous antimicrobial therapy such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are necessary. The defect leads to recurrent and uncontrolled catalase positive organisms including S. The most common infections are lymphadenitis, abscesses of the skin, and of the viscera such as liver. Treatment includes short-term treatment of the infections, prophylactic trimethoprim-sulfa, recombinant human interferon-G (enhancing the production of reactive oxygen intermediates) and bone marrow transplantation. This condition is described in further detail in the chapter on neutrophil disorders. Killing of microbes is intact, but since the cells can not be mobilized to the point of inflammation and complement-mediated phagocytosis is impaired, the result is a lack of an inflammatory response. Histories of delayed separation of the umbilical cord, recurrent bacterial infections, necrotic skin lesions, severe gingivitis, periodontitis, and alveolar bone loss leading to early loss of deciduous and permanent teeth suggest the diagnosis. Treatment includes continuous antimicrobial therapy, good oral hygiene, white blood cell transfusions and bone marrow transplantation. Page 156 Clinical Approach to Suspected Immunodeficiencythe history should include the onset and type of the infections, the frequency, chronicity, severity and the responses to the previous treatments. The associated conditions such as failure to thrive, autoimmune disease, congenital anomalies and family history of consanguinity, fetal wastage and early childhood deaths should be noted. Infection with encapsulated bacteria such as Haemophilus influenzae type B, pneumococcus, etc. Complement Defects: Early complement deficiency: Sinopulmonary infection, autoimmune disease. Congenital agammaglobulinemia typically presents during the second 6 months of life when maternally transferred antibodies wane. Certain physical findings alert one to the possibility of primary immune deficiency. Failure to thrive secondary to recurrent infections is commonly seen in some antibody deficiencies and combined T and B cell deficiencies. Persistent sinopulmonary infections, especially ear drainage, pneumonia or bronchiectasis, are seen in antibody deficiencies, T and B cell deficiencies and complement deficiencies. Several congenital and hereditary conditions with musculoskeletal abnormalities are associated with immunodeficiency. These include Bloom syndrome, Fanconi anemia, trisomy 21, Turner syndrome, short-limbed skeletal dysplasia, cartilage-hair hypoplasia, Shwachman syndrome and ectodermal dysplasia. The proper choice of laboratory tests is based on a careful history and physical examination which target specific suspected immunodeficiency possibilities. The number of neutrophils, lymphocytes, abnormalities of white blood cells or red blood cell morphology, numbers and morphology of platelets should be noted. Certain culture results may point out a specific immune defect such as: 1) Encapsulated bacteria in antibody, T cell and complement deficiencies. In blood chemistry, a decreased globulin fraction suggests hypogammaglobulinemia, malnutrition, or protein loss. If the defect of B cells or humoral immunity defect is suspected, measurements of isohemagglutinins, immunoglobulin levels of IgG, IgA, IgM, specific antibody levels against of diphtheria, tetanus, H. It should be noted that normal levels of IgG, IgM and IgA in children are lower than that in adults. A second test for specific antibody levels is required after having a booster dose of the vaccine if the first test result is low. Measurement of IgG subclass levels should not be used as a screening test and may not yield any more useful information than a total serum IgG level with Page 157 specific antibody titers. An induration of 10mm or more to one antigen or more than one antigen of indurations of 5mm or more indicates normal cell-mediated immunity. Approximately 90% of normal adults show a good response to at least one antigen when three to five antigens are applied. A mother brings her son, a 6 year old boy with severe eczema, recurrent bacteria skin infections and history of staphylococcal pneumonia for evaluation of immunodeficiency. Sonson this is a 7 year old female who presents to the office with a chief complaint of a rash on her head, arms and legs. She had undergone chemotherapy, went into remission and subsequently received an allogeneic stem cell transplantation from her older brother 20 days ago. The rash started 3 days ago on her ears, palms of her hands and the soles of her feet, progressing further to her arms and legs. It has not progressed to involve her trunk or her extremities and there is no desquamation or bullae formation. The rash is an erythematous, maculopapular rash on her palms and soles bilaterally, and on the anterior aspects her arms and legs. Transplantation is recommended only in high-risk situations or when conventional treatment fails. Major sources of stem cells for transplantation include bone marrow, peripheral blood and cord blood. Since the mid-1990s, peripheral blood-derived stem cells have been used with increasing frequency over the traditional marrow cells. Umbilical cord blood is a new and promising source of hematopoietic progenitor cells with remarkable proliferative potential, which may overcome the limitation of their relatively low absolute cell numbers. Because only a small number of cells are collected, successful transplants are typically limited to smaller sized recipients. When the stem cells are from an identical twin, the transplant is termed syngeneic. When the stem cells are harvested from the recipient, the transplant is termed autologous. And lastly, when the stem cells are from someone other than the recipient, it is termed allogeneic. A 6-of-6 match refers to matching these three genes, each of which have two alleles. When none of the 6 alleles match, it is termed a mismatch and the various degrees of mismatch are termed one-antigen mismatch, two-antigen mismatch, etc. In the United States, the National Marrow Donor Program has typed nearly 4 million volunteer donors and uses 118 donor centers and over 57 transplant centers to add 40,000 potential new donors each month. The initial phase of stem cell transplantation entails the administration of the preparative regimen: chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy. Other combinations are also used during this conditioning period and include drugs such as etoposide, melphan, carmustine, cytosine arabinoside, thiotepa, ifosfamide, and carboplatin. The combinations are designed to eliminate malignancy, prevent rejection of new stem cells, and to create space for the new cells. The stem cells infusion takes over an hour, although this time frame depends on the volume infused. Before infusion, the patient is premedicated with acetaminophen and diphenhydramine to reduce the risk of hypersensitivity reaction. After stem cell infusion, the primary focus of care is managing the high-intensity preparative regimen. During this period, patients have little or no marrow function and are neutropenic, thus they must depend on transfusions for maintaining erythrocytes and platelets at acceptable levels. The rate of engraftment is a function of the preparative regimen, the nature and dose of stem cells, and the administration of medications that can suppress recovery. Engraftment, typically defined as a neutrophil count greater than 500 per cubic mm and a platelet count of 20,000 per cubic mm can occur as soon as 10 days to as long as several weeks after infusion. Graft rejection may occur immediately, without an increase in cell counts, or may follow a brief period of engraftment.
Scurvy was described by the Crusaders medications and breastfeeding generic 100 ml mentat ds syrup with amex, during the sieges of numerous European cities symptoms west nile virus purchase mentat ds syrup with american express, and as a result of the famine in 19th century Ireland treatment genital warts cheap mentat ds syrup 100ml with mastercard. Skeletal and vascular lesions in scurvy probably arise from a failure of osteoid formation medications similar buspar purchase mentat ds syrup 100ml with visa. In infantile scurvy the changes are mainly at the sites of most active bone growth; characteristic signs are a pseudoparalysis of the limbs caused by extreme pain on movement and caused by haemorrhages under the periosteum, as well as swelling and haemorrhages in areas of the gums surrounding erupting teeth (25). In adults one of the early, principle adverse effects of the collagen-related pathology may be impaired wound healing (26). Vitamin C deficiency can be detected from early signs of clinical deficiency, such as the follicular hyperkeratosis, petechial haemorrhages, swollen or bleeding gums, and joint pain, or from the very low concentrations of ascorbate in plasma, blood, or leukocytes. The Sheffield studies (26, 27) and later studies in Iowa (28, 29) were the first major attempts made to quantify vitamin C requirements. The studies indicated that the amount of vitamin C required to prevent or cure early signs of deficiency was between 6. The Iowa studies (28, 29) and Kallner et al (30) established that at tissue saturation, whole body vitamin C content is approximately 20 mg/kg, or 1500 mg, and that during depletion vitamin C is lost at 3 percent of whole body content per day. Clinical signs of scurvy appear in men at intakes lower than 10 mg/day (27) or when the whole body content falls below 300 mg (28). Note that during infection or physical trauma, an increase in the number of circulating leukocytes occurs and these take up vitamin C from the plasma (31, 32). Therefore, both plasma and leukocyte levels may not be very precise indicators of body content or status at such times. However, leukocyte ascorbate remains a better indicator of vitamin C status than plasma ascorbate most of the time and only in the period immediately after the onset of an infection are both values unreliable. Intestinal absorption of vitamin C is by an active, sodium-dependent, energy requiring, carrier-mediated transport mechanism (33) and as intakes increase, the tissues progressively become more saturated. However, under steady state conditions, as intakes rise from around 100 mg/day there is an increase in urinary output in so that at 1000 mg/day almost all absorbed vitamin C is excreted (34, 35). Definition of population at riskthe populations at risk of vitamin C deficiency are those for whom the fruit and vegetable supply is minimal. Epidemics of scurvy are associated with famine and war, when people are forced to become refugees and food supply is small and irregular. Persons in whom the total body vitamin C content is saturated can subsist without vitamin C for approximately 2 months before the appearance of clinical signs, and as little as 6. In general, vitamin C status will reflect the regularity of fruit and vegetable consumption but also socio-economic conditions, because intake is determined not just by availability, but by cultural preferences and cost. In Europe and the United States an adequate intake of vitamin C is indicated by the results of various national surveys (36-38). In the United Kingdom and Germany, the mean dietary intakes of vitamin C in adult men and women were 87 and 76 (37) and 75 and 72 mg/day (36), respectively. Likewise a survey of Latin American children in the United States suggested that less than 15 percent consumed the recommended intake of fruits and vegetables (40). Reports from India show that the available supply of vitamin C is 43 mg/capita/day, and in the different states of India it ranges from 27 to 66 mg/day. However, it is difficult to assess the extent to which sub-clinical infections are lowering the plasma vitamin C concentrations seen in such countries. Data describing a positive association between vitamin C consumption and health status are frequently reported, but intervention studies do not support the observations. Low plasma concentrations are reported in patients with diabetes (47) and infections (48) and in smokers (49), but the relative contribution of diet and stress to these situations is uncertain (see Chapter 17). Epidemiologic studies indicate that diets with a high vitamin C content have been associated with lower cancer risk, especially for cancers of the oral cavity, oesophagus, stomach, colon, and lung (39, 50-52). However, there appears to be no effect of consumption of vitamin C supplements on the development of colorectal adenoma and 76 Chapter 6: Vitamin C stomach cancer (52-54), and data on the effect of vitamin C supplementation on coronary heart disease and cataract development are conflicting (55-74). Currently there is no consistent evidence from population studies that heart disease, cancers, or cataract development are specifically associated with vitamin C status. Dietary sources of vitamin C and limitations to vitamin C Ascorbate is found in many fruits and vegetables (75). Citrus fruits and juices are particularly rich sources of vitamin C but other fruits including cantaloupe, honeydew melon, cherries, kiwi fruits, mangoes, papaya, strawberries, tangelo, watermelon, and tomatoes also contain variable amounts of vitamin C. Vegetables such as cabbage, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, bean sprouts, cauliflower, kale, mustard greens, red and green peppers, peas, tomatoes, and potatoes may be more important sources of vitamin C than fruits. This is particularly true because the vegetable supply often extends for longer periods during the year than does the fruit supply. In many developing countries, limitations in the supply of vitamin C are often determined by seasonal factors. For example, mean monthly ascorbate intakes ranged from 0 to 115 mg/day in one Gambian community in which peak intakes coincided with the seasonal duration of the mango crop and to a lesser extent with orange and grapefruit harvests. These fluctuations in dietary ascorbate intake were closely reflected by corresponding variations in plasma ascorbate (11. Vitamin C is also very labile, and the loss of vitamin C on boiling milk provides one dramatic example of a cause of infantile scurvy. The vitamin C content of food is strongly influenced by season, transport to market, shelf life, time of storage, cooking practices, and chlorination of water. Blanching techniques inactivate the oxidase enzyme and help to preserve ascorbate as also will low pH, as in the preparation of sauerkraut (pickled cabbage). In contrast, heating and exposure to copper or iron or to mildly alkaline conditions destroys the vitamin, and too much water can leach it from the tissues during cooking. The use of citrus fruits by the British navy in the 18th century gave rise to the term limey, a colloquial term for British sailors. However, it is important to realise that the amount of vitamin C in a food is usually not the major determinant of a foods importance for supply, but rather regularity of intake. Such data can indicate the important contribution the potato can make to human vitamin C requirements even though the potato vitamin C concentration is low. An extensive study has been made of losses of vitamin C during the packaging, storage, and cooking of blended foods (maize and soya-based relief foods). In these experiments, ascorbate in the whole body was catabolised at an approximate rate of 3 percent/day (2. There is a sigmoidal relationship between intake and plasma concentrations of vitamin C (79). Under near steady state conditions, plateau concentrations of vitamin C are achieved by intakes in excess of 200 mg/day 8) (34). Figure 8 Relationship between intake and plasma concentrations of vitamin C 78 Chapter 6: Vitamin C A body content of 900 mg falls half way between tissue saturation and the point at which clinical signs of scurvy appear. An intake of 45 mg vitamin C will produce a plasma ascorbate concentrations near the base of the steep slope of the diet-plasma dose response curve 8). No turnover studies have been done in women, but from the smaller body size and whole body content of women, requirements might be expected to be lower. Purchase cheap mentat ds syrup on-line. Talk- मन की शुद्धि के बाद समझ से भक्ति ध्यान.
|