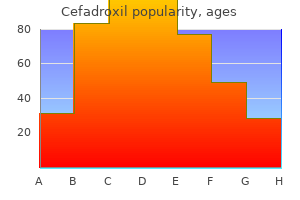
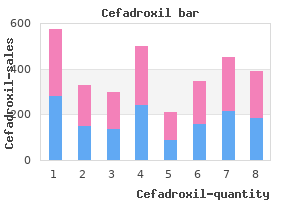
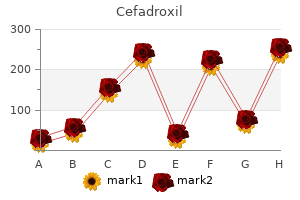
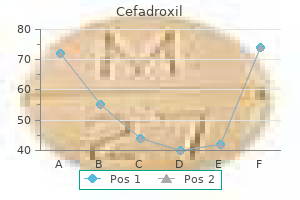
Peter Joseph Mogayzel, Jr, M.D., Ph.D.
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/0007546/peter-mogayzel There are forms that African American people learned to use when they were in the south that are now considered part of the dialect because antibiotics for uti nursing cheap cefadroxil 250 mg online, when those speakers left the south antibiotic resistance lab purchase cheap cefadroxil on line, they took those forms with them and they became part of the language of the community infection joint pain cheap cefadroxil 250mg with mastercard. Undifferentiated Pronoun Case is used more frequently by African American children than by African American adults antibiotic 48 hours generic cefadroxil 250 mg. Typically we think of double negation, or the use of two negatives in one sentence. But the negative is used for the purpose of emphasis, so you may see many multiple negatives in one sentence. When working with a typically developing African American child, the deletion of the past tense creates no ambiguity about whether what is being spoken about is in the past or in the present. But, in the case of a child who is not typically developing, for example, a child with language impairment, ambiguity is possible. It is not used frequently by young children, but rather, if it is used, we tend to see it in teenagers or adults. The plural is usually marked somewhere in the speech context so there is no ambiguity that the word which is missing the plural marker is in its plural form. The speaker is, in a sense, smoothing out irregular patterning of forming reflexive pronouns by applying the same rule to all forms in the set. Appositive Pronoun is where both the pronoun and the noun, or the noun phrase that it refers to , are included in the utterance, rather than one or the other. It is typically used by older children because the verb phrase is more sophisticated. The speaker is talking about something that happened in the remote past that is habitual or continuous. The following six forms are not typically heard from children in the early elementary grades such as preschool through grade two. However, they are used by children in the upper elementary, middle, or high school grades. Resultative Be Done: Unlike the Completive Done that tells you something is over, Resultative Be Done tells you what is going to happen if you keep doing something. Non-inverted Question is a feature that we frequently hear adults using with their children. Presence or absence of these features help to discern the density of dialect and can indicate the possible presence of morphosyntactic features within a language sample. Using Salt to Assess Written Language In our technology-driven society, brevity seems to be appreciated when we are texting or typing out 140-character tweets. However, strong written language skills are still a vital part of the language arts curriculum starting in kindergarten th and extending through 12 grade. Students are expected to write opinion pieces, informative/explanatory texts, narratives, and research texts. Both of these can be helpful repeated measures for written language samples gathered under similar conditions. When transcribing written language samples, it is important to follow the special rules for transcribing spelling errors in order to make accurate word counts. When dividing utterances into C-units (also called T-units within written language samples) it is best to treat them as if they were oral language samples. How the text was generated should also be considered when assessing written language. Or was it created by a word processing program or a speech-to-text software application such as Dragon Dictatefi The question must be considered, does the text generation method contribute to the end resultfi Hand writing can be difficult to decipher making it challenging to identify words and word boundaries. Certainly, spelling can be a challenge, particularly when consistent forms are not used. Written samples can be coded to capture any feature of writing an evaluator is interested in tracking. By marking more features within the sample, more information can be yielded from the analysis. However, samples can be compared time 1/time 2 to track progress in writing skills. The following coding scheme is recommended to capture written language performance. Type correct grapheme assuming they are Letter reversals developmentally appropriate. Numbers Example: 8 or eight Sound effects Type as they were written Extra space within written word. Figure 9-3 the Analyze menu contains a number of reports which can be used to analyze this sample. The student wrote 25 utterances (sentences) using, on average, seven words per sentence. There were eight omissions (words and/or bound morphemes) and one word or utterance marked as an error.
If missed entirely antibiotic resistance washington post purchase discount cefadroxil on-line, Child and International Society for Pediatric the person will die suggested antibiotics for sinus infection purchase genuine cefadroxil. Although there are multiple countries bacteria 4 pics 1 word order cefadroxil cheap, and is likely to be more common where precipitating causes medicine for uti relief buy cheap cefadroxil 250mg on-line, infections are the most there is food insecurity. The elderly, intravenous glucose is dificult if the health facility the chronically ill and institutionalised populations is distant or has limited opening hours. Diabetes, and the continuum of blood glucose levels even below the diabetes diagnostic threshold, are associated with a wide range of cardiovascular conditions that collectively comprise the largest cause of both morbidity and mortality for people with diabetes. Across the full spectrum of glucose levels, and using lipid- fasting glucose, haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), or lowering medications. Risk is also strongly afected mortality have declined substantially in many by smoking and by low levels of physical activity. Lowering only about 10% of the world, leaving the status high blood pressure and high glucose levels of trends and progress in most of the world and using drugs that lower cholesterol can each unclear. In addition, procedures and deaths from acute coronary community- and population-wide approaches that syndromes, myocardial infarction, ischaemic and facilitate increasing levels of physical activity and haemorrhagic stroke, as well as sudden death. The review emphasised impact on quality of life and the economic status of that more high-quality population-based studies both individuals and the society in which they live. Kong, Japan, Singapore, Spain, Sweden, the United Kingdom and the United States of America. All Over the past 20 years or so, systematic screening have underlined the heavy and increasing financial has been adopted in several countries. In the United Kingdom, 25% of people with diabetes45 and, in the United States associated risks. In some of nephropathy, whereas in type 1 diabetes, cases, consideration of pancreas and kidney hypertension is more often a consequence of transplantation should take place. In a United States and glomerular filtration as screening tests in of America study conducted between 1999 and this field. It afects ulcers and amputations result in a the distal nerves of the limbs, particularly those signifcant reduction in the quality of the feet. It mainly alters the symmetrical sensory function causing abnormal feelings and of life and increase the risk of progressive numbness. Diabetic foot complications are severe and Less than one-third of physicians chronic. The reported prevalence of diabetes-related the resulting missed diagnoses peripheral neuropathy ranges from 16% to as much contribute greatly to these high as 87%57 with painful diabetes-related neuropathy rates of morbidity and mortality. Prevalence manifestations of diabetes-related peripheral is higher for men than for women. This diabetes without foot ulcers, the cost of care for prevalence increases to 29% in people over 50 people with diabetes and foot ulcers is 5. The development of impaired glucose Hyperglycaemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes tolerance and type 2 diabetes. It is known that early onset of diabetes clinical hypoglycaemia; premature delivery; predisposes these women at particularly high shoulder dystocia and/or other birth injuries; risk of macrovascular disease and microvascular the need for intensive neonatal care; neonatal disease. Since disease duration is a major risk determinant, complications seen in adults micro- and macro-vascular complications may develop with diabetes. Therefore, children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes, after five years of disease duration, need routine screening for high blood pressure, albuminuria and retinopathy. Type 2 diabetes Children and adolescents with diagnosed before the age of 20 years is associated diabetes and those in vulnerable with an accelerated risk of retinopathy, nephropathy and nerve damage compared with type 1 diabetes at a families need special attention comparable age and duration. All of the health costs of treating the complications of diabetes, both acute and the complications of diabetes long-term, contribute significantly to the overall economic impact of the condition. This relates both account for over 50% of the to direct costs, for which the costs of hospitalisation direct health costs of diabetes. These significant economic efects of diabetes- the early detection and improved management related complications on direct costs have been of diabetes complications will have benefits not well known, from early estimates reported from pan- only for the individuals with diabetes but also for European studies89 to , for example, the most recent the wider health economy. For example, intensive assessment of diabetes health costs for the United blood pressure control among people with type States of America. As for other very cost-efective compared with no screening; aspects of the economics literature, there is a dearth and comprehensive foot care can save costs by of diabetes-wide, population-based data from low- preventing ulcers in people with high risk of ulcers and middle-income countries dealing with the costs 97 compared with routine foot care. Direct costs are clearly related to information in cost-of-illness studies in diabetes is the number of complications present, with mean the contribution of specific complications to indirect annual health expenditures for people with four or 98 costs. Also, Bommer et al have commented on the more complications 20 times more than in people need for more information on the contribution of with diabetes but without complications. Further analyses by Pearson-Stuttard et al,100 of cases of cancer of the pancreas. The equivalent show clearly that, in all regions of the world, the figure for endometrial cancer in women is 38. Some metabolic Metformin, a common oral therapy in type 2 factors associated with diabetes, such as reduced diabetes, has been suggested as protective against testosterone levels, may be involved. For some individuals at very high risk for cancer occurrence or re-occurrence, however, these issues the efects on future cancer risk of diferent blood may require more careful consideration. Gum disease raises blood glucose levels and may contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes or to poorer glycaemic control in existing diabetes. Poor oral health and missing teeth lead to poorer diet and nutrition, and poorer quality of life in people with diabetes. Dental treatment is safe for people with diabetes and good oral health should be part of diabetes management by medical care professionals. Gum disease raises blood glucose levels and may contribute to the Diabetes and oral health development of type 2 diabetes Diabetes negatively afects all soft and hard tissues or to poorer glycaemic control in 111 surrounding the teeth. Neurological consequences of diabetic ketoacidosis at initial presentation of type 1 diabetes in a the end result of untreated periodontitis is tooth prospective cohort study of children. Edited by Ogle G, Middlehurst the world report clinically significant reductions A, Silink M, Hanas R. Admission diagnosis of cerebral malaria in adults in Chairside screening for diabetes in the dental an endemic area of Tanzania: implications and clinical surgery is generally well accepted by dental care description. Diabetic ketoacidosis: a not have diabetes in, for example, Denmark,158 the silent death. Diabetes mellitus, professionals and their patients to promote early fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective diagnosis, prevention and co-management of studies. Diabetes and Cause-Specific retinopathy, diabetic macular edema and related vision loss. Global trends in diabetes complications: a review of people with type 2 diabetes mellitus attending the Diabetic current evidence. Review Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical of studies utilising retinal photography on the global consequences, and medical therapy: part I. International Diabetes Federation and the Fred Hollows experiences of diabetic retinopathy screening and treatment. Kidney disease guidelines on the management and the prevention of the in diabetes. A systematic review and meta-analysis guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, of glycemic control for the prevention of diabetic foot classification, and stratification. Sakthong P, Tangphao O, EiamfiOng S, Kamolratanakul P, diabetic foot: the economic case for the limb salvage team. Lower extremity amputations-a randomised translational trial of lifestyle intervention using review of global variability in incidence. Economic aspects in the management non-fatal cardiovascular diseases in early-onset versus of diabetes in Italy. Cost- weight losses in the Tianjin Gestational Diabetes Mellitus effectiveness of interventions to prevent and control Prevention Programme: A randomized clinical trial.
This publication has been translated into 26 languages antibiotics for acne marks purchase genuine cefadroxil on line, and more than 100 antibiotic cement spacer generic 250 mg cefadroxil with mastercard,000 copies have been distributed globally antibiotics for uti toddler cheap cefadroxil 250mg on line. As health care systems and prevalence of pathologies differ across regions in the world antibiotic resistance rates buy cefadroxil 250 mg cheap, the guidelines have to be adopted to local circumstances, if necessary. From consensus to evidence-based guidelines the initial guidelines, and each subsequent update, were developed by a consensus process and written by a panel of experts in the field. Since 2007 the guidelines have been informed by systematic reviews of the literature. We advise clinicians and other healthcare professionals to read the full guideline chapter on each topic for the specific and detailed recommendations and the rationale underpinning them, as well as the associated systematic reviews for detailed discussion of the evidence. Also new in 2019, each working group first formulated clinical questions and relevant outcomes to guide the systematic review of the available literature and the writing of recommendations. Once the drafted guidelines with recommendations were produced, these were sent for review to external experts (please see below for more detail). The six guidelines, the systematic reviews supporting them, the practical guidelines, this development and methodology document and the definitions and criteria document are all published as freely accessible articles online, We recommend that health care provides use these guidelines as the basis for developing their own local (regional or national) guidelines. The aims were to produce high-quality systematic reviews to help inform each guideline, promote consistency among the guidelines developed, and ensure high quality documents. We will describe five key tasks in the development of guidelines: 1) formulation of the clinical questions, 2) selection of relevant outcome measures, 3) performing a systematic review of the available literature, 4) writing the recommendations for clinical practice, and 5) external review and feedback 1. Formulation of clinical questions Each working group started the guideline writing process with formulating the key clinical questions they intended to address. This was to provide focus and structure to the setup of the evidence-based guidelines along the line of what a clinician or a patient would ask regarding the care provided in clinical practice to persons with diabetic foot disease. The questions generally involved diagnosis or treatment and the members of the working group reached consensus on the clinical questions they planned to address. The C is for comparator or control, and concerns the main alternative to the intervention considered, but this is not always required or available. These experts (in total 6-13 per working group) were selected by the working groups, under guidance of the Editorial Board. After revision based on these reviews the clinical questions were finalized in June 2018. Selection of relevant outcome measures Each working group devised outcome measures to help focus on selecting the relevant topic(s) for the systematic review. Working groups were informed that critical outcomes, which have a larger effect on decision-making and recommendations, were the most important to address. Performing a systematic review Each working group undertook at least one systematic review of the medical literature that was designed to form the basis for the evidence-based guidelines. Individual working groups could consult a medical librarian to help in devising their search string. Study designs included in the systematic review were meta-analyses, systematic reviews, and randomized controlled trials. Depending on the number of papers found with these higher-level study designs, working groups could also include lower level designs. Trial registries the working groups searched trial registries that can contain valuable information about studies that have been performed but as yet not published. A simplified search string derived from the original search string for the systematic review was used to search for relevant studies in these trial databases. Validation set To ensure that the search string used for the systematic review was robust, workgroups created a validation set of approximately 20 known key publications for each systematic review before performing the literature search. If each of the papers in the validation set was not identified in the literature search performed, the working group modified the search string. Date of search the time window used to conduct the literature search for all systematic reviews was between 1st and 15th of July 2018. If highly relevant studies for the systematic review and guideline appeared between the date of search and the writing of the systematic review they could be included, but only with using the set date of 1st of September 2018 for a second search of the literature, encompassing the period between the date of the first search and 1st of September 2018. Assessing retrieved publications from the search Two members of each working group independently reviewed publications by title and abstract to assess their eligibility for inclusion in the analysis based on four criteria: population; study design; outcomes; and intervention. The two reviewers discussed any disagreement on which publications to include and reached consensus. The same two reviewers independently assessed selected full-paper copies of included publications on the same four criteria for final eligibility. From relevant trials identified from these databases, related publications were searched for in the original literature search database, using the trial registration number of these relevant trials. If no publications were identified, the principal investigator of the trial was contacted and asked about the status of the trial and any possible results from the trial. The same two reviewers that reviewed publications for eligibility independently assessed included publications with a controlled study design for methodological quality. The two reviewers discussed any disagreement regarding risk of bias and reached consensus. The outcomes on the 21-item scoring list were added to the comment box in the evidence table for controlled studies. To prevent any conflict of interest, reviewers who were one of the authors of any study assessed for inclusion did not participate in the assessment, data extraction or discussion of publications of that study. Ideally, these items help to fully assess the QoE, but unfortunately we could not take them into account. Data extraction Data was extracted from each included publication that had a controlled study design and was summarized in an evidence table. This table included patient and study characteristics, characteristics of the intervention and control conditions, and primary and secondary outcomes. One of the reviewers of the original team of two extracted the data, while the other reviewer checked the table for content and presentation. Conclusions and evidence statements Finally, the working group drew conclusions for each clinical question formulated. These were based on the strength of the available evidence and formulated as evidence statements. All members of the working group participated in the discussion of these conclusions, reaching consensus on the content and formulation of the conclusions. Systematic review on diagnostic procedures We obtained specific methods to the systematic review on diagnostic studies from Brownrigg et al (15) and we asked all groups systematically reviewing studies and writing guidelines on diagnostic procedures to follow the methods used in this study (15). Systematic review on prognosis the methods used for the systematic review on prognostics in peripheral artery disease were the same as used in the 2016 systematic review on this topic (19). Writing the guideline recommendations To formulate recommendations for clinical practice, we combined the overall quality of evidence as rated in the systematic review with different factors that were considered to determine the strength of the recommendations.
Comparison of mortality associated with sepsis in the burn bible black infection purchase cefadroxil 250mg online, trauma and general intensive care unit patient: a systematic review of the literature antibiotic resistance zone of inhibition order 250 mg cefadroxil free shipping. Burn teams and burn centers: the importance of a comprehensive team approach to burn care virus infection 072 cheap cefadroxil 250 mg online. Any patients with burns and concomitant trauma (such as fractures) in which the burn injury poses the greatest risk of morbidity or mortality antibiotic resistant germs purchase 250mg cefadroxil with visa. In such cases, if the trauma poses the greater immediate risk, the patient may be stabilized initially in a trauma center before being transferred to a Burn Center. The severity of the injury is related to the temperature, composition, and length of exposure to the inhaled agent(s). A signifcant number of fre-related deaths are not due to the skin burn, but to the toxic effects of the by-products of combustion (airborne particles). In those with both a skin burn and inhalation injury, fuid resuscitation may increase upper airway edema and cause early respiratory distress and asphyxiation. Early intubation to maintain a patent airway in these individuals may be necessary. The combination of a signifcant skin burn and inhalation injury places individuals of all ages (pediatric, adult, and seniors) at greater risk for death. When present, inhalation injury increases mortality above that predicted on the basis of age and burn size. For instance, victims of house fres may exhibit symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning, upper airway and lower airway injuries at the same time. It is also important to note that early respiratory distress in a patient with a skin burn may be due to a problem other than inhalation injury. Always consider the mechanism of injury and assess for the possibility of other traumatic or medical causes. Carbon Monoxide Most fatalities occurring at a fre scene are due to asphyxiation and/or carbon monoxide poisoning. Carbon monoxide is an odorless, tasteless, nonirritating gas that is produced by incomplete combustion. Among survivors with severe inhalation injury, carbon monoxide poisoning can be the most immediate threat to life. Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin with an affnity 200 times greater than oxygen. Oxygen delivery to the tissues is compromised because of the reduced oxygen carrying capacity of the hemoglobin in the blood. Carboxyhemoglobin levels of 5-10% are often found in smokers and in people exposed to heavy traffc. At levels of 15-40%, the patient may present with various changes in central nervous system function or complaints of headache, fu-like symptoms, nausea and vomiting. At levels > 40%, the patient may have loss of consciousness, seizures, Cheyne-Stokes respirations and death. In fact, patients with severe carbon monoxide poisoning may have no other signifcant fndings on initial physical and laboratory exam. Although the O2 content of blood is reduced, the amount of oxygen dissolved in the plasma (PaO2) is unaffected by carbon monoxide poisoning. Pulse oximeter readings are normal because an oximeter does not directly measure carbon monoxide. Late effects of carbon monoxide poisoning include increased cerebral edema that may result in cerebral herniation and death. Hydrogen Cyanide Hydrogen cyanide is another product of incomplete combustion that may be inhaled in enclosed space fres. It occurs primarily from the combustion of synthetic products such as carpeting, plastics, upholstered furniture, vinyl and draperies. Cyanide ions enter cells and primarily inhibit mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase (oxidative phosphorylation). Cyanide toxicity symptoms can be vague and diffcult to distinguish from other life-threatening issues. Cardiovascular symptoms feature a hyperdynamic phase followed by cardiac failure (hypotension, bradycardia). In a patient with smoke inhalation, lactic acidosis that remains unexplained despite resuscitation suggests cyanide toxicity. Inhalation Injury Above the Glottis True thermal burns to the respiratory tract are limited to the airway above the glottis (supraglottic region) including the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and larynx. The rare exceptions include pressurized steam inhalation, or explosions with high concentrations of oxygen/fammable gases under pressure. Heat damage of the pharynx is often severe enough to produce upper airway obstruction, and may cause obstruction at any time during the resuscitation period. In unresuscitated patients, supraglottic edema may be delayed at onset until fuid resuscitation is well underway. Early intubation is preferred because the ensuing edema may obliterate the landmarks needed for successful intubation. Supraglottic edema may occur without direct thermal injury to the airway but secondary to the fuid shifts associated with the burn injury and resuscitation. Inhalation Injury Below the Glottis In contrast to injuries above the glottis, subglottic injury is almost always chemical. Noxious chemicals (aldehydes, sulfur oxides, phosgenes) are present in smoke particles and cause a chemical injury, damaging the epithelium of the airways. Smaller airways and terminal bronchi are usually affected by prolonged exposure to smoke with smaller particles. However, it must be noted that the severity of inhalation injury and the extent of damage are clinically unpredictable based on the history and initial examination. While inhalation injury below the glottis without signifcant associated skin burns has a relatively good prognosis, the presence of inhalation injury markedly worsens prognosis of skin burns, especially if the burn is large and the onset of respiratory distress occurs in the frst few hours post injury. An asymptomatic patient with suspected lower airway inhalation injury should be observed given the variable onset of respiratory symptoms. Mucosal epithelial sloughing may occur as late as 4-5 days following an inhalation injury. Careful patient monitoring during resuscitation is necessary with inhalation injury. Excessive or insuffcient resuscitation may lead to pulmonary and other complications. In patients with combined inhalation and skin burns, total fuids administered may exceed predicted resuscitation volumes based on the extent of the skin burns. Oxygen Therapy and Initial Airway Management the goals of airway management during the frst 24 hours are to maintain airway patency and adequate oxygenation and ventilation while avoiding the use of agents that may complicate subsequent care (steroids) and development of ventilator-induced lung injury (high tidal volumes). Frequent and adequate suctioning is necessary to prevent occlusion of the airway and endotracheal tube. Factors to Consider When Deciding Whether or Not to Intubate a Patient with Burns the decision to intubate a burn patient is critical. Intubation is indicated if upper airway patency is threatened, gas exchange or lung mechanics inadequate, or airway protection compromised by mental status. Also, if there is concern for progressive edema during transport to a burn center, intubation prior to transport should be strongly considered. Stridor or raspy breath sounds may indicate impending upper airway obstruction and mandate emergency endotracheal intubation. For instance, many patients with superfcial partial-thickness facial burns, singed facial and nasal hairs, and fash burns from home oxygen are frequently intubated when they can be simply observed. Orotracheal intubation using a cuffed endotracheal tube is the preferred route of intubation. In children, cuffed endotracheal tubes are also preferred using an age-appropriate size. In instances where non-burn trauma mandates cervical spine protection (falls, motor vehicle collisions), cervical spine stabilization is critical during intubation. In impending airway obstruction, X-ray clearance of the cervical spine should wait until after intubation. An endotracheal tube that becomes dislodged may be impossible to replace due to obstruction of the upper airway by edema. Discount cefadroxil online. Empowering Nurses to Protect Themselves and Their Patients: Nurses' Role in Antibiotic Stewardship. |