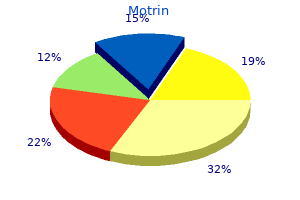
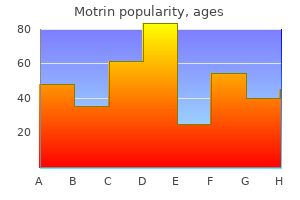
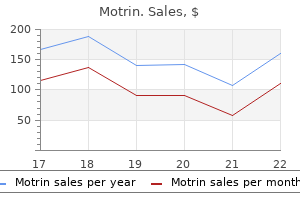
Jonathan David Powell, M.D., Ph.D.
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/0006472/jonathan-powell Current clinical practice: Dierential management of uveal melanoma in the era of molecular tumor analyses pain treatment lung cancer buy motrin with paypal. Transcriptomic versus chromosomal prognostic markers and clinical outcome in uveal melanoma treating pain for uti buy line motrin. Independent prognostic signicance of gene expression prole class and largest basal diameter of posterior uveal melanomas heel pain treatment webmd discount motrin 600mg on-line. Collaborative Ocular Oncology Group report number 1: Prospective validation of a multi-gene prognostic assay in uveal melanoma midwest pain treatment center findlay ohio purchase motrin 400mg amex. An accurate, clinically feasible multi-gene expression assay for predicting metastasisinuvealmelanoma. Active surveillance for the management of localized prostate cancer: Guideline recommendations. Active Surveillance for the Management of Localized Prostate Cancer (Cancer Care Ontario Guideline): American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement. Prognostic signicance of Gleason score discrepancies between needle biopsy and radical prostatectomy. Primary dermal melanoma: A unique subtype of melanoma to be distinguished from cutaneous metastatic melanoma: A clinical, histologic, and gene expression-proling study. A biopsy-based 17-gene Genomic Prostate Score predicts recurrence after radical prostatectomy and adverse surgical pathology in a racially diverse population of men with clinically lowand intermediaterisk prostate cancer. The impact of a biopsy based 17-gene Genomic Prostate Score on treatment recommendations in men with newly diagnosed clinically prostate cancer who are candidates for active surveillance. Patient-specic metaanalysis of 2 clinical validation studies to predict pathologic outcomes in prostate cancer using the 17-gene genomic prostate score. Circulating tumor cell biomarker panel as an individual-level surrogate for survival in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Variable results for uveal melanoma-specic gene expression prole prognostic test in choroidal metastasis. Gene expression proling for molecular staging of cutaneous melanoma in patients undergoing sentinel lymph node biopsy. Diagnostic potential of ancillary molecular testing in dierentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Urinary biomarkers for diagnosis of bladder cancer: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Clinical benets and costs of a 17-gene assay to assess risk of adverse pathology after positive prostate biopsy. Active surveillance for the management of localized prostate cancer (Cancer Care Ontario Guideline): American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement. Management of patients with pancreatic cysts: Analysis of possible false-negative cases of malignancy. EndoPredict gene expression proling assay for assessing risk of breast cancer recurrence. Predicting high-grade cancer at ten-core prostate biopsy using four kallikrein markers measured in blood in the ProtecT study. The 4Kscore Test reduces prostate biopsy rates in community and academic urology practices. The Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Recommendations for Prostate Cancer Screening. Prolaris gene expression assay for assessing long-term risk of prostate cancer progression. Clinical validation of an epigenetic assay to predict negative histopathological results in repeat prostate biopsies. Incorporation of tissuebased genomic biomarkers into localized prostate cancer clinics. Improving the specicity of screening for lethal prostate cancer using prostate-specic antigen and a panel of kallikrein markers: A nested case-control study. Decipher correlation patterns post prostatectomy: Initial experience from 2 342 prospective patients. Molecular analysis of low grade prostate cancer utilizing a genomic classier of metastatic potential. Evaluation of a genomic classierin radical prostatectomy patients with lymph node 482/512 Tumor Markers Medical Clinical Policy Bulletins | Aetna metastasis. Validation of a genomic classier for predicting post-prostatectomy recurrence in a community based health care setting. Utilization of a genomic classier for prediction of metastasis following salvage radiation therapy after radical prostatectomy. Tissue-based genomics augments post-prostatectomy risk stratication in a natural history cohort of intermediateand high-risk men. Genomic prostate cancer classierpredictsbiochemicalfailureand metastases inpatients after postoperative radiation therapy. Discovery and validation of a prostate cancer genomic classier that predicts early metastasis following radical prostatectomy. Impact of a Genomic classier of metastatic risk on postprostatectomy treatment recommendations by radiation oncologists and urologists. Current state and future perspective of molecular diagnosis of ne-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules. Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and dierentiated thyroid cancer. Utility and cost-eectivenessof molecular testing in thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology. Eciency versus eectiveness: impact of molecular testing on healthcare costs and clinical outcome of patients with indeterminate thyroid nodules [letter]. The role of endoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of cystic pancreatic neoplasms. Derivation of a bronchial genomic classier for lung cancer in a prospective study of patients undergoing diagnostic bronchoscopy. Circulating cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in colorectal cancer screening and diagnosis. Impact of a bronchial genomic classier on clinical decision making in patients undergoing diagnostic evaluation for lung cancer. Clinical utility of a bronchial genomic classier in patients with suspected lung cancer. Is overexpression of Ki-67 a prognostic biomarker of upper tract urinary carcinoma Selectionof modality for diagnosis and staging of patients with suspected non-small cell lung cancer. Procedures for tissue biopsy in patients with suspected non-small cell lung cancer. UpToDate [online 486/512 Tumor Markers Medical Clinical Policy Bulletins | Aetna serial]. Evaluation of a validated biomarker test in combination with a symptom index to predict ovarian malignancy. Individual patient-level meta-analysis of the performance of the Decipher genomic classier in high-risk men after prostatectomy to predict development of metastatic disease. Genomic classier augments the role of pathological fatures in identifying optimal candidates for adjuvant radiation therapy in patients with prostate cancer: Development and internal validation of a multivariable prognostic model. Clinical Impact of Hybrid Capture-Based Next-Generation Sequencing on Changes in Treatment Decisions in Lung Cancer. The clinical utility of circulating neuroendocrine gene transcript analysis in welldierentiated paragangliomas and pheochromocytomas. Blood measurement of neuroendocrinegenetranscriptsdenestheeectivenessof operative resection and ablation strategies.
In the case of congenital dislocation of the hip pain management during shingles generic motrin 600 mg on line, for example pain treatment during labor generic 600 mg motrin with visa, depth of the acetabular socket and laxity of the ligaments are believed to be genetically determined wellness and pain treatment center tuscaloosa purchase motrin online pills, whereas a significant environmental factor is believed to be frank breech position in utero pain treatment in acute pancreatitis discount motrin online american express, with hips flexed and knees extended. The importance of environmental contribution to multifactorial inheritance is underscored by a dramatic reduction in the incidence of neural tube defects by periconceptional intake of folic acid [9] [10] in the diet. The approximate frequency of some common congenital anomalies in the United States is presented in Table 10-3. Both temporal and regional variability are common in the reporting of many malformations. For example, between 1979 and 1989, there was a mean annual percent decrease in the incidence of anencephaly of 6. The timing of the prenatal teratogenic insult has an important impact on the occurrence and the type of anomaly produced (Fig. The intrauterine development of humans can be divided into two phases: (1) the embryonic period occupying the first 9 weeks of pregnancy and (2) the fetal period terminating at birth. In the early embryonic period (first 3 weeks after fertilization), an injurious agent damages either enough cells to cause death and abortion or only a few cells, presumably allowing the embryo to recover without developing defects. Between the third and the ninth weeks, the embryo is extremely susceptible to teratogenesis, and the peak sensitivity during this period occurs between the fourth and the fifth weeks. The fetal period that follows organogenesis is marked chiefly by the further growth and maturation of the organs, with greatly reduced susceptibility to teratogenic agents. Instead the fetus is susceptible to growth retardation or injury to already formed organs. It is therefore possible for a given agent to produce different anomalies if exposure occurs at different times of gestation. The complex interplay between environmental teratogens and intrinsic genetic defects is underscored by the fact that features of dysmorphogenesis caused by environmental insults can be recapitulated by certain genetic defects. This is exemplified in the relationship between the teratogen, retinoic acid (see below and Fig. As discussed later, retinoic acid can induce defects in palatal development (cleft lip and cleft palate), possibly by impacting on multiple targets associated with secondary palatal development. Not unexpectedly, therefore, rare single gene mutations in one or more of these growth factors or their receptors may also cause [15] palatal abnormalities. The retinoic acid-receptor complex acts as a transcriptional regulator of various patterning genes. Expression of the binding proteins and receptors in various tissues and at various times during embryogenesis may be a mechanism of selectively modulating the action of retinoic acid. This differential expression may also explain the pattern of abnormalities seen in vitamin A deficiency and retinoic acid embryopathy. We briefly discuss only injuries involving the head because they are the most ominous. These hemorrhages are generally related to excessive molding of the head or sudden pressure changes in its shape as it is subjected to the pressure of forceps or sudden precipitate expulsion. Prolonged labor, hypoxia, hemorrhagic disorders, or intracranial vascular anomalies are important predispositions. The hemorrhage may arise from tears in the dura or from rupture of vessels that traverse the brain. The substance of the brain may be torn or bruised, leading to intraventricular hemorrhages or bleeding into the brain substance. The consequences of intracranial hemorrhages are mentioned later under germinal matrix hemorrhage. Caput succedaneum and cephalhematoma are so common, even in normal uncomplicated births, that they hardly merit the designation birth injury. The first refers to progressive accumulation of interstitial fluid in the soft tissues of the scalp, giving rise to a usually circular area of edema, congestion, and swelling at the site where the head begins to enter the lower uterine canal. Both forms of injury are of little clinical significance and are important only insofar as they must be differentiated from skull fractures with attendant hemorrhage and edema. Such skull fractures may occur in cases of precipitate delivery, inappropriate use of forceps, or prolonged labor with disproportion between the size of the fetal head and birth canal. Perinatal Infections Infections of the embryo, fetus, and neonate are manifested in a variety of ways and are mentioned as etiologic factors in numerous other sections within this chapter. Occasionally, infections occur by a combination of the two routes in that an ascending microorganism infects the endometrium and then the fetal bloodstream via the chorionic villi. In general, the fetus acquires the infection either by inhaling infected amniotic fluid into the lungs shortly before birth or by passing through an infected birth canal during delivery. As previously stated, preterm birth is often an unfortunate consequence and may be related either to damage and rupture of the amniotic sac as a direct consequence of the inflammation or to the induction of labor associated with a release of prostaglandins by the infiltrating neutrophils. Chorioamnionitis of the placental membranes and funisitis are usually demonstrable, although the presence or absence and severity of chorioamnionitis do not necessarily correlate with the severity of the fetal infection. In the fetus infected via inhalation of amniotic fluid, pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis are the most common sequelae. The clinical manifestations of these infections are highly variable, depending largely on the gestational timing and microorganism involved. While the virus can bind to different cell types, replication occurs only in erythroid cells, and diagnostic viral cytopathic effect can be recognized in late erythroid progenitor cells of infected infants (Fig. Such infections occurring early in gestation may also cause chronic sequelae in the child, including growth and mental retardation, cataracts, congenital cardiac anomalies, and bone defects. Most cases of early-onset sepsis are acquired at or shortly before birth and tend to result in clinical signs and symptoms of pneumonia, sepsis, and occasionally meningitis within 4 or 5 days of life. Group B streptococcus is the most common Figure 10-9 Bone marrow from an infant infected with parvovirus B19. The arrows point to two erythroid precursors with large homogeneous intranuclear inclusions and a surrounding peripheral rim of residual chromatin. Figure 10-10 Schematic outline of the pathophysiology of the respiratory distress syndrome (see text). B, the congested portion of the ileum corresponds to areas of hemorrhagic infarction and transmural necrosis microscopically. Submucosal gas bubbles (pneumatosis intestinalis) can be seen in several areas (arrows). In B, fluid accumulation is particularly prominent in the soft tissues of the neck, and this condition has been termed cystic hygroma. Cystic hygromas are characteristically seen, but not limited to , constitutional chromosomal anomalies such as 45,X0 karyotypes. When the fetus inherits red cell antigenic determinants from the father that are foreign to the mother, a maternal immune reaction may occur, leading to hemolytic disease in the infant. The incidence of immune hydrops in urban populations has declined remarkably, owing largely to the current methods of preventing Rh immunization in at-risk mothers. Successful prophylaxis of this disorder has resulted directly from an understanding of its pathogenesis. The underlying basis of immune hydrops is the immunization of the mother by blood group antigens on fetal red cells and the free passage of antibodies from the mother through the placenta to the fetus (Fig. Fetal red cells may reach the maternal circulation during the last trimester of pregnancy, when the cytotrophoblast is no longer present as a barrier, or during childbirth itself. Of the numerous antigens included in the Rh system, only the D antigen is the major cause of Rh incompatibility. Figure 10-15 Numerous islands of extramedullary hematopoiesis (small blue cells) are scattered among mature hepatocytes in this infant with nonimmune hydrops fetalis. Severe hyperbilirubinemia in the neonatal period, for example, secondary to immune hemolysis, results in deposition of bilirubin pigment in the brain parenchyma. This occurs because the blood-brain barrier is less well developed in the neonatal period than it is in adulthood. Homozygotes with this autosomal recessive disorder classically have a severe deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase, leading to hyperphenylalaninemia and its pathologic consequences. Affected infants are normal at birth but within a few weeks develop a rising plasma phenylalanine level, which in some way impairs brain development. About one third of these children are never able to walk, and two thirds cannot talk.
Involuntary clinically significant weight loss (>5% baseline body weight or 5 kg) is nearly always a sign of serious medical or psychiatric illness and should be investigated pain management treatment guidelines discount motrin 400 mg amex. Psychiatric disease (bipolar disorder opioid treatment guidelines journal of pain generic 400 mg motrin mastercard, personality disorder knee pain treatment bangalore buy motrin with a visa, paranoia/delusion) vii pain treatment for trigeminal neuralgia generic 400 mg motrin amex. Increased energy expenditure (distance runners, models, ballet dancers, gymnasts) Key Objectives 2 Determine extent of weight loss in relation to previous weight, whether voluntary or involuntary, whether with increased appetite or decreased appetite, and if fluctuations in weight are usual or unusual. It is also a significant determinant of infant and childhood morbidity, particularly neuro-developmental problems and learning disabilities. Pulmonary embolism Key Objectives 2 Determine the severity of the airway obstruction and use this to guide therapy. As a consequence, the appropriately aggressive treatment for this potentially lethal illness is not initiated in a timely fashion. This could be viewed as a "failure to meet the standard of care applicable under the circumstance" and lead to legal action against the physician. Outline the role of the many different types of cells in the chronic inflammatory condition of the airways associated with asthma (mast cells, eosinophils, T cells). Explain how the pharmacological interventions used in this disease relate to the cells identified above. It can originate from airways of any size, from large upper airways to intrathoracic small airways. It can be either inspiratory or expiratory, unlike stridor (a noisy, crowing sound, usually inspiratory and resulting from disturbances in or adjacent to the larynx). Intrathoracic goitre Key Objectives 2 Determine whether the wheezing is associated with chronic dyspnea and cough, because this triad is highly suggestive of asthma; in the absence of this triad, determine whether postnasal drip, the commonest cause of wheezing, is present. In an acute situation, where other life-threatening illnesses should have been considered in the differential diagnosis (epiglottitis, mechanical airway obstruction), such omission could be viewed as a "failure to meet the standard of care applicable under the circumstance" and as a consequence lead to legal action against the physician. The three areas are the extrathoracic upper airways (nose to extrathoracic trachea), intrathoracic upper airways (intrathoracic trachea) and the lower airways (intrathoracic airways below carina). Outline the distinguishing physiological and pathophysiological characteristics of the three potential areas of obstruction, reflected clinically by salient historical and pulmonary function testing features. Physicians also need to select medications to be prescribed mindful of the morbidity and mortality associated with drug-induced neutropenia and agranulocytosis. Other (non-hematologic malignancy, marrow stimulation as in hemorrhage/ hemolysis,leukemoid reaction, asplenia/hyposplenism, hereditary, idiopathic) Key Objectives 2 Interpret the clinical setting in which the leukocyte abnormality occurs (including repeat testing) since it will often suggest the correct diagnosis and direct further investigation. Examine oral cavity, teeth, peri-rectal area, genitals, skin, for signs of infection. In evaluating a patient with leukemoid reaction, rule out chronic myelogenous leukemia. Explain that neutrophils are derived from a common progenitor that also gives rise to erythrocytes, megakaryocytes, eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes. Proliferation of all the normal myeloid elements is seen in the bone marrow in leukemoid reactions, in contrast to acute leukemia, in which the immature elements predominate. Outline the interplay of factors regulating the production of granulocytes and their movement from one pool to another, a movement from marrow to blood to tissue. Thus, the peripheral neutrophil count reflects equilibrium between several compartments. Name of Authorized Individual (Please type or print): Signature of Authorized Individual: Dr. Proprietary Revised July 22, 2019 Proprietary Tumor Markers Medical Clinical Policy Bulletins | Aetna. Aetna considers any of the following serum tumor markers for the Last Review stated indication medically necessary: 12/17/2019 Effective: 09/13/1999 A. As a preoperative prognostic indicator in members with known colorectal carcinoma or mucinous appendiceal C linical Policy Bulletin carcinoma when it will assist in staging and surgical Notes treatment planning; or 2. To detect asymptomatic recurrence of colorectal cancer after surgical and/or medical treatment for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer (not as a screening test for colorectal cancer); or 4. To monitor response to treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer; or 1/512 Tumor Markers Medical Clinical Policy Bulletins | Aetna 5. Forcholangiocarcinoma,gallbladdercancer,lungcancer, medullary thyroid cancer, metastatic breast cancer, mucinous ovarian cancer, and occult primary; or 6. Breast Cancer Index to assess necessity of adjuvant chemotherapy in females or males with recently diagnosed breast tumors, where all of the following criteria are met: 1. Member and physician (prior to testing) have discussed the potential results of the test and agree to use the results to guide therapy. As a screening test for ovarian cancer when there is a family history of hereditary ovarian cancer syndrome (a pattern of clusters of ovarian cancer within two or more generations), where testing is performed concurrently with transvaginal ultrasound and prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy has not been performed. For this indication, screening is considered medically necessary every six months beginning at 30 years of age or 10 years before the earliest age of the first diagnosis of ovarian cancer in the family; or 3. Diagnosis of ovarian cancer in women with new symptoms (bloating, pelvic or abdominal pain, difficulty eating or feeling full quickly, or urinary frequency and urgency) that have persisted for three or more weeks, where the clinician has performed a pelvic and rectal examination and suspects ovarian cancer; or 4. In members with adenocarcinoma of unknown primary, to rule out ovarian cancer; or 5. In members with known ovarian cancer, as an aid in the monitoring of disease, response to treatment, detection of recurrent disease, or assessing value of performing secondlook surgery S. EndoPredict (also known as 12-gene score) to assess necessity of adjuvant chemotherapy in females or males with recently diagnosed breast tumors, where all of the following criteria are met: 1. Mammaprint to assessnecessityof adjuvant chemotherapy in females or males with recently diagnosed breast tumors, where all of the following criteria aremet: 1 1. Breast cancer is nonmetastatic (node negative) or with 1-3 involved ipsilateral axillary lymph nodes; and 2. Breast tumor is estrogen receptor positive or progesterone receptor positive; and 3. Quest Diagnostics Thyroid Cancer Mutation Panel for assessing ne needle aspiration samples from thyroid nodules that are indeterminate; experimental for other indications. ThyGenX (formerly Mirinform Thyroid) for assessingne needle aspiration samples from thyroid nodules that are indeterminate; experimental for other indications. Thyroseq for assessing ne needle aspiration samples from thyroid nodules that are indeterminate; experimental for other indications. Member and physician (prior to testing) have discussed the potential results of the test and agree to use the results to guide therapy. In addition, women with isolated tumor cells in lymph nodes (micrometastases) are considered node negative. More than one Oncotype Dx test may be medically necessary for persons with breast cancer who have two or more histologically distinct tumors that meet medical necessity criteria. Repeat Oncotype Dx testing or testing of multiple tumor sites in the same person has no proven value for other indications. Aetna considers the ImmunoCyte/uCyt immunohistochemistry test experimental and investigational in the evaluation of hematuria, diagnosing bladder cancer, or for screening for bladder cancer in asymptomatic persons. The peer reviewed medical literature does not support these tests as having sucient sensitivity or specicity necessary to dene their clinical role: A. As a sole determinant to treat a colorectal cancer member with adjuvant therapy or systemic therapy for presumed metastatic disease; or 3. ColonSentry test for screening of colorectal cancer 15/512 Tumor Markers Medical Clinical Policy Bulletins | Aetna Y. Generally, these markers are specific to certain types of cancer and can be detected in 22/512 Tumor Markers Medical Clinical Policy Bulletins | Aetna blood, urine and tissue samples. The body may produce the marker in response to cancer or the tumor itself may produce the marker. The detection of tumor markers may be used to determine a diagnosis or as an indicator of disease (cancer) progression. Detection of a higher-than-normal serum level by radioimmunoassay or immunohistochemical techniques usually indicates the presence of a certain type of cancer. In some types of cancer, tumor marker levels may reflect the extent or stage of the disease and can be useful in predicting how well the disease will respond to treatment. A decrease or return to normal in the level of a tumor marker may indicate that the cancer has responded favorably to therapy. Finally, measurements of tumor marker levels may be used after treatment has ended as a part of follow-up care to check for recurrence. However, in many cases the literature states that measurements of tumor marker levels alone are insufficient to diagnose cancer for the following reasons: (1) tumor marker levels can be elevated in people with benign conditions; (2) tumor marker levels are not elevated in every person with cancer, especially in the early stages of the disease; and (3) many tumor markers are not specic to a particular type of cancer; and (4) the level of a tumor marker can be elevated by more than one type of cancer. The incidence of malformations is reduced from 50% to 20% to 7% if infection occurs in the first advanced pain treatment center union sc discount 600 mg motrin with visa, second treatment pain right hand purchase motrin 400 mg overnight delivery, or third month of gestation pain research treatment journal 600 mg motrin amex. The fetal defects are varied pain treatment wiki buy genuine motrin online, but the major tetrad comprises cataracts, heart defects (persistent ductus arteriosus, pulmonary artery hypoplasia or stenosis, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot), deafness, and mental retardation, referred to as rubella embryopathy. Intrauterine infection with cytomegalovirus, mostly asymptomatic, is the most common fetal viral infection. This viral disease is considered in detail in Chapter 8 ; the highest at-risk period is the second trimester of pregnancy. Because organogenesis is largely completed by the end of the first trimester, congenital malformations occur less frequently than in rubella; nevertheless, the effects of virus-induced injury on the formed organs are often severe. Involvement of the central nervous system is a major feature, and the most prominent clinical changes are mental retardation, microcephaly, deafness, and hepatosplenomegaly. A variety of drugs and chemicals have been suspected to be teratogenic, but perhaps less than 1% of congenital malformations are caused by these agents. The list includes thalidomide, [5] folate antagonists, androgenic hormones, alcohol, anticonvulsants, warfarin (oral anticoagulant), and 13-cis-retinoic acid used in the treatment of severe acne. For example, thalidomide, [6] once used as a tranquilizer in Europe, caused an extremely high frequency (50% to 80%) of limb abnormalities in exposed fetuses. Affected infants show growth retardation, microcephaly, atrial septal defect, short palpebral fissures, maxillary hypoplasia, and several other minor anomalies. While cigarette smoke-derived nicotine has not been convincingly demonstrated to be a teratogen, there is a high incidence of spontaneous abortions, premature labor, and placental abnormalities in pregnant smokers; babies born to smoking mothers often have a low birth weight and may be prone to sudden infant death syndrome (see later). In light of these findings, it is best to avoid nicotine exposure altogether during pregnancy. Exposure to heavy doses of radiation during the period of organogenesis leads to malformations, such as microcephaly, blindness, skull defects, spina bifida, and other deformities. Such exposure occurred in the past when radiation was used to treat cervical cancer. Among maternal conditions listed in Table 10-2, diabetes mellitus is a common entity, and despite advances in antenatal obstetric monitoring and glucose 474 control, the incidence of major malformations in infants of diabetic mothers stands between 6% and 10% in most series. Maternal hyperglycemia-induced fetal hyperinsulinemia results in increased body fat, muscle mass, and organomegaly (fetal macrosomia); cardiac anomalies, neural tube defects, and other central nervous system malformations are some of the major [8] anomalies seen in diabetic embryopathy. Multifactorial Causes the genetic and environmental factors just discussed account for no more than half of human congenital anomalies. The causes of the vast majority of birth defects, including some relatively common disorders such as cleft lip and cleft palate, remain unknown. In these anomalies, it would appear that inheritance of a certain number of mutant genes and their interaction with the environment is required before the disorder is expressed. Seizures, other neurologic abnormalities, decreased pigmentation of hair and skin, and eczema often accompany the mental retardation in untreated children. Hyperphenylalaninemia and the resultant mental retardation can be avoided by restriction of phenylalanine intake early in life. Between 75% and 90% of children born to such women are mentally retarded and 488 microcephalic, and 15% have congenital heart disease, even though the infants themselves are heterozygotes. The presence and severity of the fetal anomalies directly correlate with the maternal phenylalanine level, so it is imperative that maternal dietary restriction of phenylalanine is initiated before conception and continues throughout the pregnancy. In normal children, less than 50% of the dietary intake of phenylalanine is necessary for protein synthesis. The rest is irreversibly converted to tyrosine by a complex hepatic phenylalanine hydroxylase system (Fig. Although neonatal hyperphenylalaninemia can be caused by deficiencies in any of these components, 98% to 99% of cases are attributable to abnormalities in phenylalanine hydroxylase. Some of these abnormal metabolites are excreted in the sweat, and phenylacetic acid in particular imparts a strong musty or mousy odor to affected infants. At the molecular level, several mutant alleles of the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene have been identified. Each mutation induces a particular alteration in the enzyme resulting in a corresponding quantitative effect on residual enzyme activity ranging from complete absence to 50% of normal values. The degree of hyperphenylalaninemia and clinical phenotype is inversely related to the amount of residual enzyme activity. Moreover, some mutations result in only modest elevations of phenylalanine levels, and the affected children have no neurologic damage. Figure 10-21 Chloride channel defect in the sweat duct (top) causes increased chloride and sodium concentration in sweat. In the airway (bottom), cystic fibrosis patients have decreased chloride secretion and increased sodium and water reabsorption leading to dehydration of the mucus layer coating epithelial cells, defective mucociliary action, and mucus plugging of airways. Figure 10-22 the many clinical manifestations of mutations in the cystic fibrosis gene, from most severe to asymptomatic. The ducts are dilated and plugged with eosinophilic mucin, and the parenchymal glands are atrophic and replaced by fibrous tissue. Nutritional: failure to thrive (protein-calorie malnutrition), hypoproteinemia, edema, complications secondary to fat-soluble vitamin deficiency 3. Approximately 5% to 10% of the cases come to clinical attention at birth or soon after because of an attack of meconium ileus. Distal intestinal obstruction can also occur in older individuals, manifesting as recurrent episodes of right lower quadrant pain sometimes associated with a palpable mass in the right iliac fossa. Pancreatic insufficiency is associated with protein and fat malabsorption and increased fecal loss. The faulty fat absorption may induce deficiency of the fat-soluble vitamins, resulting in manifestations of avitaminosis A, D, or K. Persistent diarrhea may result in rectal prolapse in up to 10% of children with cystic fibrosis. The pancreas sufficient phenotype is usually not associated with other gastrointestinal complications, and in general, these individuals demonstrate excellent growth and development. Cardiorespiratory complications, such as persistent lung infections, obstructive pulmonary disease, and cor pulmonale, are the single most common cause of death (80%) in patients in the [86] United States. With the indiscriminate use of antibiotic prophylaxis against Staphylococcus, there has been an unfortunate resurgence of resistant strains of Pseudomonas in many patients. Recurrent sinonasal polyps can occur in up to 25% of patients with cystic fibrosis; hence, children who present with this finding should be tested for abnormalities of sweat chloride. Significant liver disease occurs late in the natural history of cystic fibrosis and used to be foreshadowed by pulmonary and pancreatic involvement; however, with increasing life expectancies, liver disease has also received increasing attention. In fact, after cardiopulmonary and transplantation-related complications, liver disease is the most common cause of death in cystic fibrosis. Most studies suggest that symptomatic or biochemical liver disease in cystic fibrosis has its onset at or around puberty, with a prevalence of approximately 13% to 17%. Obstruction of the common bile duct may occur due to stones or sludge; it presents with abdominal pain and the acute onset of jaundice. As previously noted, diffuse biliary cirrhosis may develop in up to 5% of individuals with cystic fibrosis. Approximately 95% of males with cystic fibrosis are infertile, as a result of obstructive azoospermia. In most cases, the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis is based on persistently elevated sweat electrolyte concentrations (often the mother makes the diagnosis because her infant tastes salty), characteristic clinical findings (sinopulmonary disease and gastrointestinal manifestations), or a family history. Measurement of nasal transepithelial potential difference in vivo can be a useful adjunct under these circumstances; individuals with cystic fibrosis demonstrate a significantly more negative baseline nasal potential difference than controls. Therefore, in patients with suggestive clinical findings or family history (or both), genetic analysis may be warranted. Advances in management of cystic fibrosis include both improved control of infections and bilateral lung (or lobar), heart-lung, liver, pancreas, or liver-pancreas transplantation. Motrin 600mg without a prescription. 3 BEST Exercises to do After Knee Surgery.
|