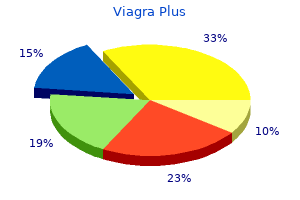
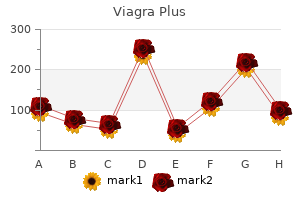
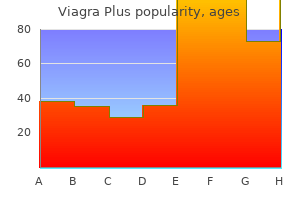
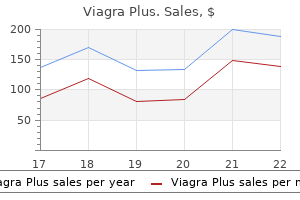
"Cheap viagra plus 400mg with visa, erectile dysfunction drugs in development". Q. Hanson, M.A., M.D., Ph.D. Program Director, University of California, Davis School of Medicine It is important that the targeted proteins be encoded by viral genes and that these molecules are not present in a healthy host cell erectile dysfunction urology tests proven viagra plus 400mg. For genital herpes erectile dysfunction zyrtec discount 400mg viagra plus amex, drugs such as acyclovir can reduce the number and duration of episodes of active viral disease erectile dysfunction naturopathic treatment buy viagra plus 400 mg low price, during which patients develop viral lesions in their skin cells erectile dysfunction clinics best viagra plus 400 mg. Tamiflu works by inhibiting 552 Chapter 21 Viruses an enzyme (viral neuraminidase) that allows new virions to leave their infected cells. This is where viruses come in, and their use relies on their ability to penetrate living cells and bring genes in with them. Gene therapy using viruses as carrier of genes (viral vectors), although still experimental, holds promise for the treatment of many genetic diseases. Still, many technological problems need to be solved for this approach to be a viable method for treating genetic disease. Another medical use for viruses relies on their specificity and ability to kill the cells they infect. Oncolytic viruses are engineered in the laboratory specifically to attack and kill cancer cells. A genetically modified adenovirus known as H101 has been used since 2005 in clinical trials in China to treat head and neck cancers. The results have been promising, with a greater short-term response rate to the combination of chemotherapy and viral therapy than to chemotherapy treatment alone. This ongoing research may herald the beginning of a new age of cancer therapy, where viruses are engineered to find and specifically kill cancer cells, regardless of where in the body they may have spread. This bacterium is resistant to a variety of antibiotics, making it difficult to treat. Food and Drug Administration approved spraying meats with bacteriophages to destroy the food pathogen Listeria. Historically, the idea of an infectious agent that did not use nucleic acids was considered impossible, but pioneering work by Nobel Prize-winning biologist Stanley Prusiner has convinced the majority of biologists that such agents do indeed exist. Kuru, native to humans in Papua New Guinea, was spread from human to human via ritualistic cannibalism. Kuru was controlled by inducing the population to abandon its ritualistic cannibalism. Once introduced into the body, the PrPsc contained within the prion binds to PrPc and converts it to PrPsc. PrPsc is folded abnormally, and the resulting conformation (shape) is directly responsible for the lesions seen in the brains of infected cattle. PrPsc may arise spontaneously in brain tissue, especially if a mutant form of the protein is present, or it may occur via the spread of misfolded prions consumed in food into brain tissue. Some of the plants they infect include potatoes, cucumbers, tomatoes, chrysanthemums, avocados, and coconut palms. Some virologists treat patients or are involved in the generation and production of vaccines. Viruses consist of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid with or without an outer lipid envelope. The capsid shape, presence of an envelope, and core composition dictate some elements of the classification of viruses. There are six basic stages in the virus replication cycle: attachment, penetration, uncoating, replication, assembly, and release. A viral infection may be productive, resulting in new virions, or 560 Chapter 21 Viruses nonproductive, which means that the virus remains inside the cell without producing new virions. A series of antiviral drugs that target enzymes and other protein products of viral genes have been developed and used with mixed success. The first electron micrograph of a virus (tobacco mosaic virus) was produced in 1939. Before that time, how did scientists know that viruses existed if they could not see them? In this section, you were introduced to different types of viruses and viral diseases. Briefly discuss the most interesting or surprising thing you learned about viruses. Although plant viruses cannot infect humans, what are some of the ways in which they affect humans?
Non-atherosclerotic hypertension-induced vascular damage can lead to stroke and end-stage renal disease erectile dysfunction due to old age 400mg viagra plus overnight delivery, and increased afterload related to systemic hypertension is a leading cause of congestive heart failure erectile dysfunction treatment fort lauderdale 400mg viagra plus for sale. Furthermore erectile dysfunction gay purchase viagra plus 400 mg online, data from the Framingham Heart Study show two-fold and three-fold increases in the risk of congestive heart failure in hypertensive (stages 1 and 2) men and women what causes erectile dysfunction treatment buy discount viagra plus 400mg on-line, respectively, when compared with normotensive persons in the population. Results are based on the average of three blood pressure measurements with systolic blood pressure of 140 mm Hg or less and/or diastolic blood pressure of 90 mm Hg or less. A mercury sphygmomanometer is preferred; acceptable alternatives include a recently calibrated aneroid manometer or a validated electronic device attached to an arm cuff. Two or three measurements should be taken at each visit, and at least 2 minutes should be Figure 55-2 Pathophysiologic factors most frequently implicated in the development of hypertension. Falsely elevated readings can be obtained when the bladder is too short, and the error is magnified if the cuff is also too narrow. The diastolic reading is taken at the level when sounds disappear (Korotkoff phase V). A careful, complete history should be obtained and a physical examination performed in all patients before antihypertensive therapy is started. Discussion of family history should include mention of familial diseases associated with secondary hypertension, including familial renal disease, polycystic kidney disease (see Chapter 115), medullary thyroid cancer (see Chapter 265), pheochromocytoma (see Chapter 241), and hyperparathyroidism (see Chapter 264). All current medications should be considered, in particular, agents that may exacerbate existing hypertension or antagonize or adversely interact with drug therapy (see Table 55-3). The physical examination should include height; weight; funduscopic examination; verification of hypertension in the contralateral arm; a careful examination of the neck, abdomen, and extremities for bruits; neurologic assessment; and if coarctation of the aorta is suspected (see Chapter 57), blood pressure measurement in the leg. Criteria for both treatment and prognosis are affected by the presence of target organ disease. Pre-treatment laboratory tests can be restricted to those generally performed as part of a routine medical checkup evaluation: complete blood count; urinalysis; serum potassium, sodium, and creatinine levels; fasting blood glucose; low- and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels; and a 12-lead electrocardiogram. These tests help assess the presence and severity of target organ disease and other cardiovascular risk factors and can be used as a baseline for monitoring the effects of antihypertensive treatment. Serial electrocardiograms and echocardiograms (see Chapters 42 and 43) may help assess the effects of hypertension and antihypertensive treatment on the heart, but their clinical utility in managing an individual patient is unclear. Consensus guidelines stratify hypertensive patients into risk groups for therapeutic decisions (Table 55-5) (Table Not Available). For those with stage 2 or stage 3 hypertension, immediate drug therapy is warranted. Risk group B includes patients with hypertension who do not have clinical cardiovascular disease or target organ damage but who do have one or more of the major cardiovascular risk factors other than diabetes mellitus. If multiple risk factors are present, immediate drug therapy should be considered. Lifestyle modification and management of reversible risk factors should accompany drug treatment. This concern appears to be most relevant to hypertensive patients with pre-existing coronary artery disease and to those with a pulse pressure greater than 60 mm Hg. Data that support this hypothesis are predominantly retrospective and inconclusive, and large prospective clinical trials have failed to substantiate the J-curve hypothesis. Beneficial effects include protection from stroke, coronary events, heart failure, progression of renal disease, progression to more severe hypertension, and most importantly, all-cause mortality (Fig. The benefits of antihypertensive treatment in elderly patients are even greater than the benefits in younger patients. A meta-analysis of 13 randomized clinical trials with 16,000 persons 60 years of age and older showed that 43 persons needed to be treated for 5 years to prevent one stroke and 61 persons needed to be treated for 5 years to prevent one coronary event. Only 18 persons needed to be treated to prevent one cardiovascular (cerebrovascular or cardiac) event. Furthermore, only 15 persons with isolated systolic hypertension needed to be treated for 5 years to prevent a cardiovascular event. Comparison with 12 trials involving 33,000 middle-aged and younger hypertensive persons revealed that for all outcomes except cardiac mortality, two to four times as many younger as older persons needed to be treated for 5 years to prevent morbid and mortal cardiovascular events. Therapy should be tailored to the individual characteristics of each patient, such as weight reduction and exercise for an overweight patient and moderation in alcohol consumption for a heavy drinker.
Half of these circulating cells adhere to endothelial cells and compose the "marginated pool" (MaP) impotence and depression discount 400 mg viagra plus free shipping. After their very brief sojourn in the peripheral blood erectile dysfunction ayurvedic drugs buy 400 mg viagra plus with amex, the neutrophils invade the extravascular compartments of most organs erectile dysfunction over 70 order viagra plus 400 mg with visa, where they are used as defenders or garbage disposal devices (a process that involves both destruction of the offending organism and self-destruction) erectile dysfunction increases with age purchase 400 mg viagra plus mastercard, or they die within 1 to 2 days. Bone marrow defects (failure to produce and release neutrophils at a normal rate) account for the majority of neutropenias in clinical practice. Failure of the marrow compartment can occur as a result of direct injury, in which case the marrow usually contains fewer than normal hematopoietic cells, or from maturation defects of hematopoietic cells, principally characterized by normal or increased numbers of morphologically abnormal hematopoietic cells. In either case, neutropenia of this type frequently occurs along with abnormalities in the number of platelets and red cells. Marrow injury can occur as a consequence of a variety of diseases, but drug-induced injury is most common (Table 172-1). Antineoplastic and immunosuppressive agents are generally designed to inflict injury on a proliferative population of cells. Drugs that usually are not myelosuppressive and well tolerated in the majority of patients can sometimes induce either marrow injury or peripheral neutrophil destruction. These drug-induced reactions can result from direct drug-mediated cytotoxicity or from an immune mechanism in which (1) neutrophils are destroyed in extramedullary sites as a result of antineutrophil antibodies. Radiation (see Chapter 19) may result in acute self-limited bone marrow injury and chronic marrow failure. Chronic radiation-induced injury can also result in the later development of myelodysplasia and non-lymphocytic leukemia, both of which may present with neutropenia. Benzene toxicity can also result in acute or chronic neutropenia and, like radiation-induced marrow failure, is associated with a high risk of acute non-lymphocytic leukemia. Immune-mediated bone marrow failure can be mediated by autoantibodies or by T lymphocytes that inhibit the growth of bone marrow precursor cells. Apart from those with acquired aplastic anemia (often immunologically mediated), most patients with immune-mediated leukopenia have concurrent rheumatic or autoimmune diseases; these diseases are especially likely if the neutropenia is the only defect in patients with normal red cell and platelet counts. Infection of the marrow per se is unusual and most often does not result in neutropenia; some exceptions include mycobacterial infection (especially those caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and M. Carcinoma of the lung, breast, prostate, and stomach as well as malignant hematopoietic disorders can occupy enough of the medullary space to cause global marrow failure. Similarly, in certain of the myeloproliferative diseases and leukemias, bone marrow fibroblasts can proliferate significantly in the marrow and contribute to bone marrow failure (see Fig. Maturation arrest can result in functional bone marrow failure even though the bone marrow is full of granulocyte precursors. In the bone marrows of patients with folate or vitamin B12 deficiency, for example, numerous, morphologically abnormal granulocyte precursors fail to mature normally and therefore suffer a high rate of intramedullary death because of the effects of the vitamin deficiency state on nuclear replication (see Chapter 163). The marrow is hypercellular but is packed with peculiar cells exhibiting dyssynchronous nuclear and cytoplasmic maturation. Hematopoietic activity in the primitive cell population is intensely active, but the proliferative activity is ineffective at delivering terminally differentiated cells into the blood stream-the process is known as "ineffective hematopoiesis. Perturbations of the peripheral blood compartment result from shifts in the circulating pool. In pseudoneutropenia, neutrophil production and utilization are normal, but the size of the marginated pool is increased and the circulating pool is decreased. Because these marginated cells, while 921 Figure 172-2 the causes of neutropenia have been arranged according to the compartment with which the pathophysiologically relevant mechanism is linked. The approach to the neutropenic patient should begin by determining which of the three major compartments is likely the critical pathophysiologic point. The approach to the neutropenic patient whose neutrophil production is reduced is entirely different than that taken for neutropenic patients whose production is normal and whose rate of delivery to the extravascular compartment is normal or appropriately increased in the context of an acute infection. Acquired pseudoneutropenia often occurs as an acute or subacute response to systemic infections; it is generally associated with acute changes in other compartments (Fig. Neutrophils and their precursors respond to a number of environmental cues in a highly regulated fashion. Rarely, increased demand for neutrophils in the extravascular compartment can lead to transient neutropenia, especially in patients with severe acute infections (see Fig. In such cases, the immediate demand for neutrophils in the zone of infection calls forth such a substantial release response that the marrow storage pool is used up before it can be restored by increased proliferative activity of granulocyte progenitor cells.
Duplex kidneys with partial ureteral duplication are harmless erectile dysfunction doctors northern virginia discount viagra plus 400 mg on line, relatively common abnormalities impotence blood pressure generic viagra plus 400mg overnight delivery. Renal duplication with complete ureteral duplication erectile dysfunction electric pump buy discount viagra plus 400mg online, on the other hand erectile dysfunction treatment in bangkok cheap 400 mg viagra plus overnight delivery, is a more serious malformation because of associated ureteral ectopy (Fig. The ureter arising from the cephalad portion of the duplicated kidney typically enters the bladder below the normal position. Stenosis of the ectopic ureteral orifice results in varying degrees of urinary obstruction. High-grade obstruction causes maldevelopment and non-function of the upper part of the kidney, and enlargement of the ureterocele compresses and mildly obstructs the lower-pole ureter. This malformation, commonly discovered during childhood because of reflux and urinary tract infection, may not become symptomatic until adulthood, also because of urinary tract infection. Simple ureteral ectopy in the urethra or vagina is associated with incontinence and an increased risk of ascending infection. Ectopic ureters in the seminal vesicle become symptomatic at the onset of sexual activity. Pelvic kidneys are occasionally injured during parturition and are susceptible to infection and lithiasis because of stasis and reflux. Bilateral renal ectopia is often associated with fusion of the two kidneys, the most common type being a horseshoe kidney (Fig. Ureteropelvic obstruction in an adult is less often congenital and more often acquired as a result of ureteritis and pyelitis. Extrinsic ureteropelvic and upper ureteral obstruction has sometimes been attributed to aberrant blood vessels that appear to kink and constrict the ureter, but intrinsic ureteral abnormalities may underlie this association. Hydrocalycosis, secondary to infundibular stenosis, and caliceal diverticula in early life are probably congenital, although the same abnormalities later in life are of uncertain pathogenesis. Both become symptomatic because of infection 631 Figure 116-1 Urographic demonstration of left renal duplication with an ectopic ureterocele in the bladder. Diverticula and mucosal folds and valves are rare, presumably congenital causes of low ureteral obstruction. Abnormal insertion of the ureter into the bladder is arguably the basis of vesicoureteral reflux. Nonetheless, reflux gradually diminishes in frequency and severity during childhood. Extreme ureteral dilation in association with severe vesicoureteral reflux (refluxing megaureter) is linked with obstructive maldevelopment of the lower urinary tract. Some boys with posterior urethral valves and reasonably functioning urinary tracts survive into adulthood with little impairment in renal function. The prune-belly syndrome consists of a distended abdominal wall with deficient abdominal musculature, cryptorchidism, dilated bladder and Figure 116-2 A horseshoe kidney, fused across the midline (arrows), is demonstrated by enhanced computed tomography. The lax, wrinkled anterior abdominal wall, from which the syndrome derives its name, smoothes out with growth into a prominent potbelly. Siblings are at some risk of developing the abnormality; surviving males have been sterile. Anterior urethral diverticula related to mucosal folds that function as flap valves partially obstruct the urethra and become complicated by local infection and lithiasis. In megalourethra, the penile urethra distends during micturition because of partial or complete absence of the corpus spongiosum. Severe forms of the abnormality are usually accompanied by other malformation, but milder forms involve only the distal end of the urethra. Vesical exstrophy and epispadias are ordinarily treated in early childhood and rarely neglected into adolescence. Late repair of exstrophy is associated with a greatly increased risk of bladder cancer. Repair may be followed by vesicoureteral reflux, and inguinal hernias are commonly present in males. Although complete epispadias causes incontinence, the less severe balanic and penile forms are usually continent. Hypospadias with a short and curved penis (chordee) is rarely allowed to persist into adulthood. A comprehensive urologic discussion of renal and upper urinary tract malformations. Approximately 29,900 new cancers are diagnosed annually, and annual cancer deaths number 11,600. |