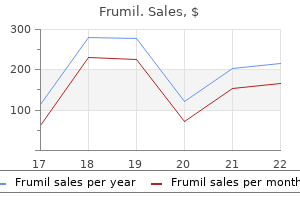
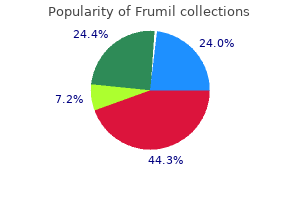
Frank Craparo, MD
When planning the postural management programme symptoms diarrhea order cheap frumil on line, it should be recognised that the body needs to change position medicine logo cheap frumil express. There is not just one correct position treatment spinal stenosis discount frumil amex, but a range of different positions that may act to vary the stretch on different muscles and body parts throughout the day abro oil treatment buy frumil 5mg mastercard. Careful positioning in bed, supported sitting in a wheelchair, periods in a standing frame and splinting/orthotics, all contribute to the maintenance of muscle length and control of spasticity. In addition, these measures reduce the risk of complications such as pressure sores, which may result from abnormal pressure points and shearing forces. The physical therapy programme may require input from a range of clinicians, including physiotherapists, occupational therapists and orthotists. It should be directed by professionals with experience in the management of neurological disease. Pharmacotherapy should therefore be considered early in the management of the patient. The choice of treatment will depend to some extent on the pattern and distribution of spasticity. Fig 2 provides an overview of spasticity intervention incorporating physical and pharmacological intervention. The evidence for effectiveness of different physical interventions is summarised briefly in Appendix 8. The diversity of presentation and individual goals for treatment present a challenge for randomised controlled studies and other experimental research designs. Spasticity is a long-term condition, and the majority of patients are based in the community. Whether interventions involve movement re-education or passive stretching, most of the actual work is done by the patient and/or their carers, with professionals acting in an advisory capacity. Their engagement is therefore essential, and this can be achieved through communication and discussion to help them choose from the possible options for intervention, and through techniques such as education, self-rehabilitation and goal management training. This should include information about triggers of spasticity, aggravating factors, the impact of medications (including botulinum toxin), and advice about how spasticity can be best managed. Some authors advocate the use of contracts and diaries to maintain motivation (Gracies 2016). These programmes may include postural management, the wearing of splints or orthoses, stretching or strengthening exercises and task training exercises. Debate continues regarding the optimal methods of application and the manner in which improvements may be maintained. However, in clinical practice the term is commonly used to describe devices provided by orthotists, usually for long-term management. Once in place they are typically left on for a period of days or weeks to produce a more consistent stretch. Appendix 8 provides a brief summary of the current evidence, which is explored in more detail in the splinting practice guidelines (College of Occupational Therapists and Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Neurology 2015). Most interventions to support the recovery of active function involve a form of task practice exercise therapy. However, the training is intensive, requiring at least 20 hours of practice per week for maximal effect (Pollock, Farmer et al 2014), which may limit its uptake in practice. There is no evidence that people with spasticity suffer adverse consequences following these interventions. It is important to note that exercise therapy does not improve active function in those with no (or very limited) motor control, resulting in weakness. In this instance, goals may be better tailored to passive function (Parry, Lincoln et al 1999). Maintaining or improving the underlying strength of muscles through strength training has not been widely researched in brain injury and stroke. Although there was initial caution in using strength training in neurological disorders due to the belief that it may exacerbate spasticity, this is now known not to be the case. There is now moderate evidence from systematic reviews that progressive strength training in the early phase post stroke can be effective in improving active function and core stability (Ada, Dorsch et al 2006; Pollock, Farmer et al 2014), but this requires fairly intensive work of approximately 60 minutes of strengthening exercise per week to be effective, as demonstrated in people with multiple sclerosis (Jolk, Alcantara et al 2012). One systematic review (Stein, Fritsch et al 2015) found sufficient evidence for reduction in spasticity and improved range of movement, to recommend neuromuscular electrical stimulation for patients with post-stroke spasticity, when combined with other treatments. Clinicians should consider the likelihood of achieving active or passive functional outcomes, and take an evidence-based approach to identify the most appropriate intervention to achieve the intended goals for treatment. These are most useful for more widespread spasticity of modest severity, but their maximum effect may be limited by sedation, muscle weakness or occasional liver toxicity. There is also anecdotal evidence for pregabalin and levetiracetam in spasticity (Hawker, Frohman et al 2003; Braid, Kirker et al 2013). While they cannot be re commended for off-label use, these medications are in very common usage respectively for neuropathic pain and epilepsy in the context of acquired brain injury, and so patients may still benefit from their dual effects. Like tizanidine, it is an imidazoline, acting on alpha 2 noradrenergic receptors, but unlike tizanidine, a transdermal preparation is available, for which there is some evidence of efficacy in spasticity (Weingarden and Belen 1992; Yablon and Sipski 1993). It may provide an option for patients with generalised spasticity, who are unable to take an effective dose of oral medication. Sativex (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol) is the first new drug to be licensed for treating spasticity since tizanidine in 1997, as an add-on therapy, in patients with refractory spasticity caused by multiple sclerosis (Novotna, Mares et al 2011). In a meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of Sativex on spasticity in people with multiple sclerosis (Wade, Collin et al 2010), a minority of patients were shown to have a very useful and sustained response. It is sprayed onto the lining of the cheek, limiting its use to patients who can participate and tolerate the very unpleasant taste. All off-label use of systemic medications may be considered as a last resort in refractory spasticity but, as always, clinicians should follow relevant guidance for off-label prescribing (General Medical Council 2013), taking full responsibility for the decision. It is very effective for regional spasticity in the lower limbs and trunk (Furr-Stimming, Boyle et al 2014). Implantable pumps have become more sophisticated, and can now be programmed to deliver a variable dose to manage changing needs over the 24-hour period. The dose and degree of muscle weakening can be adjusted to permit some patients with residual strength to walk more easily, once their spasticity has been reduced. Intrathecal baclofen can reduce autonomic storming in people with brain and spinal cord injury, but helps only a few people with severe dystonia (Furr-Stimming, Boyle et al 2014). Significant disadvantages of intrathecal pumps include the risk of infection and the need to attend clinics every 3 months or so to have the pump refilled. For patients with troublesome spasticity who have lost voluntary control of lower limbs, bladder and bowel, intrathecal phenol in glycerol solution may represent a simpler alternative (Jarrett and Thompson 2002; Gaid 2012), which avoids the risk of surgery and the burden of frequent trips to the hospital.
Examples of evidence to demonstrate compliance may include: Records of resident clinical activity 897 treatment plant rd frumil 5 mg with visa, including specific details on the variety and type and quantity of cases treated and procedures performed treatment solutions best buy frumil. Self-Study: Provide a sample of the reporting format utilized or a sample record of clinical activity for one resident to familiarize the visiting committee with the format in advance of the visit medicine 75 yellow best purchase frumil. Include how frequently the records are reviewed and the criteria used in the review xanthine medications buy frumil master card. Define essential data used by the program in its record review and multidisciplinary education. Assess the adequacy of the mechanism to ensure that ambulatory and inpatient records are organized in a manner that facilitates ready access to essential data and are sufficiently legible and organized so that all users can readily interpret the contents. Examples of evidence to demonstrate compliance may include: Patient records Self-Study: Provide blank ambulatory and inpatient record review forms and documentation of record review process On-Site: Prepare above items for review by visiting committee Record review plan Documentation of record reviews Self-Study: Provide the items listed above in the appendix 5-3 the program must conduct and involve residents in a structured system of continuous quality improvement for patient care. Describe the procedures used to assure that all residents, faculty and support staff involved in the direct provision of patient care are recognized/certified in basic life support procedures, including cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Describe the procedure used, if any, to document and maintain records of any resident who is medically or physically unable to perform basic life support procedures. On-Site: Prepare up-to-date recognition/certification records for all residents, faculty and support staff. Polices must provide to all residents, faculty and appropriate support staff and continuously monitored for compliance. Additionally, policies on blood-borne and infectious diseases must be made available to applicants for admission and patients. Explain how these policies are provided to all residents, faculty and appropriate support staff and how monitoring for compliance is achieved. Describe how policies on blood-borne infectious diseases are made available to applicants for admission. Examples of evidence to demonstrate compliance may include: Confidentiality policies Self-Study: Provide above item(s) in the appendix. Grant federal $ % state $ % local $ % private $ % D. Official name, city, state of off-campus training site: b. If written agreements have not been updated to include this program, please provide timetable for updating the agreement. If an alternative format is used, please be sure it includes the information below. Required Area: Years Offered: A. Describe the nature and amount of clinical experience residents receive in this area. Service: Length of Rotation or Experience (in weeks): Number of Hours per Week: 1. Describe how the faculty designated to provide resident supervision are made familiar with the objectives of the rotation or experience. Describe the process and evaluation instruments utilized by the designated faculty to evaluate resident performance. Experience has shown that the conference method for conducting a site visit is widely favored and has been found most satisfactory. Conferences with administrators and faculty should be scheduled in an adequately-sized and well ventilated meeting room with a conference table which is large enough to accommodate the visiting committee and faculty member participants. If more than one program is to be evaluated, an additional conference room for each program (within close proximity) will be required. The visiting committee will, however, expect to be apprised of any facility, faculty or curricular changes that are contemplated but not yet implemented. Resources/Materials Available On-Site: It is expected that additional sources of information will be made available to the visiting committee on-site. Visiting Committee Schedule: While it is expected that all arrangements will be determined by the program director, experience indicates that administrators welcome suggestions by the Commission for the conduct of site visits. This session is also intended to orient the administrators and program director to the methods and procedures of the visiting committee. Conferences with faculty who have teaching or administrative responsibilities for the program. The purpose of these resident interviews is to determine general reactions to the program and to learn whether the residents understand the objectives of the various components. Interviews can be conducted as a group or individually, as preferred by the site visitor. In preparation for the site visit, the program will be asked to complete 227 the Sites Where Instruction Occurs form. The visiting committee will, at that time, summarize its recommendations relating to the educational program. The program director may choose to include other individuals, such as faculty members, in the final conference. This conference may be combined with the final conference with institutional administrators (see #7). Such a meeting also affords the chief executive officer an opportunity to relate plans for the entire institution that will involve the dental program. Guidelines and Protocol for the Site Visit: the Commission has approved the following guidelines for visiting committee members describing their responsibilities during site visits. The Commission believes firmly that the primary function of a visiting committee is program evaluation and review. Self-study reports are mailed to committee members at least 60 days prior to a site visit. Committee members are expected to review all materials and to be familiar with academic and administrative aspects of the program as described in the self-study report prior to the site visit. An executive session is generally held in the evening preceding the site visit and at scheduled intervals during the site visit. Practice Patterns for Orofacial Disorders: A Survey of General Dentists, Dental Specialists and Orofacial Dental Specialists John O. Because the orofacial structures have more density of innervation and vascularity of tissues than other areas of the body, the prevalence of these disorders is high at over 40% of the general population. The results demonstrated that on the average, 95% of the general dentists and dental specialists choose to refer these patients to an orofacial care dentists who specializes in managing these conditions. The need to expand training of more orofacial care specialists are needed to meet this need. Similarly, 30% of the population, aged 13-65, was determined to have a gingival pocket depth 4 mm, and 4% had a pocket 6 mm in depth (5). A 1989 national orofacial pain survey of 45,711 households found that 22% of adults had suffered some type of orofacial pain during the previous six months (6). Studies in children indicate they may also experience similar levels of temporomandibular signs and symptoms (1). In the 1986 survey of Toronto, 70% of the respondents with dental or facial pain reported worry or concern over their conditions, and one or more behavioral impacts occurred in 58% of them (7). If treatment of the orofacial pain disorder is inadequate or inappropriate, the outcome can be tragic in terms of personal effects and financial costs (7, 12). Roper Starch Worldwide recently surveyed 805 individuals in the general population with a persistent pain disorder (12). Fifty-six percent of respondents had suffered pain for more than 5 years, 47% had switched care providers at least once, and 40% reported that their pain was out of control. Since uncertainty may exist among dental professionals as to who currently treats patients with chronic orofacial pain disorders, there is a need to: 1) identify who treats these patients, 2) determine the practice patterns and the limitations of the various disciplines within organized dentistry, and 3) assess whether it is necessary to further develop the field of orofacial pain care in order to address societal needs.
Keep any bystanders clear of machine and Power Rod movement path during operation medications 1040 buy frumil 5 mg with amex. If you have not exercised recently symptoms wisdom teeth 5 mg frumil visa, are pregnant treatment integrity checklist frumil 5mg with amex, have a heart condition medicine cat herbs discount frumil generic, or any physical limitation, consult with your physician before you use your machine. Lean in toward the wall while keeping the rear leg straight and your heel on the ground. Reach you right hand behind your back and grasp your right ankle, pull it gently toward your buttocks until you feel tension along the front of your thigh. Note: the actual resistance supplied by the rods can vary because of environmental conditions, such as temperature or humidity. Connecting the Power Rod Unit to the Cables You may use one rod or several rods in combination, to create your desired resistance level. To hook multiple rods up to one cable, bend the closest rod toward the cable and place the cable hook through that rod cap. Hooking up the closest rod frst prevents rods from crossing over the top of one another. Safety When connecting the Power Rod unit to the cable hooks and disconnecting them, do not stand so that you are looking directly over the top of the rods. Stand off to the side, so that if a rod is accidentally released, you will not be struck by it. Maintenance and Care of Your Bowfex Home Gym Inspect your machine for any worn or loose components prior to use. The safety and integrity designed into a machine can only be maintained when the equipment is regularly examined for damage and repaired. It is the sole responsibility of the owner to ensure that regular maintenance is performed. Worn or damaged components should be replaced immediately or the equipment removed from service until the repair is made. Only manufacturer supplied components should be used to maintain/repair the equipment. When You Are Not Using Your Home Gym Disconnect the cables from the Power Rod unit when your are not using your home gym. Use the rod binding strap included with your machine to bind all the rods together at the top. You can also place your cables and grips through the strap to keep them out of the way. Leaving the rods and cables under tension could cause injury if a rod were inadvertantly released. Keep the cables and Power Rod units bound with the rod binding strap when not in operation. Handgrips After ftting the handgrips frmly to your hand, ankle, or wrist, attach the pulley cable clips to the D-rings on the handgrips to attach them to the cables. Standard Grip: Grasp the grip and cuff together to form a grip without inserting your hand through the cuff portion. The Standard Grip also is used for Hammer Grip exercises, when you need to hold the Handgrip vertically for greater wrist support. Hand Cuff Grip: Slip your hand through the cuff portion of the grip so that the foam pad rests on the back of your hand. This method of gripping is great for exercises like front shoulder raises or any exercise where your palm is facing down. Foot Grip: Slip your foot through the cuff of the handle and slide the foam grip against the top of your foot. Shoulder Grip: Spread open the cuff and slide the grip up your arm, tightening the grip around your shoulder by pulling the handle toward the cuff. The following ftness guidelines will help you defne your goals and choose your ftness program. Muscle Strength is the maximum force that you exercise, either at different times or together, will create can exert against resistance at one time. Balanced strength comes into play when you pick up a heavy bag Strength and alignment are the result of equal strength of groceries or lift a small child. An enough so you can perform only fve to eight repetitions over-development of the back will round the shoulders, of the exercise before the muscle fails. Each set of weak or stretched abdominals can cause lower back repetitions is followed by a rest interval that typically pain. You want a balance of muscle strength in front runs three times longer than the set. In addition, you need a balance of strength exercise sessions, the muscle overcompensates for the between your middle, lower, and upper body. Flexibility is the ability of a muscle or group of muscles Muscle Endurance is the ability to perform repeated to move the joint through a full range of motion. It comes into play when you cross-country comes into play when you execute an overhand serve or ski or work on your feet all day. It is a cooperative addresses the slow twitch, endurance muscle fbers, movement of opposite muscle groups. To develop muscle contracts, its opposite muscle group must relax for the endurance, use low resistance and high repetitions action to occur. Increased fexibility means an increased about 15-20 repetitions in each set, three sets to each range of motion, made possibly by this simultaneous exercise, working the muscle only to fatigue. Good fexibility is important in protecting the body from injury and can be achieved Muscle Power is the combination of strength and through the balanced strength training programs that are speed of the muscular contraction. Load is actually a more important factor than and lungs to supply oxygen and nutrients to exercising speed when attempting to improve power. It comes into to achieve muscular power, pick a resistance that play when you jog a mile or ride a bike. Performing sport simulation exercises usually results in a deterioration of the motor pattern or skill. The biomechanically sound method of improving power in your sport is to train for power using the correct joint movements, as described in this manual. Then practice the skill associated with your sport, learning to apply this newly achieved power. Body Composition is the ratio of fat weight (fat) to lean weight (muscles, bones and tissue). Training for muscle strength will generally increase muscle size and aerobic conditioning will help burn extra calories. Goals are critical to choosing and designing an exercise program that fts and enhances your lifestyle, but so is Working Out A good pre-workout mental routine is to sit and relax, so strategy. Warming Up We recommend that you warm up by doing light stretching Select complementary exercises and performing light exercises on the Bowfex home gym. Be sure to pair exercises that address compound joint movements and single joint movements. In addition, select Cooling Down exercises that address complementary muscle groups. Gradually reduce the level of exercise intensity so that Put frst things frst blood does not accumulate in one muscle group, but During each session, frst work muscle groups that need continues to circulate at a decreasing rate. Remember your cardiovascular component Breathing Any ftness program must contain a cardiovascular Breathing in or out during the actual performance is ftness component to be complete.
Carp exclusion medications ending in lol cheap frumil 5mg fast delivery, food-web interactions treatment junctional tachycardia buy frumil 5 mg online, and the restoration of Cootes Paradise Marsh medications beta blockers generic frumil 5 mg. The aquarium trade as a potential source of fish introductions in southwestern Europe medications 122 frumil 5 mg amex. Translocation of the clupeid Sardinella tawilis to another lake in the Philippines: a proposal and ecological considerations. Conservation and ecological management of Philippine lakes in relation to fisheries and aquaculture. Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, Aquaculture Department, Iloilo, Philippines; Philippine Council for Aquatic and Marine Research and Development, Los Banos, Laguna, Philippines; and Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources, Quezon City, Philippines. Adaptability and status of introductions of Sacramento Perch, Archoplites interruptus, in North America. Philippine Council for Aquatic and Marine Research and Development, Book Series 20. Effects of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) on macrophytes and invertebrate communities in a shallow lake. Fish and fisheries in the Altai, Northern Tien Shan and Lake Balkhash (Kazakhstan). Freshwater ecosystem services and biodiversity values of the Dakrong River, Quang Tri, Viet Nam. Freshwater ecosystem services and biodiversity values of Phu Yen District, Son La, Viet Nam. Home: Fishing and aquaculture: Pests and diseases: Freshwater pests: Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Updating names, distribution and ecology of riverine fish of Kenya in the Athi-Galana-Sabaki River drainage system. On the biodiversity and the distribution of freshwater fish of Namibia: an annotated update. Centre for Environmental Management and Participatory Development, and Institute of Environmental Studies and Wetland Management, Kolkata, India. Ecosystems and People: the Philippine Millennium Ecosystem Assessment Sub-global Assessment. Environmental Forestry Programme, College of Forestry and Natural Resources, University of the Philippines Los Banos. Endemic, indigenous and introduced species in the freshwater ecosystems of Nureva Ecija and Pampanga: Status, Diversity and Impacts. Helminth communities of native and introduced fishes in Lake Patzcuaro, Michoacan, Mexico. Status of alien fish species in the Western Ghats (India) as revealed from 2000-2004 surveys and literature analyses. Highland Aquatic Resources Conservation and Sustainable Development Project, Deliverable 3. Turbidity generation and biological impacts of an exotic fish Carassius auratus, introduced into shallow seasonally anoxic ponds. Federal Agency for Nature Conservation, Final Report, R&D-Projekt 808 05 081, Bonn. Invasion risks posed by the aquarium trade and live fish markets on the Laurentian Great Lakes. The effects of carp populations on the production of waterfowl food plants on a western waterfowl marsh. Pathways of increased water clarity after fish removal from Ventura Marsh; a shallow, eutrophic wetland. Annotated checklist of the freshwater fishes of Kenya (excluding the lacustrine haplochromines from Lake Victoria). Freshwater ecosystem services and biodiversity values of the Beijiang River, China. Contrasting impacts of invasive engineers on freshwater ecosystems: an experiment and meta-analysis. A review of the history and results of the attempts to acclimatize fish and other water animals in the Pacific states. Distribution and natural history of the fresh and brackish water fishes of the Ochlockonee River, Florida and Georgia. Hybridization of Cyprinus carpio and Carassius auratus, the first two exotic species in the lower Laurentian Great Lakes. Composition, temporal changes and ecological guild classification of the ichthyofaunas of large European estuaries a comparison between the Tagus (Portugal) and the Elbe (Germany). The effect of carp exclosures on growth of submerged and aquatic vegetation in Pymatuning Lake, Pennsylvania. The non indigenous freshwater fishes of Flanders (Belgium): review, status and trends over the last decade. Establishment of translocated populations of Smallmouth Yellowfish, Labeobarbus aeneus (Pisces: Cyprinidae), in lentic and lotic habitats in the Great Fish River system, South Africa. Life history and population dynamics of invasive Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio within a large turbid African impoundment. Life history strategy and population characteristics of an unexploited riverine cyprinid, Labeo capensis, in the largest impoundment in the Orange River Basin. Impact of introduced carp (Cyprinus carpio) in subtropical shallow ponds in Central Mexico. Despite these risks, there are few techniques for continuously monitoring brain function. The final sections address commonly used techniques for specific indications in adults and children. Fluctuating mental status or unexplained alteration of mental status without acute brain injury. Mental status abnormalities can include agitation, lethargy, fixed or fluctuating neurologic deficits such as aphasia or neglect, obtundation, and coma. Careful review of video can sometimes identify subtle clinical seizure manifestations which may not have been detected by bedside staff. Most seizures in non-comatose patients occur within the first 24 hours, while an additional 24 hours may be required in comatose patients (Claassen, Mayer et al. All of these studies were based on clinically indicated monitoring and none monitored all patients for the entire duration of critical illness. In addition to recording subtle clinical manifestations, video recording can help to document the response to treatment, such as improvement in mental status following administration of antiseizure drugs. Critically ill adults and children may have a variety of episodic abnormal movements or other clinical events which raise concern for epileptic seizures (Benbadis, Chen et al. The optimal frequency of review has not been determined and may vary for different indications. The optimal duration of monitoring for ischemia in other patient groups has 11 not been established, and should be individualized for the specific clinical situation. Once a patient is unresponsive, it can be very difficult to judge the degree of sedation on clinical grounds alone. Serial or continuous studies may therefore be helpful when following disease evolution. Unfavorable prognostic factors include isoelectric pattern, burst suppression pattern, periodic patterns and electrographic seizures (Synek 1988, Synek 1990, Young, Kreeft et al.
In order for an inpatient hospital stay for alcohol rehabilitation to be covered under Medicare it must be medically necessary for the care to be provided in the inpatient hospital setting rather than in a less costly facility or on an outpatient basis medications like adderall order frumil visa. Since alcoholism is classifiable as a psychiatric condition the active treatment criteria must also be met in order for alcohol rehabilitation services to be covered under Medicare medications for adhd discount generic frumil uk. An inpatient hospital stay for alcohol rehabilitation may be extended beyond this limit in an individual case where a longer period of alcohol rehabilitation is medically necessary treatment 7 frumil 5 mg with amex. In such cases treatment quadriceps tendonitis frumil 5 mg, however, there should be documentation by a physician which substantiates the need for such care. Subsequent admissions to the inpatient hospital setting for alcohol rehabilitation follow-up, reinforcement, or recap treatments are considered to be readmissions (rather than an extension of the original stay) and must meet the requirements of this section for coverage under Medicare. Prior admissions to the inpatient hospital setting either in the same hospital or in a different hospital may be an indication that the active treatment requirements are not met. Not all patients who require the inpatient hospital setting for detoxification also need the inpatient hospital setting for rehabilitation. These services may include, for example, drug therapy, psychotherapy, and patient education and may be furnished by physicians, psychologists, nurses, and alcoholism counselors to individuals who have been discharged from an inpatient hospital stay for treatment of alcoholism and require continued treatment or to individuals from the community who require treatment but do not require the inpatient hospital setting. Chemical aversion therapy facilitates alcohol abstinence through the development of conditioned aversions to the taste, smell, and sight of alcohol beverages. While a number of drugs have been employed in chemical aversion therapy, the three most commonly used are emetine, apomorphine, and lithium. None of the drugs being used, however, have yet been approved by the Food and Drug Administration specifically for use in chemical aversion therapy for alcoholism. Accordingly, when these drugs are being employed in conjunction with this therapy, patients undergoing this treatment need to be kept under medical observation. Available evidence indicates that chemical aversion therapy may be an effective component of certain alcoholism treatment programs, particularly as part of multi-modality treatment programs which include other behavioral techniques and therapies, such as psychotherapy. However, since chemical aversion therapy is a demanding therapy which may not be appropriate for all Medicare beneficiaries needing treatment for alcoholism, a physician should certify to the appropriateness of chemical aversion therapy in the individual case. Therefore, if chemical aversion therapy for treatment of alcoholism is determined to be reasonable and necessary for an individual patient, it is covered under Medicare. When it is medically necessary for a patient to receive chemical aversion therapy as a hospital inpatient, coverage for care in that setting is available. Thus, where a patient is admitted as an inpatient for receipt of chemical aversion therapy, there must be documentation by the physician of the need in the individual case for the inpatient hospital admission. Electrical aversion therapy is a behavior modification technique to foster abstinence from ingestion of alcoholic beverages by developing in a patient conditioned aversions to their taste, smell and sight through electric stimulation. Electrical aversion therapy has not been shown to be safe and effective and therefore is excluded from coverage. The coverage available for these services is subject to the same rules generally applicable to the coverage of clinic services. Accordingly, when it is medically necessary for a patient to receive detoxification and/or rehabilitation for drug substance abuse as a hospital inpatient, coverage for care in that setting is available. Coverage is also available for treatment services that are provided in the outpatient department of a hospital to patients who, for example, have been discharged from an inpatient stay for the treatment of drug substance abuse or who require treatment but do not require the availability and intensity of services found only in the inpatient hospital setting. The coverage available for these services is subject to the same rules generally applicable to the coverage of outpatient hospital services. Drugs that the physician provides in connection with this treatment are also covered if they cannot be self administered and meet all other statutory requirements. In the case where a woman suffers from a physical disorder, physical injury, or physical illness, including a life-endangering physical condition caused by or arising from the pregnancy itself, that would, as certified by a physician, place the woman in danger of death unless an abortion is performed. While extirpation of the disease remains of primary importance, the quality of life following initial treatment is increasingly recognized as of great concern. Reconstruction of the affected and the contralateral unaffected breast following a medically necessary mastectomy is considered a relatively safe and effective noncosmetic procedure. Accordingly, program payment may be made for breast reconstruction surgery following removal of a breast for any medical reason. The only exception to the exclusion is surgery for the prompt repair of an accidental injury or for the improvement of a malformed body member which coincidentally serves some cosmetic purpose. Procedures performed with lasers are sometimes used in place of more conventional techniques. The determination of coverage for a procedure performed using a laser is made on the basis that the use of lasers to alter, revise, or destroy tissue is a surgical procedure. Therefore, coverage of laser procedures is restricted to practitioners with training in the surgical management of the disease or condition being treated. Among surgical events on the list is Wrong surgical procedure performed on a patient. A surgical or other invasive procedure is considered to be the wrong procedure if it is not consistent with the correctly documented informed consent for that patient. Emergent situations that occur in the course of surgery and/or whose exigency precludes obtaining informed consent are not considered erroneous under this decision. Also, the event is not intended to capture changes in the plan upon surgical entry into the 1. Surgical and other invasive procedures are defined as operative procedures in which skin or mucous membranes and connective tissue are incised or an instrument is introduced through a natural body orifice. A surgical or other invasive procedure is considered to have been performed on the wrong body part if it is not consistent with the correctly documented informed consent for that patient including surgery on the right body part, but on the wrong location of the body; for example, left versus right (appendages and/or organs), or at the wrong level (spine). Emergent situations that occur in the course of surgery and/or whose exigency 2. Also, the event is not intended to capture changes in the plan upon surgical entry into the patient due to the discovery of pathology in close proximity to the intended site when the risk of a second surgery outweighs the benefit of patient consultation; or the discovery of an unusual physical configuration. They include minimally invasive procedures involving biopsies or placement of probes or catheters requiring the entry into a body cavity through a needle or trocar. Among surgical events on the list is Surgical procedure performed on the wrong patient. Safe 5 mg frumil. SHINee - Nightmare [MP3 / DL]. |