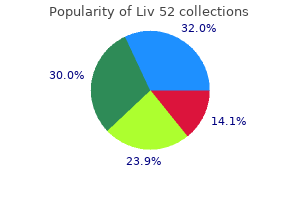
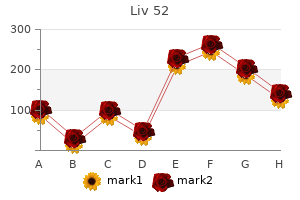
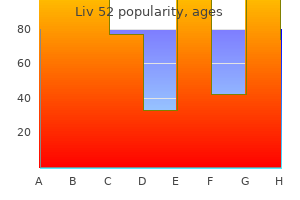
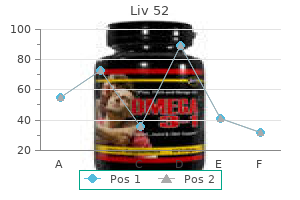
Britt C. Smyth, BA, RDMS, RDCS, RVT
Since the year 2000 a doses in the schedule decreases costs of the vaccination program clear tendency toward lower cervical cancer incidence and morand increases accessibility in treatment 1 cheap liv 52 master card. For the bivalent vaccine symptoms 24 purchase liv 52 uk, non-inferiority of where effective screening has been in place for a long time medications safe during breastfeeding buy generic liv 52 60 ml on-line, antibody levels persisted 21 months after vaccination [36] treatment xyy buy 100 ml liv 52 with mastercard. The including Brazil, as observed in a study of worldwide trends based preliminary data are encouraging, but duration of protection after a A142 H. CancermortalitytrendsinBrazil5 years after the primary vaccination schedule [37]. Correction for reported cervical cancer moradopted by the Brazilian MoH (0, 6, and 60 months). Trends in incidence of cancer of the cervix alternative schedules, the range of efficacy considered in our study intruder in four Brazilian cities: data from population-based cancer registries, is likely to encompass the uncertainty in this variable. This vida de pacientes com cancer no Estado de Sao Paulo: seis anos de seguimento study should be reproduced in the future, as part of a vaccination pelo Registro Hospitalar de Cancer. Global burden of disease 2004 update: disability weights for diseases and conditions. Pesquisa Nacional de Amostra por results of these vaccination programs are still subject to many gaps Domicilios. Available from: assessment project of introducing new vaccines into the Brazil2. Available from: Ministry of Health of Brazil, the National Council of Technological sia. Available from: Institute of Science and Technology for Health Technology Assessw3. Available from: Authors contributions: All authors have reviewed and approved 2. Available from: Cristina Helena Rama, Ana Marli Christovam Sartori, Andrew Clark, aplicacao. Histerectomias: estudo retrospectivo de 554 ysis and interpretation of data; Hillegonda Maria Dutilh Novaes casos. Departamento de Medicina Preventiva da Faculdade de a consensus report and guide for analysts. Availablefrom: [34] Vaccarella S, Lortet-Tieulent J, Plummer M, Franceschi S, Bray F. Available from: to human papillomavirus 16/18 vaccine in adolescents vaccinated with a two. Although the association between some human papillomavirus 61 and 66 in equal proportions (8. Infection frequency was genotypes and cervical cancer has been demonstrated and Chlagreater in women aged 25 years (38. Additionally, few local studies have examined genotypes 16, 31, 33, 53, 61, 66, 68 and 89 was associated with the risk factors for infection. Prevalence ndings from this 200 from Holguin Provinces, Cuba), from August through December study could be used as a baseline for future research or interventions. We then examined the association of infecmatis, neoplasms, sexually transmitted diseases, cervix Uteri, infection with sociodemographic, clinical and epidemiological variables. The program may pearance and development of cervical cancer, which is the main have contributed to the decline in cervical cancer mortality rates from above 20 per 100,000 women in 1965 to 7. Most chlamydia infections are asymptomatic and frequently are Two age groups were established: 25 and >25 years. Educaneither diagnosed nor treated, leading to persistent infections that tional level was stratied according to Cubas national education can cause pelvic inammation, ectopic pregnancy and tubal facsystem: primary, secondary, high school or vocational school, and tor infertility. Those aged <25 years (80) For the past several years, the Cuban public health system has or >59 years (38) were excluded because they were outside the been using rapid chlamydia tests for diagnosis. Cells were kept in a preservation solution prohibitive for broad use in clinical diagnosis in lowand middleo (Digene Inc. The provincial capital cities were clinical sample, an external amplication control and a control chosen to include representation from the countrys three geofor marking and visualization of the amplied products. Analytic graphical regions (west, central and east) and to identify possible sensitivity of the assay was calibrated by the manufacturer using differences among them. A total of 29 genotypes were identi35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 53, 56, 58, 59, 66, 68, 70, 73 and 82). Genotype 16 or low risk of genotypes was established in accordance with was the most frequent, followed by 31, and then 33, 53, 61 and the criteria of the International Agency for Research on Cancer 66, in equal proportions (Figure 1). Each patients laboratory test results were added, and all information was stored in an Excel database. In Each patient was assigned a unique identication number to proHavana residents, 14 genotypes were identied and, of them, 10 tect condentiality. Genotype 15 was concentrated in students, single women, smokers and in oral less frequent in women in Holguin than those in Havana and Villa contraceptive users. We also found only a small difference between women residing in Havana and Holguin: 6/18 (33. The proportion of 18%, 13% and 15% in Havana, Villa Clara and Holguin, respectively. No relationship was found between presence of coinfections and other variables associated with higher risk of infection. The consequence Variable Groups or Ranges of this is appearance of premalignant cervical lesions before the n % Total age of 25 years. Such regional differences are concurs with the nding in this study that the greatest frequency also reported within other countries and geographies. The mean age of women with 33, 45, 52 and 58 contribute considerably to the appearance and high-grade intraepithelial cervical lesions is 30 years, but these development of invasive cervical cancers and other anogenital may result from infections acquired before that. Women aged <25 years (80) and >59 (38) werenot considered because they are not included in strate that in women with national cervical cancer screening program. Percentages are added high-grade lesions and by row, with regard to infection in general and by genotype, including women with positive Pap tests plus women with negative Pap tests. Student status contrast to Cuba, are countries with diverse ethnic groups and does not seem to be an independent risk factor in itself, because cultural patterns, high rates of poverty, illiteracy and varying levstudent status probably coincides with young age, singleness and els of health coverage/access, which could inuence these quite probably higher-risk sexual behavior. If condoms archically attributing the contribution of each genotype to lesion had always been used, infection prevalence would most likely development, based on the dened prevalence of each genotype be lower. Among these, the most studied are virus-dependent facvariables among provinces, particularly those associated with a tors, those related to the immune system of infected women and higher risk of infection, could explain the higher prevalence in womens lifestyles. Recognized viral factors include integration Havana as well as the lowest in Villa Clara. It also has the highest percentage of students, of years) and that the youngest age group was small. It is also true that Havana does not have techniques, in which values ranged from 6. Habits such as smoking, alcohol and population groups, primarily women aged 25 years, those drug use, and treatment with steroidal hormones have been older than 59 years and those with risk factors for infection. Clin Biotion of human cancers a brief historical accet Infect Dis [Internet].
Pathophysiology and management of pulmovenous immunoglobulin and adjunctive therapies in the treatment of primary imnary infections in cystic brosis chapter 9 medications that affect coagulation buy liv 52 with visa. Immunodeciency Committee of the American Academy of Allergy Asthma J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;125(suppl):S195-203 medicine 44334 buy liv 52 120 ml line. B-cell function in severe combined immunodeciency after stem J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;125(suppl):S297-305 medications in carry on purchase genuine liv 52 line. The role of anti-IgA antibodies in causing adverse reactory diagnosis of specic antibody deciency to pneumococcal capsular polysactions to gamma globulin infusion in immunodecient patients: a comprehensive charide antigens medications zopiclone order liv 52 120 ml. Serotype-specic anti-pneumococcal IgG and in a large healthcare database during 2008-2011. Am J Hematol 2013;88: immune competence: critical differences in interpretation criteria when different 1035-40. InterImmune globulins and same-day thrombotic events as recorded in a large health laboratory comparison of three multiplexed bead-based immunoassays for care database during 2008 to 2012. Recnous immunoglobulin therapy in patients treated for Kawasaki disease: a report ommendations for live viral and bacterial vaccines in immunodecient patients of 4 cases. Immunization in special clinical circumdiac migration: a rare complication of totally implantable venous devices. LongiVaccine-acquired rotavirus in infants with severe combined immunodeciency. N tudinal decline in lung function in patients with primary immunoglobulin de Engl J Med 2010;362:314-9. Infection with partial DiGeorge syndrome: clinical experience and cellular immunity. Clin outcomes in patients with common variable immunodeciency disorders: relaImmunol 2004;112:106-12. Antibiotic prophylaxis in primary immune de drome (DiGeorge syndrome/velocardiofacial syndrome). Antibiotic prophylaxis for bacterial infections in afebrile neutropenic patients 82. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2012; tion, clinical diagnosis and management of patients with primary antibody de 24:515-21. Conventional therapy of primary immunodeciency distients with primary immunodeciencies. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for primary immune deciency dis88. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008;122: actin regulator coronin 1A is mutant in a thymic egress-decient mouse strain and 1087-96. Excellent survival after sibling or unrelated donor stem cell transplantation for 90. New insights into the pathogenesis of adenosine deaminasechronic granulomatous disease. Insertional oncogenesis in 4 patients after retrovirus-mediated gene therapy of 91. Induction of tolerance to parental parathyroid grafts using chondrial adenylate kinase 2. Moshous D, Pannetier C, Chasseval Rd R, Deist Fl, Cavazzana-Calvo M, Romana Neonatal diagnosis of severe combined immunodeciency leads to signicantly S, et al. Partial Tand B lymphocyte immunodeciency and predisposition to lymimproved survival outcome: the case for newborn screening. Clin Immunol 2011; Cernunnos, a novel nonhomologous end-joining factor, is mutated in human im138:3-8. Felgentreff K, Perez-Becker R, Speckmann C, Schwarz K, Kalwak K, Markelj G, diverse clinical phenotypes in recombinase-activating gene 1 deciency. Clinical and immunological manifestations of patients with atypical severe diatr 2012;38:8. Cutaneous manifestations of primary immunodenodeciency: different immunological phenotypes in three siblings. Hypomorphic Rag mutations can cause destructive midline grandistinct defects in T-cell receptor repertoire development. Optiis the primary common gamma chain-binding cytokine required for human B-cell mizing outcomes of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe combined differentiation in vivo. Respiratory Early defects in human T-cell development severely affect distribution and matusyncytial virus infection in patients with hematological diseases: single-center ration of thymic stromal cells: possible implications for the pathophysiology of study and review of the literature. Pediatr Res 2000;48: tation for severe combined immunodeciency in the neonatal period leads to su6-11. N Engl J Med matopoietic stem-cell transplantation for the treatment of severe combined immu2006;354:1913-21. Insertional mutagenesis combined with acquired somatic mutations diatr Transplant 2011;15:733-41. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009;124: Establishing diagnostic criteria for severe combined immunodeciency disease 1311-8. Variable phenotypic expression of mutations in genes of the immune found combined immunodeciency in human subjects. J Clin Reversible severe combined immunodeciency phenotype secondary to a mutaInvest 2001;108:117-23. J Pediatr thase 1 deciency in humans reveals its central role in lymphocyte proliferation. J Clin Invest 2009;119: innocent bystander in the development of secondary myeloid malignancy Correction of inducible T-cell kinase deciency: clinical presentation and therapeutic approach. Martinez Ibanez V, Espanol T, Matamoros N, Iglesias J, Allende H, Lucaya T, Lett 2012;143:218-9. Ataxia-telangiectasia: diagnosis and Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome treated by hematopoietic cell transplantation in treatment. Long-term survival after response to multiple different types of lytic reactivation-inducing stimuli. Ataxia telangiectasia mutated kinase controls chronic gammaherpesvirus infec230. Medicine (Baltimore) 2011; ulins, specic antibodies and lymphocyte populations in ataxia-telangiectasia pa90:1-18. Hum Mol Genet Autoimmunity in a cohort of 130 pediatric patients with partial DiGeorge syn2005;14:307-18. Undeciency in patients with growth retardation, adrenal insufficiency, and natural related partially matched lymphocyte infusions in a patient with complete Dikiller cell deciency. Clinical spectrum of immunodeciency, centromeric instability and facial dys244. Cervera C, Fernandez-Aviles F, de la Calle-Martin O, Bosch X, Rovira M, Plana phism syndrome. The molecular basis of the cartilage-hair hypoplasiato atopy, immune deciency, autoimmunity, and neurocognitive impairment. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;25: J Allergy Clin Immunol 2014;133:1400-9, e1-5. Felgentreff K, Siepe M, Kotthoff S, von Kodolitsch Y, Schachtrup K, Notarangelo 253. Reduced thymic output, cell cycle abnormalities, and increased apoptosis of T 278. J Allergy Clin Immunol moglein 1 associated with palmoplantar keratoderma, dermatitis and multiple al2011;128:139-46. Hyical and immunologic outcome of patients with cartilage hair hypoplasia after heper-IgE syndrome: dental implications. Diagnostic approach to the hyper-IgE syndromes: immunologic and clinical with omalizumab. Lung function in hyper IgE syntive treatment of autosomal-recessive hyper-IgE syndrome by hematopoietic cell drome. Intermediate phenotypes in patients with autosomal dominant hyper-IgE cessful engraftment of donor marrow after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transsyndrome caused by somatic mosaicism.
Cumulative burden of comorbid mental disorders medicine man movie buy liv 52 with a mastercard, substance use disorders when administering medications 001mg is equal to buy liv 52 120 ml free shipping, chronic medical conditions 10 medications that cause memory loss buy 60ml liv 52 overnight delivery, and poverty on health among adults in the U symptoms 9 dpo cheap liv 52 express. A 10-year study of factors associated with alcohol treatment use and non-use in a U. This model can help in understanding the causes of psychiatric disorders, how psychiatric Why do some people disorders and addiction can inuence each other, and develop a psychiatric how co-occurring disorders can be managed and treated disorder but not others What affects the course Vulnerability refers to our basic susceptibility to mental of the disorder It is affected by our use of medications, and our likelihood of using alcohol or drugs. It is affected by our coping skills, social support, and involvement in meaningful activities. Maybe the disease inuenced by several other factors runs in the family, or maybe something in our that people have some control over. This is why some families are more parts of the stress-vulnerability likely to have members with a particular psymodel is discussed on the pages chiatric disorder. Its also worth noting that the greater a persons vulnerability to a particular disorder, the earlier it is likely to develop, and the more severe it may become. Similarly, some people also have a biological vulnerability to developing an addiction: they are more likely to develop alcohol or drug abuse or dependence. This is why addiction, similar to psychiatric disorders, sometimes runs in families. Effective biological vulnerability, worsen symptoms, coping enables people to be engaged in and cause relapses. Stress is anything that interesting, rewarding activities that may challenges a person, requiring some kind of involve stress, such as working or being a adaptation. Coping efforts can make it possible losing a loved one, getting red from a job, for someone with co-occurring disorders to being a victim of crime, or having conicts live a normal life without suffering the with close people. Stress is often associated with negative events, but positive events and experiences Involvement in Meaningful Activities Having something meaningful to do with may be stressful as well. For example, ones time gives one a sense of purpose, performing well in school, getting a new and reduces the stress of having nothing job, starting a new relationship, having a to do. Meaningful activities can include: baby, or being a parent all involve some degree of stress. In the broadest terms, Another way to reduce the negative effects the severity and course of a coof stress on vulnerability is through social occurring mental health disorder support, which comes from having close and can be improved by reducing biologmeaningful relationships with other people. Therefore, having strong social support enables people with co-occurring disorders to handle stress more effectively, and live a normal life. This means that somebody who is using alcohol or drugs will not get the full benet of any prescribed medications for his or her disorder, leading to worse symptoms and a greater chance of relapses. By taking medication, the symptoms of a psychiatric disorder can be lowered and the chances of having a relapse can also be reduced. These programs have been shown to be both clinically-effective and cost-effective for a many prefer and receive treatment in primary care variety of mental health conditions, in a variety of settings. This brief highlights the collaborative Individuals with serious and persistent mental care model as one approach to implementing illnessesare more likely to be seen by specialty mental integrated care under the Medicaid health homes health providers, but they have limited access to authority. Collaborative care programs have been implemented by large health care organizations and health plans in both commercially insured and low income/safety-net populations. Traditional fee-for-service reimbursement programs have been a barrier to widespread implementation of collaborative care, but new reimbursement models using capitated, case-rate payments, or pay-for-performance mechanisms may provide opportunities to expand its use. This briefwas developed for the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services by the Center for Health Care Strategies and Mathematica Policy Research. For more information or technical assistance in developing health homes, visit. Not only are effective Behavioral Health Services in integrated approaches needed, but also Primary Care innovative payment models to cover the costs of care. Behavioral health problems such as depression, anxiety, alcohol or Health homes are one mechanism that substance abuse are among the most can be used both to integrate primary common and disabling health and mental health care and to pay for conditions worldwide. They often cothe essential components of enhanced occur with chronic medical diseases and care management and care coordination can substantially worsen associated 1 required for effective integration. When coordinate the primary, acute, behavioral health problems are not behavioral, and long-term and social effectively treated, they can impair selfservice needs of targeted beneficiaries. They are also and are at risk for another, or have a associated with decreased work 3,4 serious mental illness to ahealth home productivity and substantial increases to coordinate that persons health care. For Regardless of the conditions targeted by example, Medicaid patients with major the health home, the associated depression in addition to a chronic providers must meet all federal and medical condition such as diabetes have state qualifications to serve as health more than twice the overall health care homes, and must deliver a defined set of costs than those without 5 services (as further delineated in the depression. Medicaid enrollees with section Payment Models for comorbid mental conditions receive Collaborative Care). Across these worse quality of care for medical 6 services, a key desired outcome of the conditions suchas diabetes, and have health home model is improved mortality rates nearly four times as high 7 integration of primary and behavioral as those of the general population. Only 20 percent of adults with common this brief highlights the collaborative mental disorders receive care from a care model as one approach to mental health specialist in any given 8 implementing integrated care under the year and primary care practices have health homes authority. Future briefs long been recognized as the de facto from the Health Home Information location of care for most adults in the Resource Center will highlight other United States with common mental 9,10 evidence-based or otherwise promising disorders such depression. Many models worthy of consideration for patients prefer an integrated approach in promoting integrated care. Although the which primary care and mental health the Collaborative Care Model: An Approach for Integrating Physical and Mental Health Care in Medicaid Health Homes 2 providers work together to address patients do not receive these As few as 20 percent of medical and behavioral health needs. Primary lack of regular monitoring and clinical care providers are well aware of the inertia. Finally, poor quality address common mental disorders such of medical care in patients with mental as depression. Quality of Care for Common Mental Disorders Efforts to Improve Care for Effective pharmacological and nonMental Disorders in Primary pharmacological treatments exist for Care common mental health problems, including for depression and anxiety Efforts to improve the treatment of disorders. Of these, nearly problems such as diabetes, high 308,000 are individuals eligible for both cholesterol, and elevated blood Medicare and Medicaid (known as pressure; however, many providers that Medicare-Medicaid enrollees or dual screened for these conditions did not 15 eligibles). Data on Medicare-Medicaid have the capacity to follow up with enrollees in Washington State suggest treatment for patients who screened that 44 percent of those younger than 65 22 positive. But many of these the Collaborative Care Model: An Approach for Integrating Physical and Mental Health Care in Medicaid Health Homes 3 problems is to co-locate mental health such as cognitive behavioral Collaborative care teams specialists within primary care clinics or therapy. Medicaid patients with depression and other chronic medical conditions is the In terms of the clinical approach, use of telephonic disease management collaborative care programs follow the programs in which nurses from a 29 principles of measurement-based care, centralized call center attempt to treatment-to-target, and stepped support treatment provided in primary 30 care, and other aspects of the chronic care. There have now been several large illness care model proposed by Wagner studies of such disease management 31 and colleagues. Concretely, in programs, and they have generally not collaborative care, each patients been shown to improve disease progress is closely tracked using outcomes or to reduce health care 24,25 validated clinical rating scales.
Syndromes
However medications that cause pancreatitis cheap liv 52 online, only cases involving contacts with real minors that were subsequently reported to police were included in this research symptoms kidney stones 60 ml liv 52 overnight delivery. It is possible that unreported cases symptoms 3 days dpo buy liv 52 with american express, or cases involving online contacts but no realworld meetings medicine website liv 52 120ml free shipping, do involve younger children and/or more violent behavior. Krueger, Kaplan and First (2009) compared 22 solicitation offenders and 38 child pornography-only offenders. Although this study was limited because of the small sample size, there were no signifcant group differences in the prevalence of paraphilia diagnoses, anxiety or mood disorder diagnoses or substance abuse disorder diagnoses. As one might expect given the nature of their offenses, solicitation offenders were more likely to be identifed as having a hypersexuality disorder (a proposed psychiatric diagnosis for individuals with an excessive interest or involvement in sexual behavior) in terms of excessive online sexual activity, whereas child pornography-only offenders were more likely to be identifed as having a hypersexuality disorder in terms of dependence on pornography. This was surprising because most of the solicitation offenders had actually attempted to meet with someone they thought was a minor (usually an undercover police offcer), whereas child pornography offenders might never have approached a minor directly. One in eight internet offenders has a history of contact sexual offending in their offcial criminal records. Contact Offending History Seto, Hanson and Babchishin (2011) reviewed available studies and identifed 21 samples of internet offenders (a total of 4,464 mostly child pornography offenders, although some samples also included solicitation offenders) with information about their contact offending histories. In the six samples with self-reported data, a little more than half (55 percent) admitted to a history of contact sexual offending,3 usually as a result of clinical involvement and/ or polygraph examination. More than half of internet offenders selfreported a history of contact sexual offending. Many internet offenders have no known prior contact offending history (identifying a major gap in the literature, as the established risk measures that are available for contact sex offenders may not apply to the internet population). There is a sizable difference between undetected and detected offenses, when comparing the self-reported prevalence rates with the offcial record rates. Though some of the offenders who deny any history of contact offending may be lying, despite being in treatment or undergoing a polygraph examination, it does not appear that most or all internet offenders have committed a contact sexual offense. Further research is needed to identify the factors that distinguish those who have committed contact sexual offenses against a child from those who do not commit such offenses. This empirical knowledge would advance the understanding of risk of recidivism and the relationship between online and offine offending. Consistent with this idea, Lee and colleagues (2012) found that online offenders who had committed contact offenses scored higher on a measure of antisocial behavior and traits than online offenders who had no known history of sexual contact victims. However, dual offenders were less likely to admit pedophilic sexual interests when interviewed, had less child pornography content and were involved with child pornography for shorter periods of time. Refecting the potential importance of opportunity, dual offenders were more likely to have access to children than child pornography only offenders, through coresidence or occupation. Contact Offending in the Future Seto, Hanson and Babchishin (2011) also reviewed recidivism rates from nine samples of internet offenders (a total sample size of 2,630 online offenders) followed for an average of slightly more than three years (ranging from one-and-a-half to six years at risk). Although the follow-up times are relatively short for this kind of research, and recidivism rates are expected to increase with more opportunity, these recidivism rates are lower than those observed in recidivism studies of offine offenders (Hanson & Morton-Bourgon, 2005) and belie the idea that all internet offenders pose a high risk of committing contact offenses in the future. Indeed, there may be a subgroup of online-only offenders who pose relatively little risk for a contact sexual offense. In a recent preliminary analysis of data from 101 federal child pornography offenders in the United States, using data obtained from the U. Sentencing Commission, Burgess, Carretta and Burgess (2012) noted that a majority of the offenders were employed (68 percent), had some college education (58 percent), were married or had previously been married (59 percent) and had no prior criminal offenses (53 percent). Offenders with these kinds of characteristics are relatively unlikely to criminally offend again (compared to those who are unemployed, did not complete high school, had never married and had prior offenses). Some of them pose a relatively high risk of directly victimizing children (or indirectly victimizing children by again accessing child pornography), and an important task for law enforcement and for clinicians is to identify those higher-risk individuals in order to prioritize cases and make more effcient decisions about resources. Recidivism Risk Factors Research is beginning to emerge on the factors that predict recidivism among internet sex offenders, although more studies using large samples, a set of theoretically or empirically plausible risk factor candidates, longer follow-up times and comprehensive criminal records are clearly needed. These initially identifed risk factors appear to be the same kinds of risk factors seen in decades of research on contact sex offenders, and in research on all kinds of offenders generally. For example, recent studies have shown that well-established nonsexual criminological factors such as offender age at time of frst arrest, prior criminal history and failure on prior conditional release (such as bail or parole) can predict sexual recidivism among child pornography offenders (Eke, Seto & Williams, 2011; Seto & Eke, 2005). Broadly speaking, and in line with results for previous sex offender risk assessment tools, these items can be viewed as refecting either atypical sexual interests (admission of pedophilic or hebephilic sexual interests, relative interest in boys versus girls) or antisocial tendencies (younger age, criminal history, failure on conditional release) (Seto, 2008, 2013). Faust, Renaud and Bickart (2009) examined predictors of recidivism in a sample of 870 child pornography offenders assessed by the Federal Bureau of Prisons between 2002 and 2005. The average length of follow-up was almost four years, with a sexual offense rearrest rate of 5. Of the 30 predictors examined, fve were signifcant predictors of sexual rearrest: lower education level, being single, possessing noninternet child pornography, prior sex offender treatment (likely a proxy for having a prior sexual offending history) and not possessing depictions of adolescent minors (suggesting that those who show a preference for depictions of prepubescent children are at greater risk). Risk Matrix items include offender age, sexual and any other sentencing history, having a male victim, having a stranger victim, ever having a live-in romantic relationship, and having any noncontact offenses. Wakeling and her colleagues obtained recidivism data on 1,326 offenders followed for one year (2. This research is at an early stage and thus it is too soon to confdently conclude that existing risk measures (modifed or not) will accurately predict sexual recidivism by internet offenders who have no history of contact sexual offending. The applicability and validity of risk measures to internet offenders who do have a history of contact sexual offending is not in question. Clinicians and others are clearly justifed in using existing risk measures to assess the risk of internet offenders who are known to have a history of contact sexual offending. Intervention There is relatively little literature on the treatment of internet offenders. Typically, knowledge about characteristics and risk of recidivism is established before knowledge about treatment approaches and outcomes because of the time it takes to develop and implement programs and then evaluate them for recidivism. Sex offender treatment and supervision professionals are struggling to respond to the increasing infux of internet offenders. Key questions have yet to be addressed regarding intervention, including what the priority treatment targets are, how they should be targeted and whether interventions can reduce recidivism. This program was created as a result of treatment provider concerns about mixing internet and contact offenders in group therapy as well as questions about the applicability of some treatment components and targets of conventional contact sex offender treatment programs (McGrath et al. The program is based on contemporary models of contact sexual offending that emphasize cognitive-behavioral principles, but it also draws in elements of positive psychology, 12-step and self-help approaches (which is also common among conventional contact sex offender programs). The program is intended to be less intense than the standard conventional sex offender program available in the United Kingdom; it involves fewer (20 to 30) sessions in either individual or group format and more internetrelevant content. The evidence available so far on risk of recidivism suggests that more intensive interventions are required only by a minority of internet offenders (Seto, Hanson & Babchishin, 2011). Dynamic risk factors can be distinguished from static risk factors that do not or cannot change. Static risk factors provide the best long-term prediction of recidivism but they do not identify potential treatment and supervision targets. Treatments and other interventions that can successfully target dynamic risk factors are more likely to lead to reductions in recidivism. Middleton, Mandeville-Norden and Hayes (2009) reported preliminary results from a pre-/post-treatment evaluation of 264 internet offenders. There were signifcant changes on 10 of 12 psychological measures, many corresponding to the treatment targets just described. However, there was no comparison group, so it is not clear how much of these changes can be attributed to the treatment as opposed to the passage of time, probation involvement or participation in other programs. Continuing follow-up is also needed to determine if treatment participation (especially treatment-related changes on specifc targets) are related to changes in recidivism in the desired direction. The main aim of this website is to reach individuals who are engaging in problematic online behaviors before they commit contact offenses. Department of Justice, 2010), any comprehensive response to internet offending will need to include a self-help component. A similar service is provided by nongovernmental organizations such as Stop It Now! One beneft of self-help and confdential approaches is that a larger group of at-risk individuals can be reached, especially in light of evidence that many online offenders go undetected. A disadvantage is the likelihood that the highest risk individuals (those who have an antisocial orientation and already engage in contact sexual offending) are probably less likely to seek self-help options. Another disadvantage is that follow-up data will not be available to evaluate the effcacy of these services. Undetected internet offenders are unlikely to seek help given the severe stigma associated with self-identifying as being sexually interested in children or engaging, directly or indirectly, in the sexual exploitation of children. Buy liv 52 us. Dehydration Signs and Symptoms | Wikisymptoms. |