CG Nanda Kumar MBBS FRCA
It has been used in several trials to treat brain gastritis diet ����������� purchase misoprostol with amex, liver diet during gastritis attack order misoprostol 200mcg line, lung and bone metastases gastritis symptoms yahoo answers discount misoprostol online master card. It is usually well tolerated gastritis reviews buy 200mcg misoprostol amex, and brain necrosis that occurred in less than 10% of cases is usually limited and had no clinical consequences. The patient outcome depends mostly on the progression rate of extra cerebral lesions (1015). Data on lung and liver metastases are available only in retrospective studies on low numbers of patients and with a median follow-up of less than 1 year in most cases and in one prospective study (1016). This study included patients with many different primary tumors, including 10% of the patients having thyroid cancer. They showed a local control rate ranging from 63% to 98% in lung lesions, from 57% to 100% in liver lesions with a cumulative dose delivered ranging from 20-75 Gy in 5-15 fractions. The local tumor control seems to be long lasting with complete response ranging form 70 to 90 % at 2-3 years. Furthermore, rare (<3%) grade 3-4 toxicities (pneumonitis, pleural effusion, intestinal complications) were reported (1017). These toxicities are much less common that those associated with percutaneous treatment modalities. Percutaneous thermal ablation is aimed to destroy tumor foci by increasing (radiofrequency ablation) or decreasing (cryoablation) temperatures sufficiently to induce irreversible cellular damages. A multicenter prospective trial on 183 lung metastases from cancer other than colorectal showed a complete response rate of 88 % at 1 year and an overall survival of 92% and 64% at 1 year and at 2 years, respectively (1022). Cases of delayed recurrence have also been reported, and long-term follow up is needed. Furthermore, repeated treatments can be performed on the same lesion and multiple lesions can be treated in the same patient. The association of cryoablation and cementoplasty seems promising in purely lytic bone metastases from thyroid cancer. Published experience using thermal ablation and stereotactic radiation in thyroid cancer patients is limited, and recommendations are currently based on more robust evidence in other solid tumors. Randomized prospective studies comparing the efficacy and tolerability of these different techniques are lacking, and their choice in clinical practice is based on local experience, lesion location as well as patient status and preference. Surgical resection and stereotactic external beam radiotherapy are the mainstays of therapy (933;1029;1030). Stereotactic radiation therapy is preferred to whole brain irradiation because life expectancy in patients with brain metastases may be prolonged, and stereotactic irradiation induces less short and long-term toxic damages to the brain toxicity compared with whole brain irradiation (fatigue, headache, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes), and it may be effective even in patients with multiple brain lesions. Clinicians considering referral of patients for trials should review available treatment options and eligibility criteria, preferably through discussions with trial center personnel and review of trial materials at the website 246 Page 247 of 411 247 The reasons for this association are unclear, but there is no evidence to suggest that trial participation is deleterious to patient outcomes, and it may be beneficial. Participation in a clinical trial should be considered in any situation wherein there exists no effective or proven standard of care, or when a standard of care is being compared with a promising new or investigational therapy. However, given the indolent nature of metastatic disease in most patients, therapeutic clinical trial participation should not be considered for patients with stable, asymptomatic metastatic disease unless agents with significant likelihood of complete remission, prolongation of survival, or biologic impact such as redifferentiation that could sensitize to definitive therapy are available (see section [C37]). Benefit has been demonstrated in the form of improved progression free survival (delay in time to disease progression or death) in three randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, clinical trials (vandetanib (1033); sorafenib (1013); lenvatinib (1034). Benefit has also been demonstrated in the form of induced durable tumor regression (1035-1037). In the absence of definitive data related to improved overall survival and/or quality of life to inform As a guide, evidence-based recommendations with expert consensus have been recently published (953). It is also critically important to assure that the disease prompting therapy represents metastatic thyroid cancer. In particular, because pulmonary nodules attributable to benign causes are common, the presence of pulmonary nodules does not in and of itself justify the application of systemic therapy. Thus, in cases of diagnostic uncertainty where the result would have definitive therapeutic implications, biopsy is required, especially when thyroglobulin levels are low/unhelpful (such as in the presence of anti-thyroglobulin antibodies). The introduction of systemic therapy requires that both the clinician and the patient agree that clinical benefits are expected to exceed risks for that individual patient. Finally, it is important that the involved care team (physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, nurses) be experienced in the use and management of toxicities associated with these therapies. Appropriate informed consent should be obtained and documented in the medical record prior to initiation of any therapy, regardless of whether the patient is being treated in the context of a clinical trial. Kinase inhibitors, however, are associated with numerous adverse effects including diarrhea, fatigue, induced hypertension (requiring initiation of antihypertensive therapy in about half of all 251 Page 252 of 411 252 previously normotensive individuals), hepatotoxicity, skin changes, nausea, increased levothyroxine dosage requirement, changes in taste and weight loss. These potential side effects have high probability of negatively impacting quality of life and/or necessitating dosage reductions in nearly two-thirds of treated many patients, and treatment discontinuation in up to 20% of patients. Overall, the risk of therapy-related death in cancer patients treated with oral kinase inhibitors is about 1. While risk of drug-related death is relatively low, this knowledge of potentially fatal therapeutic outcomes should prompt considerable restraint in the use of kinase inhibitors in patients with stable or slowly progressive disease who likely have a disease-specific mortality that may also be low over 1-3 years. While risk of drug-related death is relatively low, the knowledge of potentially fatal therapeutic outcomes should prompt considerable restraint in the use of kinase inhibitors, especially in patients who are asymptomatic and/or with stable or slowly progressive disease, and in patients who can otherwise be effectively treated using directed therapies. Three randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials (phase 2, vandetanib; phase 3, sorafenib and lenvatinib) had been published by the time of the writing of these guidelines, each demonstrating delayed time to disease progression among kinase inhibitor-treated, relative to 252 Page 253 of 411 253 placebo-treated, patients (1013;1033;1034). Sorafenib or vandetanib treatement were each associated with progression free survival prolonged by 5 months, with <15% objective response rates, but with no improvement on overall survival demonstrated to date. Assessments comparing sorafenib to placebo outcomes demonstrated overall lower quality of life among sorafenib-treated patients relative to those treated with placebo, despite improved progression free survival. Lenvatinib therapy was associated with longer prolonged median progression free survival by 14. Despite these very encouraging results and regulatory approval, however, no statistically significant impact of lenvatinib (or any other kinase inhibitor) therapy on overall survival has yet been observed; moreover, lenvatinib toxicities were reported in 100% of treated patients (1034). None of the yet-completed randomized trials have demonstrated survival benefit for kinase inhibitor therapy relative to placebo, perhaps in part reflecting crossover from placebo to kinase inhibitor therapy among progressing placebo-treated trial patients, raising the question of whether delay of therapy initiation adversely affected patient outcomes among enrolled trial patients. In some situations, however, the decision to initiate kinase inhibitor therapy is straightforward. For patients with disease between these two extremes, it is critical that risks and benefits of therapy, anticipated side effects, goals, patient context, and the therapeutic 254 Page 255 of 411 255 philosophy of each particular patient be thoroughly vetted so as to best individualize therapy. This decision is ideally made within the context of specialized centers with comprehensive knowledge of the natural history of the disease and of the effects of available therapies. Specific characteristics impacting enthusiasm for starting such therapy are outlined in Table 16. Patients who are candidates for kinase inhibitor therapy should be thoroughly counseled with regard not only to potential benefits, but also with regard to potential side effects and risks of therapy, as well as with regard to alternative therapeutic approaches including best supportive care, as should be the case with any medical therapeutic decision-making (1044). Such extensive and comprehensive discussions are particularly important to undertake in the context of kinase inhibitor therapy because of the high probability of side effects of these agents and because of their presently uncertain effects on patient overall survival and quality of life (1045). Another critical and complex question often faced in treating patients with kinase inhibitor therapy is that of when treatment should be discontinued once initiated. In general, therapy should be continued so long as net benefit exceeds net detriment. However, there are times when focal/oligometastatic disease progression 255 Page 256 of 411 256 amenable to directed therapies is noted. In such instances, superimposed loco-regional therapies in the setting of maintained systemic therapy can sometimes be in the best interest of a particular patient. For instance, in the setting of regressed lung metastases and yet progression at a solitary bone site, maintained systemic therapy with superimposed directed radiation therapy may be reasonable. Ideally, such therapy should be undertaken within the context of therapeutic clinical trials. Hence, the selection of an agent for initial therapy may be in some senses less critical, as many patient will go on to receive several kinase inhibitors over their disease courses. Cardiotoxicity is also important to be aware of and to monitor according to patient risk factors, agent used, and induced symptoms/signs.
A positive family features of autoimmunity (ie chronic gastritis with intestinal metaplasia buy cheap misoprostol 100mcg, autoantibodies or autoreactive T history can be helpful gastritis medical definition generic 200mcg misoprostol otc, but de novo mutations do occur in patients cells) gastritis gi bleed cheap misoprostol 200 mcg on-line. All of mast cell proliferation or degranulation and is caused by affected patients exhibit a rash severe gastritis diet plan buy 100 mcg misoprostol mastercard, with the majority presenting at neutrophilic infiltrates. Blau syndrome should be suspected arthritis rarely presents before 6 months of age. Unlike sarcoidosis, respiratory involvement is rare in pa649 tients with Blau syndrome. Patients presenting at or soon after of low titer, and rheumatoid factor is typically negative. Infectious and environmental susceptibility factors, such as the specific 666,667 triggers are associated with disease fiares. It was not reported whether these values normalize mation of the underlying fascia, arthralgia, and/or periorbital 646,648,668,669 between episodes. Febrile fiares are longer lasting than in pa666,667 patients exhibited laboratory evidence of autoimmunity. Colchicine can considered a recessive disorder, a substantial percentage of paalso cause lactose intolerance. Mediterranean and For infrequent attacks, short courses of prednisone at the time Middle Eastern populations have a higher carrier frequency of of a fiare might be effective. Consistent lymphadenopathy, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, arthralgia, with the evidence for increased infiammatory mediators, there are 684 rash, aphthous ulcers, and splenomegaly. Cherubism can be mistaken for affecting metaphyses of the long bones can be seen on plain Noonan syndrome when the clinical findings are limited to sym709,710 radiographs. Familial cases have 711-713 sensorineural hearing loss, hypogonadism, short stature, hallux also been affected with bullous skin lesions. Plasma C3 levels are depleted, leading to a similar propen737,742 mately every 28 days. Clinical manifestations are characterized sity toward bacterial (mainly respiratory tract) infection. Some of these might be at increased risk of infection, of symptoms is highly effective in aborting febrile episodes, particularly as infants. Prognosis is good, with a strong trend toward resolution of Ficolin 3 is another member of the collectin family having 720-722 symptoms on the average of 5 years after onset. Carnevale-Mingarelli-Malpuech-Michels syndrome (facial dysHereditary angioedema is due to defects in the plasma protein morphism, growth deficiency, cognitive impairment, hearing C1 esterase inhibitor. This protein regulates the complement, loss, craniosynostosis, radioulnar synostosis, and eye and ear abkinin-generating, clotting, and fibrinolytic mediator pathways. Patients with susceptibility to neissewith C2 deficiency present with recurrent bacterial respiratory rial infections should be suspected of having a terminal pathway tract infections resembling those of patients with antibody deficomplement deficiency. Defects in the complement lysis of antibody-sensitized sheep erythrocytes by fresh serum. This test is relatively insensitive compared factor H, a C3 regulatory protein, is inherited as an autosomal with functional tests of single complement proteins. Diagnosis of these autoantibodies is important because phosphate and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in solution, and 754 patients will respond to plasma exchange treatment. In a solidcomponents are unstable and tend to degrade with time, especially if blood or plasma phase method plates are coated with mannan and incubated with is warmed. If complement consumption is possible or suspected, while C1q binding is inhibited. The amount of hospital laboratories to test for consumption is to measure levels of factor B and C4, refiecting activation of the alternative or classical pathway, respectively. Note that deficiency of factor H, factor I, or should be the major modes of treatment for complement defiproperdin could lead to a diminished level of C3 and other components. In the presence of an appropriate clinical history, low C4 levels in the presence of normal C3 levels might Patients with complement deficiencies require immunization suggest hereditary angioedema, and the levels and function of C1 inhibitor should be with relevant vaccines (S pneumoniae, H infiuenzae, and N menexplored. Autoimmune diseases associated must be distinguished from complement consumption, as can occur with complement deficiency are treated as they would be in other during infection or autoimmune disease (see below). There is no available gene therapy at the present time, usually results from complement component use caused by and in most situations, supplying the missing complement protein 734,752,762 activation, as can occur in autoimmune disease or during infection. Antibody formation ative should be studied for associated anti-cytokine during acute infection can create immune complexes, which can autoantibodies. This is most often directed toward evaluation of responses by autoantibodies to humoral components, such as clotting facagainst vaccine antigens, but assessment of responses to natural 768 tors. However, to our knowledge, this has not yet been reported exposure or infections is also useful. Where uncertainty regarding evaluation or management ocPrimary immunodeficiencies are inherited disorders of immune curs, consultation with physicians experienced with immunodefisystem function that predispose affected subjects to an increased ciencies is essential. They are most often categorized according to a combinaentire range of possible pathogens, including opportunistic organtion of mechanistic and clinical descriptive characteristics. Laboratory abnormalities can include panhywhich are subdivided into humoral or antibody deficiencies, and pogammaglobulinemia, lymphopenia, or alymphocytosis and the combined deficiencies affecting both humoral and cellular absence of cellular immune function, as determined by using mechanisms. The laboratory phenotype often depends dromes with characteristic phenotypes is distinguished, along on the specific molecular defect (Table E7). Recently, the importance of anticytokine improved by the earliest possible intervention. Also included in the category of phagocytic cell defects are the A variety of syndromes of immunodeficiency have been syndromes classified under Mendelian susceptibility to mycodescribed. Many of these diseases have Toll-like receptor signaling, such as nuclear factor kB essential ancillary clinical features that might infiuence or guide the modulator syndrome, often exhibiting ectodermal dysplasia along diagnostic approach. Laboratory abnormalities of specific imwith infection susceptibility with a narrow (eg, predominantly mune function vary depending on the specific gene defect and can pyogenic bacteria or fungi) to a wide range of pathogens (Fig E5). This category also inimmunity, as determined by using in vivo and in vitro assays. The principal clinical manifestations of humoral immunodefithese diseases are characterized by episodic fever often in associency are recurrent bacterial infections of the upper and lower ciation with other infiammatory manifestations that can affect the respiratory tract. Both X-linked and autosomal forms of agamskin, joints, and gastrointestinal tract. For agammaglobulinemia or common variable immufections, but there could be other host factors that interact to create nodeficiency, therapy is either with antibiotic prophylaxis, IgG such susceptibility in a patient. Functional management and to have the best outcomes with respect to patient studies show most often a defect in oxidative metabolism because and family health, education, and planning. In patients with other disorders, there might be simply sethe authors and editors are grateful to the following individuals for their vere neutropenia or variable impairment of chemotaxis (leukocontributions: Dr Jean-Laurent Casanova, Rockefeller University, New York, cyte adhesion defects), phagocytosis, or intracellular killing. PracProgressive specific immune attrition after primary, secondary and tertiary immutice parameter for the diagnosis and management of primary immunodeficiency. Severe phenotype of chronic granulomatous disease presenting in a female 125(suppl):S182-94. In: Rezaei N, Aghamohammadi A, Notaranby extremely skewed X-chromosome inactivation. Clinical consequences of defects in B-cell developdrome as a result of X chromosome lyonization. Haematologica 2007; Invasive pneumococcal disease in children can reveal a primary immunodefi92:281-2. Immunodeficiency Committee of the American Academy of Allergy Asthma J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;125(suppl):S195-203. Am J Hematol 2013;88: immune competence: critical differences in interpretation criteria when different 1035-40. InterImmune globulins and same-day thrombotic events as recorded in a large health laboratory comparison of three multiplexed bead-based immunoassays for care database during 2008 to 2012. Recnous immunoglobulin therapy in patients treated for Kawasaki disease: a report ommendations for live viral and bacterial vaccines in immunodeficient patients of 4 cases. N tudinal decline in lung function in patients with primary immunoglobulin defiEngl J Med 2010;362:314-9. Infection with partial DiGeorge syndrome: clinical experience and cellular immunity.
Total contact casting of the diabetic foot in daily practice: a prospective follow-up study gastritis weight loss effective 100mcg misoprostol. Treatment of chronic plantar ulcer of the diabetic foot using an irremovable windowed fibreglass cast boot: prospective study of 177 patients gastritis length purchase 100 mcg misoprostol overnight delivery. Nonremovable gastritis diet india order discount misoprostol online, windowed treating gastritis through diet generic misoprostol 200 mcg free shipping, fiberglass cast boot in the treatment of diabetic plantar ulcers: efficacy, safety, and compliance. Efficacy of removable casts in difficult to off-load diabetic foot ulcers: a comparative study. Total Contact Cast Use in Patients With Peripheral Arterial Disease: A Case Series and Systematic Review. Role and Determinants of Adherence to Off-loading in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing: A Prospective Investigation. Effectiveness of Daily Use of Bilateral Custom-Made Ankle-Foot Orthoses on Balance, Fear of Falling, and Physical Activity in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Effects of foot and ankle devices on balance, gait and falls in adults with sensory perception loss: a systematic review. The effectiveness of footwear and offloading interventions to prevent and heal foot ulcers and reduce plantar pressure in diabetes: a systematic review. A randomized trial of two irremovable off-loading devices in the management of plantar neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers. An off-the-shelf instant contact casting device for the management of diabetic foot ulcers A randomized prospective trial versus traditional fiberglass cast. Use of locally made off-loading techniques for diabetic plantar foot ulcer in Karachi, Pakistan. Removable cast walker boots yield greater forefoot off-loading than total contact casts. Reducing dynamic foot pressures in high-risk diabetic subjects with foot ulcerations. Effect of different casting design characteristics on offloading the diabetic foot. Total contact cast wall load in patients with a plantar forefoot ulcer and diabetes. A proof-of-concept study of the effectiveness of a removable device for offloading in patients with neuropathic ulceration of the foot: the Ransart boot. Comparison of forefoot ulcer healing using alternative off-loading methods in patients with diabetes mellitus. Lower-extremity dynamics of walking in neuropathic diabetic patients who wear a forefoot-offloading shoe. The efficacy of a removable vacuum-cushioned cast replacement system in reducing plantar forefoot pressures in diabetic patients. Vacuum cushioned removable cast walkers reduce foot loading in patients with diabetes mellitus. A comparative study between total contact casting and conventional dressings in the non-surgical management of diabetic plantar foot ulcers. Caravaggi C, Faglia E, De Giglio R, Mantero M, Quarantiello A, Sommariva E, et al. Effectiveness and safety of a nonremovable fiberglass off-bearing cast versus a therapeutic shoe in the treatment of neuropathic foot ulcers: a randomized study. The use of felt deflective padding in the management of plantar hallux and forefoot ulcers in patients with diabetes. The effects of applied felted foam on wound healing and healing times in the therapy of neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers. The effectiveness of felt padding for offloading diabetes-related foot ulcers, at baseline and after one week of wear. Tendon lengthening and fascia release for healing and preventing diabetic foot ulcers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tendo-achilles lengthening and total contact casting for plantar forefoot ulceration in diabetic patients with equinus deformity of the ankle. Conservative surgical approach versus nonsurgical management for diabetic neuropathic foot ulcers: a randomized trial. Clinical efficacy of the pan metatarsal head resection as a curative procedure in patients with diabetes mellitus and neuropathic forefoot wounds. Efficacy of fifth metatarsal head resection for treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulceration. Comparison of Metatarsal Head Resection Versus Conservative Care in Treatment of Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Effect of metatarsal head resection for diabetic foot ulcers on the dynamic plantar pressure distribution. Clinical efficacy of the first metatarsophalangeal joint arthroplasty as a curative procedure for hallux interphalangeal joint wounds in patients with diabetes. Modified resection arthroplasty for infected non-healing ulcers with toe deformity in diabetic patients. One stage resection and pin stabilization of first metatarsophalangeal joint for chronic plantar ulcer with osteomyelitis. Preventing loss of the great toe with the hallux interphalangeal joint arthroplasty. Resection Arthroplasty for Resistant Ulcers Underlying the Hallux in Insensate Diabetics. Flexor Tenotomy Improves Healing and Prevention of Diabetes-Related Toe Ulcers: A Systematic Review. Effectiveness of percutaneous flexor tenotomies for the management and prevention of recurrence of diabetic toe ulcers: a systematic review. Safety and effectiveness of flexor tenotomies to heal toe ulcers in persons with diabetes. Percutaneous flexor tenotomy for preventing and treating toe ulcers in people with diabetes mellitus. The effect of flexor tenotomy on healing and prevention of neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers on the distal end of the toe. Tendon Achilles lengthening for the treatment of neuropathic ulcers causes a temporary reduction in forefoot pressure associated with changes in plantar flexor power rather than ankle motion during gait. Examine the feet of all patients with diabetes annually for the presence of peripheral artery disease, even in the absence of foot ulceration. At a minimum, this should include taking a relevant history and palpating foot pulses. Clinically examine (by relevant history and palpation of foot pulses) all patients with diabetes and foot ulceration for the presence of peripheral artery disease. Always consider vascular imaging in patients with a diabetic foot ulcer, irrespective of the results of bedside tests, when the ulcer is not healing within 4-6 weeks despite good standard of care. Always consider revascularisation in a patient with a diabetic foot ulcer and peripheral artery disease, irrespective of the results of bedside tests, when the ulcer is not healing within 4-6 weeks despite optimal management. Do not assume diabetic microangiopathy, when present, is the cause of poor healing in patients with a diabetic foot ulcer, therefore always consider other possibilities for poor healing. Evaluate the entire lower extremity arterial circulation with detailed visualisation of below-theknee and pedal arteries, in an anteroposterior and lateral plane. When performing revascularisation in a patient with a diabetic foot ulcer, aim to restore direct blood flow to at least one of the foot arteries, preferably the artery that supplies the anatomical region of the ulcer. After the procedure, evaluate its effectiveness with an objective measurement of perfusion. As evidence is inadequate to establish whether an endovascular, open or hybrid revascularisation technique is superior, make decisions based on individual factors, such as morphological distribution of peripheral artery disease, availability of autogenous vein, patient co-morbidities and local expertise. Ensure that after a revascularisation procedure in a patient with a diabetic foot ulcer, the patient is treated by a multidisciplinary team as part of a comprehensive care plan. Order misoprostol on line. 18 Amazing Uses & Health Benefits of Tamarind Seeds including Knee Pain.
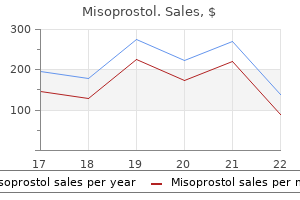
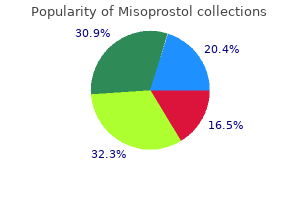
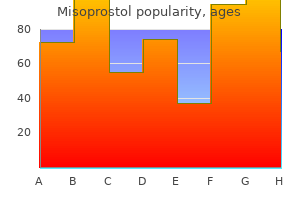
|