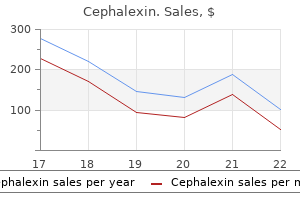
"Cephalexin 500mg with visa, antibiotics for uti and birth control". K. Farmon, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D. Associate Professor, Duquesne University College of Osteopathic Medicine Calving dates for bison in northern Yellowstone precede those of bison in central Yellowstone by about 14 days due to the earlier onset of snow melt and new plant growth in northern Yellowstone (Gogan et al infection 1 mind games buy cephalexin 250 mg low price. Seventy-two percent (47 of 65) of births in northern Yellowstone occurred by May 7th can antibiotics for acne make it worse purchase cephalexin 250mg without prescription, while 63 percent (50 of 79) of births in central Yellowstone occurred after May 8th antibiotics for uti missed period cephalexin 500 mg. The calving period in central Yellowstone was prolonged antibiotic unasyn cephalexin 500mg cheap, likely due to harsher winter conditions that predispose female bison to poorer body condition. Individual radio-collared females have given birth on high-elevation summer areas 6 the data and findings reported in this chapter reflect analyses revised from Geremia et al. Calving dates of 79 radio-collared bison in central Yellowstone during 2005-2012 and 65 radio-collared bison in the northern region of Yellowstone National Park during 2008-2012 (Geremia et al. Calving often overlaps with spring migrations from winter to summer ranges, and birth locations likely depend on when these migrations commence-which could be delayed due to prolonged snow pack or late emergence of new vegetation at higher elevations (Geremia et al. As a result, many births occur on winter ranges near or outside the boundary of Yellowstone National Park during some years (Jones et al. Reproductive Rates After reaching sexual maturity, female plains bison generally produce one calf every one or two years for the rest of their lives (Meagher 1973; Fuller et al. In central Yellowstone, monitored females did not produce calves in sequential years during 1997 to 2003. Rather, most pregnancies were observed in animals greater 86 Yellowstone Bison: Conserving an ameriCan iCon in modern soCietY than 3 years old that were not lactating (Kirkpatrick et al. Lactating bison may not be able to replenish sufficient fat and protein reserves to support pregnancy during summers when drought or competition with other herbivores limit their nutritional intake (Cook et al. However, 54 radio-collared bison monitored between two and nine sequential years during 1997 through 2012 produced a calf more than 60% (136 of 211) of the time, suggesting that bison in central Yellowstone may calve somewhat more frequently than in alternate years. In contrast, sequential calving is more common in northern Yellowstone where 39 radio-collared bison monitored between two and six sequential years produced a calf more than 80% (110 of 132) of the time. Twenty of these females were monitored for at least four consecutive years, with thirteen (60%) producing a calf every year. The probability of giving birth was lowest at 3 years of age and increased with age (Table 5. A leveling off or decrease of birth rate in older animals has not been detected, which may, in part, be due to limited observations of older animals. In many ungulate populations, birth rates decrease as abundance increases towards the food-limited capacity of the environment to support them (Caughley 1976; Eberhardt 1977, 2002). The number of bison in northern Yellowstone has varied between 400 and 3,500 since 1980, while the number in central Yellowstone has varied between 1,400 and 3,600 bison, with no apparent effects of bison density on birth rates. Instead, population growth has been limited by the capture and shipment of bison to meat processing facilities, and to a lesser extent, hunting in Montana during winter (White et al. Random variations in weather conditions such as drought or deep snows can limit the availability of forage for bison and increase energetic costs (Clutton-Brock et al. Birth rates for Yellowstone bison were lower following winters with deep or hard snow pack, but no drought-related effects were detected. One hundred and fifty-three adult female bison were repeatedly monitored between two and nine years for birth and survival during 1996 through 2012 in Yellowstone National Park (Geremia et al. Effects of Brucellosis Some diseases rapidly influence the dynamics of wildlife populations by reducing the survival and fecundity of infected animals (Hudson et al. Other diseases establish long-term, endemic infections in populations that persist without a noticeable effect on survival and fecundity (Ewald 1994). Endemic diseases are characterized by a relatively constant proportion of the population being infected, with little variation in the prevalence of 88 Yellowstone Bison: Conserving an ameriCan iCon in modern soCietY Figure 5. Age-specific probabilities of giving birth for radio-collared bison in the central and northern regions of Yellowstone National Park that were not exposed (red) and chronically exposed (blue) to Brucella abortus bacteria (see Chapter 2). Birth probabilities for recently exposed, seroconverting bison are not reported by age but averaged near 0. Brucellosis has existed in the Yellowstone bison population for about one century (Meagher and Meyer 1994). The disease does not significantly affect bison survival, but females generally have decreased fecundity during their first pregnancy following infection (Dobson and Meagher 1996; Thorne 2001; Joly and Messier 2005; Rhyan et al.
If this test has been done with good results on a representative batch of the test vaccine antibiotic resistance kit discount cephalexin 500 mg with amex, it does not have to be repeated routinely on other vaccine lots prepared from the same seed lot and with the same manufacturing process infection 5 weeks after c-section purchase cephalexin 250mg free shipping. Immunogenicity in mice the same technical procedures indicated for immunogenicity calculation of S19 vaccine (see Chapter 2 infection xpk generic 500mg cephalexin fast delivery. Conditions of the control experiment are satisfactory when: i) the response in unvaccinated mice (mean of Y) is at least of 4 antibiotics for acne while breastfeeding generic 250 mg cephalexin fast delivery. However, growing field evidence shows that the immunity conferred declines with time, and revaccination could be advisable in endemic areas. Allowance for this phenomenon is normally made by ensuring that the viable count immediately following lyophilisation is well in excess of the minimum requirement. Maintenance of a cold chain during distribution of the vaccine will ensure its viability. For preparation of the freeze-dried vaccine, a stabiliser as described in Section C2. Accordingly, cell cultures and suspensions must be handled under appropriate conditions of biohazard containment (see Chapter 1. Vaccine residues and injection equipment should be decontaminated with a suitable disinfectant. Cloning, nucleotide sequence and expression of the Brucella melitensis bp26 gene coding for a protein immunogenic in infected sheep. Evaluation of serological tests for diagnosis of Brucella melitensis infection of goats. Comparison of serological tests for detection of ovine and caprine antibody to Brucella melitensis. Evaluation of serological tests for the detection of caprine antibody to Brucella melitensis. Comparison of fluorescence polarization assay with card and complement fixation tests for the diagnosis of goat brucellosis in a high prevalence area. Cloning of Brucella abortus gene and characterisation of expressed 26 kilodalton periplasmic protein: potential use for diagnosis. Accordingly, the main consequences of the disease are reduced fertility in rams, infrequent abortions in ewes, and an increased perinatal mortality. The disease has been reported in Latin American, North American and European countries as well as Australia, New Zealand and South Africa, but probably occurs in most sheep-raising countries. Identification of the agent: the existence of clinical lesions (unilateral or, occasionally, bilateral epididymitis) in rams may be indicative of the existence of infection, but laboratory examinations are necessary to confirm the disease. Molecular biological methods have being developed that could be used for complementary identification based on specific genomic sequences. However, indirect diagnosis based on serological tests is preferred for routine diagnosis. Requirements for vaccines and diagnostic biologicals: Seed cultures for antigen or vaccine production should be obtained from internationally recognised laboratories. This vaccine strain should meet minimal quality standards: adequate concentration, absence of dissociation, adequate residual virulence and immunogenicity and free of extraneous agents (see Chapter 2. Passive venereal transmission via the ewe appears to be a frequent route of infection, but ram-to-ram transmission is also common1 (2). Direct ram-to-ram transmission during non-breeding periods is quite frequent and has been suggested to take place by several routes, including the rectal mucosa. Accordingly, the ewes are as relevant as rams in the epidemiology of infection, and control or eradication of B. The demonstration of the existence of genital lesions (unilateral or, occasionally, bilateral epididymitis) by palpating the testicles of rams may be indicative of the presence of this infection in a given flock. However, this clinical diagnosis is not sensitive enough because only about 50% of rams infected with B. Moreover, the clinical diagnosis is extremely nonspecific due to the existence of many other bacteria causing clinical epididymitis.
As in previous years virus zero buy 250 mg cephalexin mastercard, a high Age and gender distribution Information on gender and age was provided for 217682 confirmed cases antibiotic 875mg 125mg buy cephalexin 500mg visa. Discussion Human campylobacteriosis is the most commonly reported gastrointestinal disease in Europe treatment for dogs with dementia cheap 500 mg cephalexin fast delivery, reported about twice as frequently as salmonellosis1 antibiotics for uti keflex order 500mg cephalexin with amex. In 2010, 470 foodborne outbreaks associated with Campylobacter were reported by 19 Member States, affecting over 1700 persons, of whom 132 were hospitalised1. In 27 reported foodborne out breaks with strong evidence, broiler meat was the most commonly implicated vehicle. In 2010, Denmark reported a waterborne outbreak due to Campylobacter jejuni in a Danish town, with over 400 cases recorded among 20000 residents3. Scientific Opinion on Campylobacter in broiler meat production: control options and per formance objectives and/or targets at different stages of the food chain. The clinical course is characterised by the onset of waterydiarrhoea,nausea,vomiting,dehydration,acido sis, followed by renal failure and death. The main route of transmission is the ingestion of faecal-contaminated water or food. Epidemiological situation in 2010 In2010,26(21confirmed)casesofcholerawerereported by four countries (Table 2. The United Kingdom reported 13 cases and Germany six, while France, Slovenia and Sweden reported one each. Cholera is a very infectious acute bacterial disease caused by Vibrio cholerae serogroups O1 and O139. Cholera outbreaks are not unusual in developing world countries; in 2010 and 2011 outbreaks were reported in several African countries, the Middle East, and south ern Asia. A cholera outbreak in Haiti and the Dominican Republic began in mid-October 2010, ten months after the earthquake on 12 January1-4. Seasonality Case numbers are small, but there is an apparent trend for increased case reporting in late summer, possibly due to the reporting of cases acquired abroad during summer vacations. A cluster of acute diarrhea suspected to be chol era in French travelers in Haiti, December 2010. Transmission is through the faecal-oral route, pre dominantly via contaminated water and soil. The most common vehicles are drinking water, fresh agricultural produce and recreational water. Direct human-to-human transmission can occur when people handle infected faeces,usuallyfromtoddlers,andthroughsexualactivi ties. Theoocystsare resistant to chlorine at concentrations normally used for treating drinking water and there are well-documented large outbreaks of cryptosporidiosis as a result of con tamination at the source of reticulated water supplies2. The overall rate of confirmed cases in the 20 countries which have cryptosporidiosis surveillance systems with national coverage was 2. Cryptosporidiosis is an infection of the small intestine caused byintracellular protozoan parasitesofthegenus Cryptosporidium. The parasite is a common cause of acute diarrhoeal disease worldwide and has the poten tial to cause large outbreaks through the contamination of communal water supplies. There is no clear trend in the number of cryptosporidiosis cases reported by the 15 countries which contributed data since 2006, as illustrated by the 12-month moving average in Figure 2. Four countries reported zero cases, five countries reported only one or two cases each, and nine countries did not notify Cryptosporidium cases. The differences in incidence acrossEuropearelikelytoreflectdifferencesinnational surveillance systems and diagnostic practices.
Since droplets are relatively large bacterial yeast infection symptoms cephalexin 250mg overnight delivery, the use of surgical or other non-N-95 type masks are acceptable to prevent transmission antibiotics not working for strep buy cephalexin 500 mg cheap. Working with specimens behind a clear Plexiglas shield on the benchtop also provides a barrier to droplet transmission; however antibiotics for uti if allergic to penicillin buy 250mg cephalexin with amex, this approach may create a false sense of security since small aerosols may extend beyond the edges of the barrier antimicrobial beer line order cephalexin 250 mg with mastercard. Other general procedural controls can further minimize the risk of aerosol exposure when working with infectious specimens. Tubes with snap-type lids should be avoided in favor of threaded screw-on caps to reduce creation of droplets when these containers or opened. Further, gauze pads can be used when opening specimen containers to mitigate aerosols released by surface tension bubbles at the mouth of the container. When using a manual pipette, the retention volume should not be expelled since this can be a source of aerosol. This will ensure contact between the agent and disinfectant and reduce the risk of infectious aerosols when ejecting the pipette tip. This enables transmission on air currents over long distances (>1 m) and for extended periods of time. Rubeola (measles), Variola (smallpox), Varicella (chickenpox), Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Hantavirus, bacterial endospores. The source of airborne transmission can be aerosol micronuclei, but may also be dust, skin flakes, or the naked organism itself. When delivered via airborne route, inhalation of as few as 10 of these organisms can cause disease with mortality rates of 40-99% if untreated (2). However, transmission may occur through generation of micronuclei during medical procedures such as mechanical ventilation or during episodes of projectile vomiting or diarrhea. Prevention of airborne transmission within the hospital and laboratory relies on directional airflow and physical containment specimens and cultures. Negative pressure is measured as the difference in pressure between two adjacent rooms, and should be > 0. If maintained, negative pressure contains airborne pathogens within the designated room and prevents exposure events within the main laboratory. If a spill occurs, sufficient time should be allowed to reduce the presence of airborne contaminants by 99% (23). A paper towel soaked in disinfectant can be used to initially cover the spill and inactivate microorganisms prior to a more thorough decontamination and cleaning protocol. Unlike masks recommended for prevention of droplet transmission, respirators must effectively prevent inhalation of small airborne particles. Therefore, these respirators must be tight-fitting around the nose and mouth and remove >95% of particulates 0. Importantly, these respirators should only be used after appropriate training and fit testing to ensure maximal protective benefit. Disposable N-95 respirators are adequate for relatively low risk activities such as processing of respiratory specimens or cultures suspected to contain M. Additional respiratory protection may be warranted if working with pure cultures or specimens suspected to contain higher risk group pathogens such as Ebola, or for laboratory staff who cannot wear standard N-95 type respirators (see section 4. The functionality of the blower pack should be tested prior starting work with clinical specimens using a "floating ball" air tube to ensure a constant airflow rate of 115-170 liters/min (26). Included in this policy should be instruction for hospital or provider group(s) to notify the laboratory when diagnostic specimens are collected from patients with symptoms and/or history compatible with these agents. These exposures and resulting infections are often attributable to a low index of suspicion for these agents or failure of the hospital service to notify the lab when there is a compatible patient history and/or clinical presentation. Failure to notify the laboratory of a case of presumed acute pulmonary tularemia resulted in exposure of 11 laboratory workers to cultures of F. It also underscores the need to implement and maintain protocols for safe work practices that pertain to all clinical specimens and cultures. Always perform a risk assessment for all procedures performed in the laboratory and remember to continually update the risk assessment over time. Specimen containers that are visibly leaking pose an increased risk of transmission, but also indicate potential external contamination of the specimen. This is the result of a higher concentration of organism and the conduct of aerosol-generating procedures during routine identification of culture isolates (see section 4. These factors contribute to the increased relative risk of infection among laboratory workers, ranging 8. |