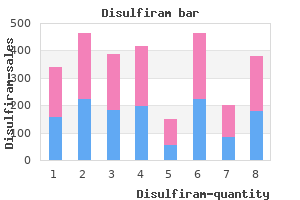
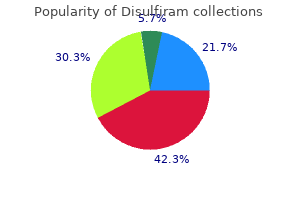
Michael D. Burg, MD, FACEP
The prevalence of this directive message was unsettling and fostered critical reflection on the ways that certain common metaphors promote particular ideological messages lanza ultimate treatment order disulfiram without prescription. The calculation shows the chance that a fetus has some sort of aneuploidy treatment 7 purchase disulfiram with visa, including an open 5 Holloway does not connect this term with traditional Reflective Practice scholarship and related terms medicine to stop contractions order 250mg disulfiram with amex, although there is an echo of critical reflection in his description of the purpose and operation of theoretical reflection symptoms 3 weeks into pregnancy cheap disulfiram online visa. There are many accepted variations of prenatal screening tests, depending on the resources of the geographical area in which the test is performed, and the time at which the woman presents for prenatal care (Summers et al, 2007). Prenatal screening tests are not definitive, but are a non-invasive way of determining a probability. If the probability of aneuploidy is judged to be high, the woman can choose to engage in an invasive testing technique (such as chorionic villus sampling, or amniocentesis) that will provide a definitive result. The invasive tests have risks of miscarriage, bleeding, malformation, and amniotic fluid aspiration (Brambati & Tului, 2005; Farrell et al, 1999) so they are not used unless a non-invasive test establishes a probability of aneuploidy that is worrisome for the woman. There is no cure or treatment for most of the aneuploidies detected by prenatal screening, and women who receive a positive screen for aneuploidy have the options of abortion, adoption, or increased time to prepare to raise a child with this condition. A 2007 Clinical Practice Guideline issued by the Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists of Canada (Summers et al, 2007) mandated that prenatal screening must be offered to all pregnant women, in a non-directive way that promotes informed consent and choice (p. The opportunity to access prenatal screening can be an important choice for Canadian women. However, the offer of prenatal screening and ensuing decisions require careful consideration. Public education pamphlets are used widely in medical screening programs (Fox, 2006) and are highly valued by women considering prenatal screening as a preferred way of obtaining information, second only to discussions with their physician (Dahl, Kesmodel, Hvidman & Olesen, 2006). However, the tone of information, word choice, and balance 161 of content provided can effect the way that patients make decisions about whether or not to engage in prenatal screening (Bryant et al, 2001; Dahl et al, 2006; Loeben, Marteau & Wilfond, 1998). Dixon-Woods (2001) discusses the discourse embedded in patient information pamphlets. Raffle (2001) discusses the way screening pamphlets are used to encourage uptake of screening, rather than provide information to encourage choice. A recent review of the literature about patient education pamphlets reveals that they are used to save time in a medical consultation, achieve cost-benefits for the health care system, and as a substitute for expensive professional time (Dixon-Woods, 2001). Patient empowerment pamphlets aim to provide information as a means of empowering patients to make informed choices, rather than correcting them or persuading them to acquiesce to biomedical priorities. Current public education materials about prenatal screening and testing in these countries have been critiqued for: requiring literacy levels above that of a general audience (Freda, Damus & Merkatz, 1999); insufficient information to make decisions about testing (Shepperd et al, 2006); negative tone (Bryant et al, 2001; Loeben et al, 1998); omission of information (Van den Heuvel et al 2008); and language that may be viewed as prejudicial (Hodgson, Hughes & Lambert, 2005). Public education materials with these issues are problematic with respect to the goal of facilitating non-directive counseling and informed choice as necessitated by the Clinical Practice Guideline governing this procedure (Summers et al, 2007). Previous studies often mention the affect that word choice can have on the perception of particular conditions and decision making, however such studies do not investigate particular words and their implicit messages. Non-directive counseling, which involves providing sufficient and comprehensive information in a neutral fashion in order to encourage the client to make an informed choice, is one of the original tenets of genetic counseling (Fine, 1993; Weil, 2003). Nonetheless, the current guidelines (Summers et al, 2007) advocate non-directive counseling as an imperative to prenatal screening counseling; the central concern of this study is to analyze the pamphlets with attention to implicit messages that may be directive. What does critical reflection on these metaphors reveal about implicit messages embedded within the educational materials What are the implications for the design of future prenatal screening health education pamphlets A metaphor is a linguistic device that describes one 163 (abstract) idea by comparing it to another (concrete) idea (Lakoff & Johnson 1980a). This is described in terms of a concrete idea (a picture is a visual image that is not the interpretation of sonic data). This level of literal detail can be cumbersome; the metaphor facilitates understanding by comparing the abstract idea to a concrete one. However, when a comparison is made certain similarities are highlighted while differences are de-emphasized. This emphasis/de-emphasis may direct a particular understanding of the abstract idea. Metaphoric textual analysis is an approach that analyzes metaphors within textual material in order to critically reflect on various interpretive messages, and ideological strains within the text. Such an approach is based on the assumption that metaphors are fundamental to how humans understand the world (Lakoff & Johnson, 1980a), and that different levels of reflection may be engaged through metaphoric thought (Charteris Black, 2004). An examination of metaphoric systems can help to reveal particular ideologies which may inform that system (Charteris-Black, 2004; Lakoff 2002). Metaphor can also be used to prompt reflection (Kinsella, 2000), examine unstated opinions and assumptions (Charmaz, 2006), uncover bias created by provision of unintentional information (Kitzinger, 1999), and to foster insight into the way an individual or society systematically organizes the world (Lakoff & Johnson, 1980a). Metaphor has been used in critical textual analysis to reveal ideologies (Fraser, 2006; Lule, 2004; Martin, 1984, 1987, 1991; Sontag, 1978; Taylor, 1998, 2008) and has been developed into an analytical technique (Schmitt 2000, 2005). More than just a linguistic flourish, metaphor is a way of thinking and persuading (Charteris-Black, 2004). Metaphor acts as an interpretive bridge between abstract and 164 concrete ideas, thus structuring the way we conceptualize the world (Lakoff & Johnson, 1980a). Metaphor creates particular boundaries around the way we can think about and interact with a particular topic. Lakoff and Johnson (1980a, 1980b) explain how the way we conceptualize a concept systematically influences the way that concept takes place, the way we think about that concept, the way we interact with that concept. Metaphors also act to fill gaps in a lexicon; this may be semantic, accommodating changes in a conceptual system, or pragmatic, conveying specific intentions of the speaker (Charteris Black, 2004). Lakoff and Johnson (1980a) use the example of Argument Is War; there are multiple metaphors about arguing that compare it to battling. How might our interpretations be different if we thought and spoke about argument in terms of metaphors of dancing Dancing metaphors may encourage consideration of the co operative and artful aspects of arguing, ideas which are hidden or de-emphasized when describing argument with the metaphors of war. It questions the taken-for-granted meanings of the language used, encouraging these meanings to be challenged and reconsidered. Critical reflection is a term with multiple meanings that has been used across several disciplines. In this project we engaged with the idea of critical reflection as ideology critique (Brookfield, 1998, 2000, 2005). This approach to critical reflection focuses on becoming aware of the ways in which an 165 ideology affects social relations by imposing particular assumptions and belief systems (ideologies) which encourage, support, and maintain particular ways of viewing the world (Brookfield, 2000, 2005). Critical reflection is the first step to ideology critique, encouraging recognition of the ways ideology operates in the world. Such a recognition aids in the identification and analysis of the way we work in the world and the way the world works in us (Kincheloe, 2008). Critical reflection is based on the idea that decisions and actions originate from a consideration of the broader moral, ethical, political and historical context (Yost, Sentner & Forlenza-Bailey, 2000) with a focus on ends as well as means (Zeichner, 1981). In short, critical reflection informs the methodology of the current study in a number of ways. Many drug-dependent pregnant women do not seek early prenatal care and in treatment online cheap disulfiram online mastercard, therefore symptoms juvenile rheumatoid arthritis order disulfiram 250mg with mastercard, are at increased risk of medical and obstetric complica tions medications given for migraines disulfiram 250mg line. Warning signs of drug abuse include nonadherence to prenatal care (eg symptoms adhd discount disulfiram, late entry to care, multiple missed appointments, episodic or no prenatal care), evidence of poor nutrition, encounters with law enforce ment, and marital and family disputes during the pregnancy. Screenings at delivery are likely to have a negative result when drugs were used early in pregnancy, and a urine screening can have a negative result even when women have taken certain drugs during the 48 hours before delivery. States vary in their requirements for the evidence of drug exposure to the fetus or newborn in order to report a case to the child welfare system. Infants of mothers who are depressed display delayed psychologic, cognitive, neurologic, and motor development. Pregnancy and the postpartum period represent an ideal time during which consistent contact Preconception and Antepartum Care 131 with the health care delivery system will allow women at risk to be identified and treated. Examples of highly sensitive screening tools include the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale, Postpartum Depression Screening Scale, and Patient Health Questionnaire-9. Women who have been receiving treatment for depression before pregnancy should receive counseling concerning management options during pregnancy. Research indicates that most abused women continue to be victimized during pregnancy. In women who are being abused, 27% have demonstrated abusive behavior toward their children while living in the violent environment. In many cases, how ever, women will not disclose their abuse unless asked directly. The physician should inquire about her immediate safety and the safety of her children. Additionally, physicians should be familiar with state laws that may require reporting of intimate partner violence. First-Trimester Patient Education ^102^108^217^229^239 Patient education is an essential element of prenatal care. Dietary counseling and intervention based on special or individual needs usually are most effectively accomplished by referral to a nutritionist or registered dietitian. The recommended dietary allowances for most vitamins and minerals increase during pregnancy (Table 5-6). The National Academy of Sciences rec ommends 27 mg of iron supplementation (present in most prenatal vitamins) be given to pregnant women daily because the iron content of the standard American diet and the endogenous iron stores of many American women are not sufficient to provide for the increased iron requirements of pregnancy. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all pregnant women be routinely screened for iron-deficiency anemia. Iron absorption is facilitated by or with vitamin C supplementation or ingestion between meals or at bedtime on an empty stomach. Recent evidence suggests that vitamin D defi ciency is common during pregnancy especially in high-risk groups, including vegetarians, women with limited sun exposure (eg, those who live in cold cli mates, reside in northern latitudes, or wear sun and winter protective clothing), and ethnic minorities, especially those with darker skin. In view of the evidence linking folate intake with neural tube defects in the fetus, it is recommended that all women capable of becoming pregnant consume 400 micrograms from supple ments or fortified foods in addition to intake of food folate from a varied diet. For pregnant women thought to be at increased risk of vitamin D deficiency, maternal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels can be considered and should be interpreted in the context of the individual clini cal circumstance. Recommendations concerning routine vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy beyond that contained in a prenatal vitamin should await the completion of ongoing ran domized clinical trials. Increasingly, however, women are becoming pregnant when they are obese, they gain more weight than is necessary during pregnancy, and retain the weight postpartum. These same recommendations are made for adolescents, short women, and women of all racial and ethnic groups. Progress toward meeting these weight gain goals should be monitored and specific individualized counseling provided if significant devia tions are noted. Health care providers caring for pregnant women should determine a Preconception and Antepartum Care 137 Table 5-7. In the absence of either medical or obstetric complications, 30 min utes or more of moderate exercise per day on most, if not all, days of the week is recommended for pregnant women. Generally, participation in a wide range of recreational activities appears to be safe during pregnancy; however, each sport should be reviewed individually for its potential risk, and activities with a high risk of falling or those with a high risk of abdominal trauma should be avoided. Recreational and competitive athletes with uncomplicated pregnancies can remain active during pregnancy and should modify their usual exercise routines as medically indicated. Additionally, a physically active woman with a history of or risk of preterm delivery or intrauterine growth restriction may be advised to reduce her activity in the second trimester and third trimester. Caries, poor dentition, and periodontal disease may be associated with an increased risk of preterm delivery. If dental X-rays are necessary during pregnancy, the American Dental Association advises the use of a leaded apron to minimize exposure to the abdo men and the use of a leaded thyroid collar. The American Dental Association guidelines recommend timing elective dental procedures to occur during the second trimester or first half of the third trimester and postponing major surgery and reconstructive procedures until after delivery. Many dentists will require a note from the obstetrician stating that dental care requiring local anesthesia, antibiotics, or narcotic analgesia is not contraindicated in pregnancy. For women with prior pregnancies complicated by nausea and vomiting, it is rea sonable to recommend preconceptional and early pregnancy use of a multivi tamin because studies show this reduces the risk of vomiting requiring medical attention. Other effective nonpharmacologic treatments for mild cases include increasing protein consumption and taking powdered gin ger capsules daily, which has been found to be effective in reducing episodes of vomiting. Effective and safe treatments for more serious cases include antihistamine H1-receptor block ers, phenothiazines, and benzamides. Dietary intake of vitamin A in the United States is adequate to meet the needs of most pregnant women throughout gestation. Vitamin tablets containing 25,000 inter national units or more of vitamin A are available as over-the-counter prepara tions; however, pregnant women or those planning to become pregnant who use high doses of vitamin A supplements (and topical retinol) should be cau tioned about the potential teratogenicity because excess vitamin A is associated with anomalies of bones, the urinary tract, and the central nervous system. Excessive vitamin and mineral intake (ie, more than twice the recom mended dietary allowances) should be avoided during pregnancy. Also many fish are a uniquely rich food source of long chain omega-3 fatty acids and long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. There is strong evidence to suggest that these fatty acids are impor tant in central nervous system development and that maternal consumption of these fatty acids benefits fetal development and provides good nutrition for the mother. Some large fish, such as shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish are known to contain high levels of methylmercury, which is known to be terato genic. As such, pregnant women and women in the preconceptional period and lactation period should avoid these fish. To gain the benefits of consuming fish, while avoiding the risks of methyl mercury consumption, pregnant women should be encouraged to enjoy a vari ety of other types of fish, including up to 12 ounces (2 average meals) a week of a variety of fish and shellfish that are lower in mercury. If no advice is avail able, they should consume no more than 6 ounces (one average meal) per week of fish caught in local waters and no other fish during that week. To prevent pregnancy-related listeria infections, pregnant women are advised not to eat hot dogs or luncheon meats unless they are steaming hot and to avoid Preconception and Antepartum Care 141 unpasteurized soft cheeses. The possible occurrence of a major birth defect is a frequent cause of anxiety among pregnant women. There is little scientifically valid infor mation on which a risk estimate in human pregnancy can be based. Relatively few patients are exposed to agents that are known to be associated with increased risk of fetal malformations or mental retardation. Prenatal lead exposure has known adverse effects on maternal health and infant outcomes across a wide range of maternal blood lead levels. Buy disulfiram 250 mg without a prescription. Symptoms Of HIV - Various HIV Symptoms Faced By The Patients.
These exercise tolerance should be regarded as an indication for valve infants may require a univentricular approach symptoms in spanish disulfiram 500mg for sale. Signs of congestive heart failure (dyspnea medications while pregnant buy 250mg disulfiram, tachycardia medicine 44334 purchase disulfiram master card, tachypnea medications prescribed for depression discount generic disulfiram canada, low output) I B 3. Adolescents and young adults almost invariably have normal or increased cardiac output. It is apparent that regurgitation begets Management of valve regurgitation following balloon aortic valvotomy as a late complication regurgitation and aortic insufficiency is a progressive disease. Nevertheless, the protracted clinical course of chronic aortic Indication Prosthesis Class regurgitation is well documented (4,22). Sex, specifically female Autograft I B state without serious hemodynamic compromise may last for 2. In general, following balloon aortic valvotomy, as a late complication, is homografts are contraindicated in children because of early managed by valve repair or replacement with an autograft degeneration. In addition, mechanical pros Mitral stenosis theses can have a high reoperative rate, usually secondary to Etiology: In developed countries, mitral stenosis, like mitral nonstructural dysfunction due to subvalvular pannus and regurgitation, is the result of a wide spectrum of morphologi hemolysis from paravalvular leak (29). The detailed functional classification trophied or single papillary muscles, etc) (30). Due to the frequent asso to commissure papillary muscle fusion, short chordae, with ciation of atrial septal defect and mitral stenosis, transmitral abnormal papillary muscle and parachute mitral valve, ham gradient should not be the only criteria used to define the mock mitral valve and papillary muscle hypoplasia. However, many infants with congenital mitral stenosis Pathophysiology: Similar to mitral regurgitation in adults. Valve repair should be the preferred an uncommon valvular entity characterized by a wide spectrum option in small children even if the result is suboptimal. The artificial chordae can delay or possibly Indications for intervention: the procedure of choice is percu prevent the need for mechanical prostheses (38). Mechanical taneous balloon valvotomy for symptomatic patients or those prostheses may require replacement in a growing child; a larger with high right ventricle to pulmonary artery peak gradients prosthesis can be implanted because the mitral valve annulus can (48-50). The reduction in gradient and survival is similar with grow even when fixed to a prosthetic sewing ring. Etiology: Most cases of pulmonary stenosis are congenital in Special consideration: A newborn with critical pulmonary origin. The valve is either conical or dome-shaped with fusion stenosis who remains cyanotic after balloon valvotomy may of the leaflets. The valve may be thickened and dysplastic with require a systemic-pulmonary shunt (54). Natural history: the mode of presentation is either in the Good results have also been reported with balloon valvotomy newborn period with symptomatic critical pulmonary stenosis in adults. Infants need close follow-up following dilation or later when an asymptomatic patient is referred for murmur because reintervention is needed in 12% to 25% of patients in evaluation (46). The Natural moderate regurgitation can be associated with an abnormal History of Congenital Heart Defects study (10,47) revealed appearing bicuspid pulmonary valve with elongated leaflets that the 25-year survival rate (greater than 95%) was compa and no evidence of pulmonary stenosis. Of the pulmonary regurgitation will be secondary to intervention for patients presenting with a gradient greater than 50 mmHg, pulmonary stenosis or Tetralogy of Fallot. Natural history: the Natural History of Congenital Heart Defects study (47) identified moderate to severe pulmonary Tricuspid valve disease regurgitation following balloon valvotomy for pulmonary steno Etiology: the etiology of congenital tricuspid valve regurgitation sis in 6% of patients clinically and 20% by echocardiography. The latter group includes dis ful repair of Tetralogy of Fallot but the natural history is less eases such as unguarded tricuspid valve, tricuspid regurgitation well documented and still in evolution (55,56). Therefore, it echocardiographic diagnostic criteria and quantitative assess appears that an increasing number of these patients will ment of the severity of the anomaly are available, have been require reoperation for chronic severe pulmonary regurgita proven to be of prognostic value, and should therefore be fol tion. There is little additional role for cardiac catheterization peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis will increase the amount in the diagnosis of this malformation. Although it carries a better tions of congestive heart failure and documented ventricular outcome than the neonatal group, the natural history still ectopy. Pulmonary valve replacement, usually with an allograft reveals a suboptimal survival rate. In view of the outcome of the critical against immulogical and biochemical stress. Unstable cyanotic newborn in congestive heart failure, in need of mechanical ventilation, prostaglandin dependent and failed medical therapy I B 2. Progressive cyanosis with arterial saturation <80% at rest or with exercise I B 5. Progressive cyanosis with arterial saturation <80% at rest or with exercise I B 4. If stability is achieved the valve leaflets are not adherent with redundancy and by medical treatment, avoidance or delay in surgical inter prolapse, there is associated varying degrees of tricuspid vention can be possible. Indications for surgery the critical neonate may be an unstable cyanotic newborn with Anticoagulation for mechanical prostheses congestive heart failure in need of mechanical ventilation, Anticoagulation remains strongly recommended for the man prostaglandin dependence and massive cardiomegaly. Ann Thorac Surg cava to pulmonary artery anastomosis: An adjunct to biventricular 1994;57:1387-94. Ann Thorac Surg Guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart 1998;65:496-502. Guidelines for evaluation of the aortic root with a pulmonary autograft in children and young and management of common congential cardiac problems in adults with aortic-valve disease. Fate of left professionals from the Committee on Congential Cardiac Defects sided cardiac bioprostheses in children. Surgery for mitral derived valvar aortic stenosis gradient and the influence of aortic valve disease in the pediatric age group. The natural history of 271 patients with mitral stenosis study on the Natural History of Congenital Heart Defects. J Thorac septal defect: Report from the second Joint Study on the Natural Cardiovasc Surg 1998;115:84-93. Clinical results of mitral results of balloon dilation of congenital aortic stenosis: Predictors of valve repair by reconstructing artificial chordae tendineae in success. J Thorac aortic stenosis: Analysis of 29 patients having more than 1 cardiac Cardiovasc Surg 2001;122:229-33. Prog in Ped Cardiol maze procedure for right atrial arrhythmias in congenital heart 1992:1:3-16. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of stenosis in the neonate: A multi-institutional study of management, tachycardia in children with and without congenital heart disease: outcomes, and risk factors. Sudden unexpected Location of acutely successful radiofrequency catheter ablation of death from cardiovascular disease in children: A cooperative intraatrial reentrant tachycardia in patients with congenital heart international study. Am Heart J replacement after repair of pulmonary atresia and ventricular septal 1995;130:281-6. Second natural history Echocardiographic and clinical features in the fetus and neonate. J Thorac Cardiovasc Morphologic and hemodynamic consequences after percutaneous Surg 1992;104:1195-202. Pihkala J, Nykanen D, Freedom R, Benson L, Pediatric Clinic of Circulation 1997;96(Suppl I):I507. Bidirectional of fallot: 36-year follow-up of 499 survivors of the first year after cavopulmonary shunt associated with ventricular and valvuloplasty repair. Bioprostheses are particularly satisfactory in the elderly he definition of elderly is 75 years of age or older. The with excellent 10 and 15-year durability and avoidance of Tpotential for surgical management of valvular disease in anticoagulants and associated bleeding complications.
This has developed over the past 10 days medications peripheral neuropathy generic disulfiram 250mg online, and she is now breathless after walking 50 yards symptoms at 6 weeks pregnant order disulfiram 500mg with amex. About 2 weeks ago she had a flu-like illness with generalized muscle aches and fever medicine expiration purchase 500 mg disulfiram overnight delivery. She feels extremely tired and has noticed palpitations in association with her breathlessness treatment low blood pressure cheap disulfiram 250 mg otc. In addition she has some discomfort in her anterior chest which is worse on inspiration. Profound hypocalcaemia, hypophos phataemia, and hypomagnaesaemia can all cause myocardial depression. The clinical picture of myocarditis is non-specific, but common symptoms include myal gia, fatigue, shortness of breath, pericardial pain and palpitations. Patients usually have a marked sinus tachycardia disproportionate to the slight fever. There may be atrial or, more com monly, ventricular arrhythmias or signs of conducting system defects. Chest X-ray may be normal if the myocarditis is mild, but if there is cardiac failure there will be cardiomegaly and pulmonary congestion. The differential diagnoses in this case include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, pericarditis and myocardial ischaemia. Echocardiographic changes may be focal affecting only the right or left ventricle, or global. An endomyocardial biopsy is performed as soon as possible, and will show evidence of myocardial necrosis. Paired serum samples should be taken for antibody titres to Coxsackie B and mumps. Coxsackie virus can be cultured from the throat, stool, blood, myocardium or pericardial fluid. Corticosteroids tend to be used in patients with a short history, a positive endomyocardial biopsy, and the most severe disease. Most cases are benign and self-limiting, and cardiac function will return to normal. However a minority will develop permanent cardiac damage leading to a dilated cardiomyopathy. Four days prior to presentation he felt unwell and complained of muscle aches and headache. However his symptoms worsened, and by the day of presentation he was com plaining of a dry cough and marked shortness of breath. Percussion is reduced, and auscultation reveals bilateral crackles and bronchial breathing in both lower zones posteriorly. As the illness progresses the patient develops a dry cough, chest pain, shortness of breath and acute confusion. On examination, the patient is usually dehydrated, tachycardic and tachypnoeic with widespread rhonchi and crackles. The diffuse infiltrates on chest X-ray suggest atypical pneumonia, whereas a lobar pattern tends to occur with streptococcal pneumonia. Hypo natraemia occurs in cases of severe pneumonia and is a poor prognostic factor. Legionella outbreaks have often been due to infected water tanks in warm climates in institutions such as hotels and hospitals. He needs to receive high concentration of inspired oxygen, and also intravenous fluids to correct his dehydration. These should cover the common community-acquired pneumonias until the pre cise microbiological diagnosis is obtained and the antibiotics can then be rationalized. Blood cultures should be sent, and blood sent to screen for antibodies to atypical organisms such as Legionella, Mycoplasma, Chlamydia psittaci and influenza. Ten to fourteen days later a further blood sample should be sent and a fourfold rise in antibody titre is evidence of current infection. A faster diag nosis is made by testing broncheoalveolar lavage fluid, blood and urine for the presence of Legionella antigen. Over the past 10 years she has had previous episodes of loin pain which have occurred on both sides and resolved spontaneously over a few days. Examination of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems is otherwise unremarkable. The palpable abdominal masses in both flanks have the characteristic features of enlarged kidneys. The other principal causes for palpable kidneys are renal cell carcinoma and massive hydronephrosis. Flank pain is the most common symp tom, and may be caused by cyst rupture, cyst infection or renal calculi. Macroscopic haematuria due to cyst haemorrhage occurs commonly and usually resolves spontaneously. Hypertension occurs early in the course of this disease affecting 60 per cent of patients with normal renal function. The pattern of inher itance in this family is consistent with an autosomal dominant trait. Ultrasound is the preferred initial screening technique as it is cheap, non-invasive and rapid. For a certain diagnosis, there should be at least three renal cysts with at least one cyst in each kidney. Ultrasound in this patient shows the typical appearance of multiple cysts (black areas) surrounded by thickened walls (Fig. She should be referred to a nephrologist for long-term follow-up of her renal failure, and plans should be made for renal replacement therapy. Clinical trials are starting of vasopressin receptor antagonists which show promise at inhibiting cyst growth. Her proximal interphalangeal joints and metacarpophalangeal joints are swollen and painful with effusions present. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder principally affecting joints in a periph eral symmetrical distribution. The peak incidence is between 35 and 55 years in women and 40 and 60 years in men. The acute presentation may occur over the course of a day and be associated with fever and malaise. More commonly, as in this case, it presents insidiously, and this group has a worse prognosis. Rheumatoid arthritis characteristically affects proximal interphalangeal, metacarpophalangeal and wrist joints in the hands, and metatarsophalangeal joints, ankles, knees and cervical spine. As the disease pro gresses damage to cartilage, bone and tendons leads to the characteristic deformities of this condition. In patients with lond-standing rheumatoid arthritis, renal infiltration by amyloid may occur. These usually cause an asymmetrical arthritis affecting medium and larger joints as well as the sacroiliac and distal interphalangeal joints. This patient should be referred to a rheumatologist for further investigation and manage ment. |