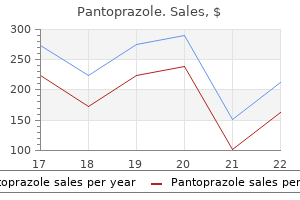
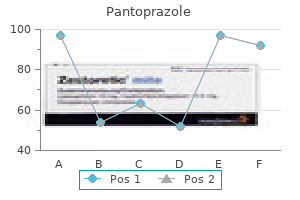
Dan E. Berkowitz, MD
And gastritis pain remedy generic 20 mg pantoprazole amex, if you do need to take largish doses of licorice gastritis severe pain buy 20 mg pantoprazole with mastercard, even with other herbs juice diet gastritis generic pantoprazole 40 mg without a prescription, for severe viral infections diet chart for gastritis patient buy 40 mg pantoprazole overnight delivery, please add these supplements to your regimen and carefully monitor for side efects. Luckily all these conditions tend to abate within 2 to 4 weeks after licorice intake ceases. A number of studies have found that large doses of licorice taken long term during pregnancy have detrimental efects on the unborn children. Again, this plant should not be used in large doses or for lengthy periods of time especially if you are pregnant. The herb is contraindicated in hypertension, hypokalemia, preg nancy, hypernatremia, and low testosterone levels. However, for short term use in those conditions (10 days or less), in low doses combined with other herbs, it is very safe. It should not be used along with estrogenic pharmaceuticals, hypertensive drugs, cardiac glycosides, diuretics such as thiazides, loop diuretics, spironolactone, amiloride, corticosteroids, hydrocortisone. The plants are perennials, can grow to 6 feet (2 m) in height, and bush out to 3 feet (1 m). The plant sends out both roots and rhizomes, the roots thick and feshy, up to 4 inches in diameter, going as deep as 3 feet (1 m). The creeping rhizomes spread out from the pri mary root, up to 26 feet (8 m) in length, often sending up shoots of new plants far from the original. The roots and rhizomes of the cultivated species are light in color, the wild species darker. The inside of most of the species is yellowish, and, in the commercial species at least, quite sweet. The native American species is not very sweet, though a lot of sources say it is (I frst tasted it in 1987, still waiting for that sweet taste to emerge on my tongue). The American species, though low in sweet ness, possesses many of the same medicinal actions, according to most sources, as the more prominent medicinal species. The genus ranges from semiarid desert to lush, wet climes such as Yorkshire, England, and from sea level to 8,500 or so feet (2,500 m) in altitude. The American species is endemic throughout Canada and most of the United States excluding the Southeast. If you look around you will probably fnd a licorice native in your ecorange someplace. The seeds need to be stratifed for several weeks, then scarifed and soaked for 2 hours in warm water before sowing if you want an easy germination. Treated seeds will germinate at about an 80 percent rate, untreated at around 20 percent. Once started, the plants are pretty intent on remaining and spreading wherever they want to . Both the European and Chinese varieties warrant planting in the wild and letting them go; they are well able to look after themselves if released from captivity. The plants like a free-draining friable soil with a pH between 6 and 7 but they can take on a greater range than that and do quite well. They are drought tolerant and like the sun but do need a bit of water; they often grow wild along streambeds, where they are very tenacious. It takes a few years for the plants to establish themselves (3 years is a good minimum period of time; earlier than that and the glycyrrhi zin content in the roots is too low) but once they do, you will be able to harvest from them pretty much forever. You will rarely, if ever, be able to dig the entire root system of an established plant, so it will continue to grow and spread from what is left. Commercial growers generally achieve somewhere between 15 and 50 tons per hectare (2. The plants produce a lot of root 214 215 Herbal Antivirals: the Materia Medica mass. You can get enough medicine for an entire family from just one established plant, pretty much forever. The glycyrrhizin content begins to fall in early August, becom ing very low by November. It begins to rise again in M arch, reaching its peak between late June and mid-July. In general, studies have found that wild plants are higher in glycyrrhi zin than domesticated plants. Finding it You can buy very good-quality organic licorice root from Pacifc Botanicals ( Regrettably there is no way to determine the glycyrrhizin content of their product. Note: Some of the licorice in commerce comes from eastern Europe (which possesses some of the highest levels of soil and air pollution in the world). It makes no sense to buy potentially contaminated herbs to use for their broad-spectrum immune and liver actions. The herb has other actions as well: Adrenal cortex Antitussive Prevents bioflm stimulant Antiulcer formation Adrenal tonic Cardioprotective Protects from effects Analgesic Demulcent of radiation exposure Antibacterial Estrogenic Smooth muscle Anticancer/tumor Expectorant relaxant inhibitor Gastric secretion Stimulates pancreatic Antihemolytic inhibitor secretions Antihyperglycemic Hepatoprotective Synergist (potent) Anti-infammatory Immunomodulant Thymus stimulant Antioxidative Immunostimulant Tyrosinase inhibitor Antispasmodic Laxative (gentle) Xanthine oxidase Antistressor Mucoprotective inhibitor As an immunostimulant, it stimulates interferon production, enhances antibody formation, stimulates phagocytosis. As an immunomodulant, it will reduce interferon-gamma levels if they are high and upregulate them if they are low. It has been found to potentiate the action of antituberculosis drugs, increasing positive outcomes in treat ment. It potentiates the action of oseltamivir against resistant infuenza Continued on next page 216 217 Herbal Antivirals: the Materia Medica Continued from previous page strains. It reduces toxicity and potentiates other medications in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Licorice potentiates the effect of the neuromuscular blocking agent paeoniforin, enhances the solubility of com pounds from other plants (during tincturing) by a factor of up to 570. It takes 4 to 8 hours (depending on what and how it is taken) for the glycyrrhizin to reach maximum serum concentration after oral ingestion; then it is slowly excreted and eventually eliminated entirely about 72 hours after ingestion. It strongly inhibits the ability of many viruses to create the membrane pores through which the viruses then enter cells. For other viruses, it is directly virucidal, and for others it stimulates the host immune system specifcally to attack the invading virus. Licorice, and its constituent glycyrrhizin, are especially effective against enveloped viruses, and this covers a wide range: herpesviruses, poxviruses, hepadnaviruses, faviviruses, togaviruses, coronaviruses, hepatitis D, orthomyxoviruses, paramyxoviruses, rhabdoviruses, bunyaviruses, floviruses, and retrovi ruses. It is not active against all viruses in these groups but it is against many of them. Chinese skullcap and licorice in combination should be considered the main antivirals to use for any viral infection. Glycyrrhizin has been found to inhibit cellular infection by 11 different faviviruses, including some of the most damaging: dengue, Japanese encephalitis, tick-borne encephalitis, and yellow fever. The herb does have a good range of other antimicrobial actions as well, against: Arthrinium sacchari Haemophilus Shigella dysenteriae Bacillus coagulans infuenzae Staphylococcus aureus Bacillus megaterium Helicobacter pylori Streptococcus lactis Bacillus Klebsiella pneumoniae Streptococcus mutans stearothermophilus Mycobacterium Streptococcus sobrinus Bacillus subtilis tuberculosis Toxocara canis Candida albicans Plasmodium spp. It is a synergist with other herbal medicines, increasing their potency, adds immune-boosting activity, and has numerous other supportive actions specifc for many different types of viral infections. Glycyrrhiza glabra is also a potent plant remediator for reclaiming saline-heavy soils. These include triterpenoids, polyphenols, polysaccharides, essential oils, favonoids, saponins, and so on. Diseases
It is only when the initial letters are affected that any great displacement in alphabetical order is caused gastritis diet 911 cheapest generic pantoprazole uk, and in this case gastritis diet ��������� discount 40 mg pantoprazole free shipping, the word is usually also listed with the British spelling and a reference given to the American spelling gastritis diet 6 months pantoprazole 20mg free shipping, thus: "Oedema gastritis symptoms reflux buy cheap pantoprazole 20mg line, oedematous see Edema". Conventions used in the Index Parentheses In the Index, as in the Tabular List, parentheses have a special meaning which the coder must bear in mind. A term that is followed by other terms in parentheses is classified to the given code number whether any of the terms in parentheses are reported or not. Cross-references Some categories, particularly those subject to notes linking them with other categories, require rather complex indexing arrangements. To avoid repeating this arrangement for each of the inclusion terms involved, a cross-reference is used. On looking up the latter term, the coder will find listed various forms of osteomyelitis: acute, acute hematogenous, chronic, etc. There alternative codes will be found for the condition if further or otherwise qualified as, for example, due to drugs or syphilitic. Enlargement, enlarged see also Hypertrophy If the coder does not find the site of the enlargement among the indentations beneath "Enlargement", he or she should look among the indentations beneath "Hypertrophy" where a more complete list of sites is given. Bladder see condition Hereditary see condition As stated previously, anatomical sites and very general adjectival modifiers are not usually used as lead terms in the Index and the coder is instructed to look up the disease or injury reported on the medical record and under that term to find the site or adjectival modifier. For other abdominal conditions, the coder should look up the disease or injury reported. They are added after terms classified to residual or unspecific categories and to terms in themselves ill defined as a warning that specified forms of the conditions are classified differently. If the medical record includes more precise information the coding should be modified accordingly. A distinction is made between an episode of care at which a disease or injury and result ing complications or manifestations are treated together "current episode" and an episode of care for complications or manifestations of diseases or injuries treated previously "subse quent episode". For each site there are five possible code numbers according to whether the neoplasm in question is malignant (primary); malignant, secondary; in situ; benign; or of uncertain behavior or unspecified nature. The description of the neoplasm will often indicate which of the five columns is appropriate. Where such descriptors are not present, the remainder of the Index should be consulted, where guidance is given to the approriate columns for each morphological (histological) variety listed. However, the guidance in the Index can be overridden if one of the descriptors mentioned above is present. Carcinomas and adenocarcinomas, of any type other than intraosseous or odontogenic, of sites marked with the sign. Hawkinsc,d, Shannon Fishere, Patrick Sipsa, Brecht Guillemyna, Jan Willem Beka, Petra Vermassena, Hanna De Saffela, Paul Eckhard Witten,f MaryAnn Weisb, Anne De Paepea, David R. According to the original ders present with a broad disease spectrum and large clinical vari classification by Sillence et al. In this study, we systematically analyzed skeletal phe chemical level are effected by either quantitative or qualitative notypes in a large set of zebrafish, with diverse mutations in the defects in type I collagen fibrils. This Significance will improve diagnostic strategies and enable the discovery of new targetable pathways for pharmacological intervention. Type I collagenopathies are a heterogenous group of connec skeletal phenomics type I collagen type I collagenopathies tive tissue disorders, caused by genetic defects in type I colla | | | zebrafish models osteogenesis imperfecta gen. Inherent to these disorders is a large clinical variability, of | which the underlying molecular basis remains undefined. By systematically analyzing skeletal phenotypes in a large set of ollagens are a large family of diverse, structural extracellular type I collagen zebrafish mutants, we show that zebrafish C matrix proteins, among which fibril-forming molecules models are able to both genocopy and phenocopy different dominate. This study illustrates the future potential of genes that express the 1(I) and 2(I) chain, respectively. In the zebrafish as a tool to further dissect the molecular basis of endoplasmic reticulum, after extensive posttranslational modifi phenotypic variability in human type I collagenopathies, to cation of proline and lysine residues, two associated pro 1(I) improve diagnostic strategies as well as promote the discovery chains and one pro 2(I) chain fold into a left-handed triple-helical of new targetable pathways for pharmacological intervention linear molecule. Caffey disease, or infantile cortical hy 2To whom correspondence should be addressed. Following the Sillence assess to which extent key features of human type I collageno et al. We systematically analyzed skeletal pheno proteins that interact with type I collagen, acting as key players in types in a large set of zebrafish models carrying different mu processes such as collagen synthesis, collagen folding and post tations in the zebrafish type I collagen-encoding genes col1a1a, translational modification, intracellular trafficking of collagen, or col1a1b, and col1a2 (Table 1). Severe morphological abnormalities present in utero that may cause perinatal lethality (7). S2) to quantify position of mutations along the chains can modulate the out 200 different descriptors of bone morphology and mineralization come. Nevertheless, numerous exceptions to these guidelines in the axial skeleton of each animal. In total, we analyzed 28,000 phenotypic data crucial to enable a more profound understanding of molecular points derived from 140 different animals. In general, we ob models are increasingly being used as a valuable complementa served a large diversity of skeletal phenotypes throughout the tion or predecessors to the traditional murine models (13, 14). We found that phenotypic severity Besides their unique attributes, such as the rapid development, (as measured by the absolute value of the z-score) tended to be large offspring numbers, and ease and speed in generating mu highest for mutants associated with collagen processing (plod2, tant lines, zebrafish bone mutants tend to survive into adulthood bmp1a) and qualitative collagen defects. Remarkably, some mutants with qualitative defects conservation of developmental programs in osteogenesis be (and collagen processing defects) exhibited a pronounced en tween teleosts and mammals, functional gene and pathway richment of positive z-scores for some traits. Detailed reports have already documented simi mutants associated with qualitative or quantitative collagen de larities and differences between teleost and mammalian bone fect, as well as the variability in direction of effect. One of these differences is the composition of type I otypes, to reflect the clinical variability observed in human type collagen in zebrafish, which harbors not one but two orthologs of I collagenopathies. However, these studies were focused on a detailed col1a1a encoding 1(I) and col1a1b encoding 3(I). Advances in processing and analysis have now allowed analysis of hundreds abnormalities (Fig. S4 and S5), which is of morphological and densitometric traits in large sets of most likely related to functional redundancy between both zebrafish skeletal mutants (25). Hence, we generated a double-heterozygous knockout tematic collagen analysis with skeletal phenomics to characterize mutant (col1a1a+/;col1a1b+/), which displays a mild skeletal a large set of zebrafish with mutations in type I collagen genes, as phenotype, with a low frequency of spontaneous fractures (calluses E8038 | List of mutant zebrafish alleles analyzed in this study Effect on homologous Gene Allele Effect on protein level human protein Type I collagen knockout alleles (quantitative defect) col1a1a sa1748 p. For alleles causing an amino acid substitution, the corresponding effect on the homologous human protein is listed in the p-notation (35). Quantitative measures of bone were not found to be statistically significant throughout the entire Fig. The microwaved (col1a1amed/med) mutant carries a homozygous Glu substitution in 1(I). Callus formation in ribs (arrowheads), local compressions of the vertebral column (brackets), and kyphosis (arrow), are indicated (also listed in Table 2). The presence of kyphosis (K) and or scoliosis (S) was also evaluated on 3D-scan images. Upon ther demonstrated by the much larger spread of values for the detailed examination of the finfold, these actinotrichia were different skeletal parameters in the group of mutant fish compared found to be absent in col1a1a / mutant larvae (Fig. We next assessed the effect of a complete (homozygous) loss of 1(I) or 3(I) on survival and on skeletal Complete Loss of 2(I) in Zebrafish Leads to Soft Connective Tissues +/ integrity. We studied a +/ col1a1b mutant fish, all possible genotypes were shown to be zebrafish mutant with a splice mutation in col1a2, resulting in the present at 7 d postfertilization (dpf), while from 15 dpf on some absence of 2(I) (Fig. Homozygous mutant / connective tissue disorder characterized by skin fragility, joint col1a1b mutants [loss of 3(I)] were present by the age of hypermobility, early-onset, severe and progressive cardiac valvular 3 mo, however at reduced numbers if combined with heterozy +/ / defects, and mild osteopenia with increased risk of fractures in some gous loss of col1a1a (col1a1a;col1a1b). Similarly, zebrafish with a heterozygous col1a2 plete loss of 3(I), but intact 1(I) did not show significant knockout are asymptomatic (Fig. FishCuT Because the knockout of col1a1a compromises viability from analysis demonstrated a slightly lower mineralization in the verte / / 7 dpf on, the general morphology of col1a1a mutant larvae bral column of col1a2 mutant fish, although this was found not was assessed at this stage. Furthermore, Histological analysis showed local alterations in bone thickness, the distal margins of the pectoral fins, and the finfold, were fusions at some of the vertebral endplates, and loss of typical shown to be ruffled in these mutants (Fig. On the y axis, mutants associated with a collagen processing defect are indicated in green, mutants with a qualitative defect in type I collagen are indicated in dark blue, and mutants with a quantitative defect in type I collagen are indicated in orange. Discount pantoprazole express. Cure Gastritis Forever in just 3 days.
Radiologically gastritis and gastroparesis diet buy pantoprazole in united states online, hugely expansile and osteolytic growth with foci of giant cell tumour appears as a large gastritis diet ���� buy pantoprazole 40mg low price, lobulated and osteolytic calcification gastritis bad breath 20 mg pantoprazole. Grossly gastritis blood test discount pantoprazole on line, giant cell tumour dissemination, commonly to the lungs, liver, kidney and is eccentrically located in the epiphyseal end of a long bone brain. The tumour is well-circumscribed, dark-tan and covered by a thin shell of subperiosteal bone. Grossly, chondrosarcoma Cut surface of the tumour is characteristically haemor may vary in size from a few centimeters to extremely large rhagic, necrotic, and honey-combed due to focal areas of and lobulated masses of firm consistency. These tumour cells show cytologic features Giant cells often contain as many as 100 benign nuclei of malignancy such as hyperchromatism, pleomorphism, and have many similarities to normal osteoclasts. These two or more cells in the lacunae and tumour giant cells cells have very high acid phosphatase activity. Histologic features include invasion of the tumour into adjacent soft tissues and cytologic characteristics of malignancy in the tumour cells. Sectioned surface shows circumscribed, dark tan, haemorrhagic and necrotic tumour. Though designated as giant cell tumour Stromal cells are mononuclear cells and are the real tumour cells and their histologic appearance determines or osteoclastoma, the true tumour cells are round to spindled the biologic behaviour of the tumour. Available evidence suggests that osteoclasts are derived from fusion of circulating monocytes, Other features of the stroma include its scanty collagen content, rich vascularity, areas of haemorrhages and the process being facilitated by transforming growth factor presence of macrophages. These are: its cell of origin, its are present in several other benign tumours and tumour differentiation from other giant cell lesions and its biologic like lesions from which the giant cell tumour is to be behaviour. Microscopy reveals osteoclast-like multinucleate giant cells which are regularly distributed among the mononuclear stromal cells. The common sites are Approximately 4% cases result in distant metastases, mainly shafts and metaphysis of long bones, particularly femur, tibia, to lungs. Metastases are histologically benign and there is humerus and fibula, although some flat bones such as pelvis usually history of repeated curettages and recurrences. These signs and symptoms may lead to an tumour is the role of radiotherapy resulting in development erroneous clinical diagnosis of osteomyelitis. However, X of post-radiation bone sarcoma though primary (de novo) ray examination reveals a predominantly osteolytic lesion malignant or dedifferentiated giant cell tumour may also with patchy subperiosteal reactive bone formation producing occur. Since its tissue is characteristically grey-white, soft and friable first description by James Ewing in 1921, histogenesis of this (Fig. Characteristic microscopic features are irregular lobules of uniform small tumour cells with indistinct cytoplasmic outlines which are separated by fibrous tissue septa having rich vascularity. Radiographically, the tumour usually the lobules are small and uniform resembling lymphocytes appears as an osteolytic lesion. Symptoms of spinal cord and have ill-defined cytoplasmic outlines, scanty compression may be present. Based on these Recurrences after local excision are frequent and the tumour cytological features the tumour is also called round cell almost invariably proves fatal. There differentiation between chordoma and chondrosarcoma may be areas of necrosis and acute inflammatory cell or mucin-secreting carcinoma may sometimes be difficult. But currently, use of combined regimen consisting of radiotherapy and systemic chemotherapy has improved the outcome greatly (5-year survival rate 40-80%). Notochord is the primitive axial skeleton which subsequently develops into the spine. Normally, remnants of notochord are represented by notochordal or physaliphorous (physalis = bubble, phorous = bearing) cells present in the nucleus pulposus and a few Figure 28. Chordomas thus occur having characteristic bubbly cytoplasm (physaliphorous cells) and in the axial skeleton, particularly sacral and spheno-occipital anisonucleocytosis. On electron microscopy, two types of synoviocytes are distinguished: type A and type B. Type A synoviocytes are more numerous and are related to macrophages and produce degradative enzymes, while type B synthesise hyaluronic acid. Diseases of joints are numerous and joints are also invol ved in several systemic disorders. In the following discussion, only those joint diseases which are morphologically significant are described. Synovial tumours are discussed in the next chapter together with other soft tissue tumours. It is characterised by progressive degenerative changes in the articular cartilages over the Figure 28. Most decade and then progressively and steadily increases skeletal metastases are derived from haematogenous spread. Some of the common carcinomas metastasising to be regarded as a reward of longevity. Probably, wear and the bones are from: breast, prostate, lung, kidney, stomach, tear with repeated minor trauma, heredity, obesity, aging thyroid, cervix, body of uterus, urinary bladder, testis, per se, all contribute to focal degenerative changes in the melanoma and neuroblastoma of adrenal gland. Usual radiographic appearance is of an such as previous injury, fracture, inflammation, loose bodies osteolytic lesion. Osteoblastic bone metastases occur in cancer and congenital dislocation of the hip. The regressive changes are most joint cavity, and synarthrodial or nonsynovial joints without a marked in the weight-bearing regions of articular joint cavity. In diarthrodial joints, the ends of two bones (proteoglycans) resulting in progressive loss of normal are held together by joint capsule with ligaments and tendons metachromasia. The articular chondrocytes, and at other places, proliferation of surfaces of bones are covered by hyaline cartilage which is chondrocytes forming clusters. Further progression of the thicker in weight-bearing areas than in nonweight-bearing process causes loosening, flaking and fissuring of the areas. The joint space is lined by synovial membrane or articular cartilage resulting in breaking off of pieces of synovium which forms synovial fluid that lubricates the joint cartilage exposing subchondral bone. The synovium may be smooth or thrown progressive loss of cartilage is apparent as narrowed joint into numerous folds and villi. The onset of disease is insidious, beginning with prodrome of fatigue, weakness, joint stiffness, vague arthralgias and myalgias. This is followed by pain and swelling of joints usually in symmetrical fashion, especially involving joints of hands, wrists and feet. Approximately 20% of patients develop rheumatoid nodules located over the extensor surfaces of the elbows and fingers. Advanced cases show characteristic radiologic abnormalities such as narrowing of joint space and ulnar 2. The denuded subchondral bone appears like deviation of the fingers and radial deviation of the wrist. These changes result in remodelling infrequently produce symptoms, but when present of bone and changes in the shape of joint surface leading complicate the diagnosis. Achiote (Annatto). Pantoprazole.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96073 |