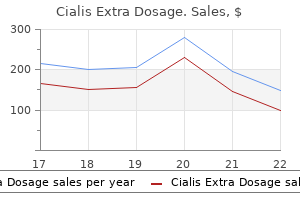
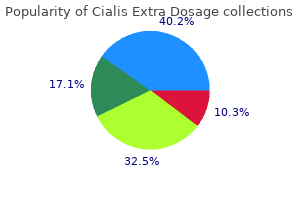
Baha Al-Shaikh
However erectile dysfunction medication patents cheap cialis extra dosage 100mg mastercard, if the tonsillitis is caused by a bacterial infection erectile dysfunction doctors minneapolis buy cialis extra dosage 50 mg line, antibiotics may be prescribed that needs to be completed erectile dysfunction pink guy generic cialis extra dosage 200 mg fast delivery. Stopping the antibiotics prematurely may lead to the bacteria developing a resistance to it best erectile dysfunction doctor buy cialis extra dosage without a prescription. Persons diagnosed with infectious mononucleosis should not exert themselves or engage in strenuous activity for a month for fear of splenic rupture. Children should not be prescribed A complete recovery may take up to aspirin because of the risk of 2 weeks. The lump you feel may be either a solitary nodule or a dominant nodule in a background of multiple nodules, or even a diffusely enlarged thyroid gland. It is taken up by functioning for thyroid cancer, but this is a rare thyroid cells, which will show up on a occupational or treatment risk for a scan. You will be able to return or hypothyroid symptoms or if you home or to work immediately. Depending on the size of and also to take measurements to track the tumour, either half or the entire the growth of the nodules. Most importantly, it allows the Additional treatment like radio iodine doctor to identify features that may treatment or radiotherapy may be be suggestive of cancer, including necessary. The risk of your nodule being usually temporary, but may cancerous depends on the exact be permanent. The surgery may be Your surgeon will explain to you which endoscopic or robot assisted. Skin operation you require and the reason incisions are located in the axilla or for it. This surgery may be recommended to improve the voice Diagnosis or remove a growth for laboratory Diagnosis is made by taking a history analysis. If a lesion proves to be of the voice problem and by physical cancerous, further treatment will be examination. Vocal fold paralysis is less common A more detailed examination than the first two groups of disorders. It is sometimes needed using usually involves paralysis of one vocal videostroboscopy. In this procedure, fold, and results in inability to close a rigid telescope tube with a the vocal folds completely. If the vocal stroboscopic light is passed through folds do not close completely, the voice the mouth (after spraying the throat is weak and hoarse and there may be with anaesthetic) to view the voice box. In this situation, a surgical procedure called Diagnosis a tracheostomy may be needed. This As with other voice disorders, involves placing a breathing tube examination of the vocal folds with (known as a tracheostomy tube) nasoendoscopy or videostroboscopy through an opening in the windpipe. Muscle Tension Dysphonia discuss transnasal oesophagoscopy to examine the food passage (this can be Muscle tension dysphonia refers to carried out in the clinic); and laryngeal hoarseness and difficulty in using electromyography, which uses a fine the voice due to excessive tightness needle to measure function of the or imbalance of the muscles in and vocal fold muscle. It can be due to habitual misuse of the voice muscles Treatment or can result from voice muscles trying Sometimes recovery occurs by itself to compensate for an underlying and no action is needed. Depending on inflammatory or neurological the cause of paralysis, this may take up condition, or growth on the vocal fold. Typically treatment is multi faceted, and involves correcting all underlying causes. Speech therapy may be necessary to improve voicing techniques and overcome bad vocal habits which put unnecessary strain on the voice. Often lifestyle changes are necessary including dietary changes and stress reduction. Avoiding unnecessary voice use can sometimes allow the voice muscles to relax and rest. The partial abnormalities that put tremendous obstruction can lead to complete stress on the heart and body. Genetic predisposition (night after night) should be referred to leading to facial and jaw abnormalities an Otolaryngologist, who will perform are known predisposing risk factors. Mild or including an endoscopic upper airway intermittent snoring may be a result of evaluation to determine an appropriate medications (like sedatives to help you treatment plan. The septum that divides Conservative treatment the nose into two sides may also be this includes eliminating outside crooked and needs to be straightened. In the nose, normal structures Conservative treatment called turbinates may be enlarged this includes eliminating outside from allergic rhinitis causing airflow factors that may be playing a role. Techniques levels of airway obstruction, usually include straightening the septum, in multiple sites, which may include turbinectomy and nasal valve regions of the nose, soft palate and reconstruction. Abnormal structures at the palate level include large tonsils, redundant lateral pharyngeal mucosal, thick and long Surgical procedures serve to remove soft palate and hypertrophied posterior or reposition tissues that partially or tonsillar pillar muscles and mucosal. All completely block the upper airway these contribute to a narrow airway at during sleep. An open nasal airway establishes normal breathing and In carefully selected patients, the minimises mouth breathing. It involves tongue base tissue collapses easily the forward movement of the lower during sleep. The individualised either increasing airway size to make use of staged soft tissue and more room for the tongue or reducing skeletal procedures for upper airway the tongue size. Both soft tissue reconstruction ensures that the most techniques and skeletal work may be conservative treatment is offered and required.
Disability: the effect on a person of the conjunction of a physical or mental impairment and the social lloyds pharmacy erectile dysfunction pills discount cialis extra dosage 60 mg online, political and economic conditions in which they live impotence meaning in english purchase 100 mg cialis extra dosage otc. There is disagreement over the relative weight of each of these factors in disability erectile dysfunction doctor in nashville tn order cialis extra dosage mastercard. Eugenics: projects that attempt deliberately to influence the physical impotence after 60 buy cialis extra dosage 50 mg low cost, mental or genetic characteristics of a population, often associated with state coercion. Genetic exceptionalism: the view that genetic information has a special status to which policy and practice should be sensitive and/or that the ethical issues raised by genetic information are different in kind to those raised in other areas of health. Genome sequencing: technique for determining the entire sequence of nucleotides in a genome. Genomics: a discipline in genetics that applies technologies such as genome sequencing methods and bioinformatics to the study of the function and structure of genomes. Genotype: the genetic make up of a cell, an organism or an individual, usually with reference to a specific characteristic under consideration. Germ cells (also referred to as gametes) transmit genomes from one generation to the next. During fertilisation, male derived germ cells (sperm) combine with female derived germ cells (eggs) to produce a new cell (a one cell embryo) that is distinct from either, with a unique genome. Germ line: cell lineage (gametes or cells that give rise to gametes) through which the genome of an organism is inherited by each generation from the preceding one. Heterozygous: having different alleles; that is, the sequence of a given region inherited from one parent differs from the sequence of the corresponding region inherited from the other. Homozygous: possession of identical alleles; that is, identical sequences from each parent for a given genomic region (cf. Mitochondria: essential organelles containing enzymes that convert metabolic products of the cytoplasm into cellular energy. Pleiotropy: influence on multiple phenotypic features of a single gene, such as genes that affect both skin and hair pigmentation. Transhumanism: an ideology that valorises the transformation of the human condition through the transformation of the human body, such as to promote life extension or cognitive and physical enhancement. Variant: sequence of a part of the genome that differs from its counterpart in other genomes, usually genomes that have a commonly encountered sequence at that position. Zygote: one cell embryo produced by the union of sperm and egg (the gametes) at fertilisation. Zygotes are totipotent, in that through successive divisions they can engender an entire individual. The cause of albinism is a mutation in a gene for melanin, a protein found in skin and eyes. Such a mutation may result in no melanin production at all or a significant decline in the amount of melanin. Although most mutations have no effect on the organisms in which they occur, some mutations are beneficial. These mutations are especially significant because they can be transmitted to offspring and every cell in the offspring will have the mutation. These mutations may have little effect on the organism because they are confined to just one cell and its daughter cells. Mutations may change the structure of a chromosome or just change a single nucleotide. A Russian publication concludes that 985,000 excess cancers occurred between 1986 and 2004 as a result of radioactive contamination. The 2011 report of the European Committee on Radiation Risk calculates a total of 1. Chromosomal Alterations Chromosomal alterations are mutations that change chromosome structure. They occur when a section of a chromosome breaks off and rejoins incorrectly or does not rejoin at all. An example of a human chromosomal alteration is the mutation that causes Down Syndrome. It is a duplication mutation that leads to developmental delays and other abnormalities. Point mutations can be silent, missense, or nonsense mutations, as shown in Table 7. They are neutral because they do not change the amino acids in the proteins they encode. Many other mutations have no effect on the organism because they are repaired before protein synthesis occurs. The effects of mutations can vary widely, from being beneficial, to having no effect, to having lethal consequences, and every possibility in between. Beneficial Mutations Some mutations have a positive effect on the organism in which they occur. They lead to new versions of proteins that help organisms adapt to changes in their environment. Mutations in many bacteria that allow them to survive in the presence of antibiotic drugs. The mutation protects them from developing atherosclerosis, which is the dangerous buildup of fatty materials in blood vessels. Harmful Mutations Imagine making a random change in a complicated machine such as a car engine. The chance that the random change would improve the functioning of the car is very small. The change is far more likely to result in a car that does not run well or perhaps does not run at all. A mutation in a single gene causes the body to produce thick, sticky mucus that clogs the lungs and blocks ducts in digestive organs. You can watch a video about cystic fibrosis and other genetic disorders at this link. You can learn more about hereditary cancer by watching the video at the following link. Some of the disorders are caused by mutations in autosomal genes, others by mutations in X linked genes. You can click on any human chromosome at this link to see the genetic disorders associated with it. A mutant dominant allele is expressed in every individual who inherits even one copy of it. If it causes a serious disorder, affected people may die young and fail to reproduce. A mutant recessive allele, such as the allele that causes sickle cell anemia (see Figure 7. They do not have the disorder themselves, but they carry the mutant allele and can pass it to their offspring. The mutation that causes the disorder affects just one amino acid in a single protein, but it has serious consequences for the affected person. Order cialis extra dosage discount. Erectile dysfunction pills that WORK!.
Antipsychotic Therapy Antipsychotic drugs include typical and atypical neuroleptics erectile dysfunction fruit generic cialis extra dosage 40mg otc. These agents are used to treat schizophrenia erectile dysfunction urinary tract infection order generic cialis extra dosage on line, psychotic mood disorders impotence statistics cialis extra dosage 40mg online, and some personality disorders erectile dysfunction doctor type purchase cialis extra dosage 100mg on line. Many of the conditions are associated with behaviors and symptoms such as impulsiveness, disturbances in perception and cognition, and an inability to sustain attention. Neuroleptics can cause a variety of side effects that can interfere with driving, such as motor dysfunction that affects coordination and response time, sedation, and visual disturbances (especially at night). You should not certify the driver until the medication has been shown to be adequate/effective, safe, and stable. Anxiolytic and Sedative Hypnotic Therapy Anxiolytic drugs used for the treatment of anxiety disorders and to treat insomnia are termed sedative hypnotics. Studies have demonstrated that benzodiazepines, the most commonly used anxiolytics and sedative hypnotics, impair skills performance in pharmacologically active dosages. The effects of benzodiazepines on skills performance generally also apply to virtually all non benzodiazepines sedative hypnotics, although the impairment is typically less profound. However, barbiturates and other sedative hypnotics related to barbiturates cause greater impairment in performance than benzodiazepines. Epidemiological studies indicate that the use of benzodiazepines and other sedative hypnotics are probably associated with an increased risk of automobile crashes. Waiting Period No recommended time frame You should not certify the driver until the medication has been shown to be adequate/effective, safe, and stable. Clinical experience has shown that acute side effects usually resolve rapidly and almost invariably within a few months. Monitoring/Testing You may on a case by case basis obtain additional tests and/or consult with a mental health specialist, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist to adequately assess driver medical fitness for duty. Lithium Therapy Lithium (Eskalith) is used for the treatment of bipolar and depressive disorders. Studies suggest that there is little evidence of lithium interfering with driver skill performance. Bipolar Mood Disorder Mood disorders are characterized by their pervasiveness and symptoms that interfere with the ability of the individual to function socially and occupationally. Bipolar disorder is characterized by one or more manic episodes and is usually accompanied by one or more depressive episodes. During a manic episode, judgment is frequently diminished, and there is an increased risk of substance abuse. Treatment for bipolar mania may include lithium and/or anticonvulsants to stabilize mood and antipsychotics when psychosis manifests. Symptoms of a depressive episode include loss of interest and motivation, poor sleep, appetite disturbance, fatigue, poor concentration, and indecisiveness. A severe depression is characterized by psychosis, severe psychomotor retardation or agitation, significant cognitive impairment (especially poor concentration and attention), and suicidal thoughts or behavior. In addition to the medication used to treat mania, antidepressants may be used to treat bipolar depression. Other psychiatric disorders, including substance abuse, frequently coexist with bipolar disorder. Monitoring/Testing At least every 2 years the driver with a history of a major mood disorder should have evaluation and clearance from a mental health specialist, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, who understands the functions and demands of commercial driving. Major Depression Major depression consists of one or more depressive episodes that may alter mood, cognitive functioning, behavior, and physiology. Symptoms may include a depressed or irritable mood, loss of interest or pleasure, social withdrawal, appetite and sleep disturbance that lead to weight change and fatigue, restlessness and agitation or malaise, impaired concentration and memory functioning, poor judgment, and suicidal thoughts or attempts. Hallucinations and delusions may also develop, but they are less common in depression than in manic episodes. Page 197 of 260 Most individuals with major depression will recover; however, some will relapse within 5 years. A significant percentage of individuals with major depression will commit suicide; the risk is the greatest within the first few years following the onset of the disorder. Although precipitating factors for depression are not clear, many patients experience stressful events in the 6 months preceding the onset of the episode. In addition to antidepressants, other drug therapy may include anxiolytics, antipsychotics, and lithium. The actual ability to drive safely and effectively should not be determined solely by diagnosis but instead by an evaluation focused on function and relevant history. Page 198 of 260 Monitoring/Testing At least every 2 years the driver with a history of a major mood disorder should have evaluation and clearance for commercial driving from a mental health specialist, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, who understands the functions and demands of commercial driving. Personality Disorders Any personality disorder characterized by excessive, aggressive, or impulsive behaviors warrants further inquiry for risk assessment to establish whether such traits are serious enough to adversely affect behavior in a manner that interferes with safe driving. A person is medially unqualified if the disorder is severe enough to have repeatedly been manifested by overt acts that interfere with safe operation of a commercial vehicle. Waiting Period No recommended time frame You should not certify the driver until the etiology is confirmed and treatment has been shown to be adequate/effective, safe, and stable. Monitoring/Testing You may on a case by case basis obtain additional tests and/or consult with a mental health specialist, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, to adequately assess driver medical fitness for duty. Schizophrenia and Related Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia is the most severe condition within the spectrum of psychotic disorders. Individuals with chronic schizophrenia should not be considered medically qualified for commercial driving. Risks for Commercial Driving Clinical experience shows that a person who is actively psychotic may behave unpredictably in a variety of ways. For example, a person who is hearing voices may receive a command to do something harmful or dangerous, such as self mutilation. Except for a confirmed diagnosis of schizophrenia, determination may not be based on diagnosis alone.
Adequate aeromedical training for potential examiners and recurrent training for those designated as medical examiners is necessary but the examiner must also develop the skills needed to conduct a thorough examination in an atmosphere of trust erectile dysfunction pills free trials discount 200 mg cialis extra dosage free shipping. Applicants are more likely to be forthcoming with personal information if they believe that impotence quoad hoc meaning cialis extra dosage 60mg with amex, should they declare a condition that could have aeromedical significance erectile dysfunction statistics australia order cialis extra dosage 50 mg amex, they will be treated fairly by the Authority erectile dysfunction drugs patents cheap 40mg cialis extra dosage visa, and that efforts to keep the applicant operating will be made wherever possible by those having decision making authority over the issuance of Medical Assessments. No basic medical curriculum or post graduate training in a speciality other than aviation medicine provides the specific instruction desirable for a designated medical examiner. Improving the quality of aviation medical examinations in a State will result in a more rational and uniform application of the medical provisions of Annex 1. This in turn may not only positively affect the general flight safety level within the country, but may also be expected to favour increased international recognition and reciprocity with regard to medical fitness requirements of personnel licences. However, for examiners to function effectively in this role, it is desirable that they receive formal instruction on fundamental procedures. Whilst such training may be included in an aviation medical examiner training course curriculum, normally additional, specific training is required. It contains guidance for providers of training as well as for States who are implementing such training or assessing it. The aim is to encourage States to adopt a systematic approach to aeromedical training so that medical examiners attain an appropriate and harmonized level of expertise. Accordingly, the discussion which follows will refer primarily to this group and their work environment. However, most of the principles are also applicable to the other categories of applicant. In some States, the process for medical certification for Class 2 applicants differs from other classes in that there may be greater authority delegated to examiners of Class 2 applicants. Most of the medical considerations for Class 1 also apply to Class 3, and therefore the same core set of competencies is likely to be required of their medical examiners. The guidance given in this chapter is also applicable to medical examiners designated to examine Class 3 applicants. The States that responded to the survey represented a variety of geographical regions and regulatory approaches. In some, the examiners were entitled or required to issue the Medical Assessment (even if only as a temporary Medical Assessment) while in others the examiner only performed examinations and the Assessment was issued centrally, based on examination findings. In terms of prerequisites to undergo training, some States required only basic medical qualifications, while others required additional qualifications, skills or experience. In some States, completion of the training allowed the doctor to commence working as a medical examiner but in others, further requirements were added, sometimes including a probation period. In about half the States, there was an established process for review or audit of examiner performance. In some States the Licensing Authority itself provided the training, and in others this was done by external organizations. The principal training method was by lectures, often with clinical demonstrations and sometimes practical visits (to altitude chambers or aviation worksites, for example). A variety of written reference material was used including textbooks, on line resources and regulatory documents. The experience or training required of trainers also varied greatly, but in general there were few explicit requirements. The successful implementation of competency based training for medical examiners should take into account the variety of State specific parameters while at the same time ensuring that internationally agreed competency standards are met. Although the framework lists those units and elements sequentially, in reality they do not necessarily occur in a specific order or as individual units, as many functions are conducted concurrently or iteratively. The purpose of the examination is to facilitate the decision concerning fitness for issuance of a Medical Assessment, and the two parts of the process (clinical examination, and issuance decision based on the examination and any other clinical findings) should be considered in totality rather than in isolation. The goal of the examination process is to optimize flight safety through managing aeromedical risk. Whether or not the State requires the examiner to make certification decisions, the ultimate goal of the examination and evaluation process is to minimize the risk of safety being compromised as a result of aeromedical factors. These factors include, but are not limited to , incapacitation of pilots or other licence holders. Competency based aviation medical examiner training should contribute to achieving the goal in (1) above. In order to provide appropriately targeted evaluations, medical examiners should have a clear understanding of the considerations which underlie aeromedical decisions. The periodic medical examination and evaluation process should use a risk based approach. Characteristics of the applicant will help determine the areas on which the examination should focus. For example, in older applicants, cardiovascular risk becomes relatively more important as a potential cause of incapacitation. Aside from age, a number of demographic and other considerations may be important including gender, ethnic background, culture, and type of flying. Potential examiners are fully registered/licensed medical practitioners who already have acquired core clinical skills. Being registered to practice medicine is taken to denote an acceptable level of competence in basic skills of history taking, physical examination, diagnosis and medical treatment. It is therefore assumed that medical examiner training does not need to ensure that all basic clinical skills or core medical knowledge are in place. Rather, it is accepted that this has been verified within each State prior to training commencement. The aim of medical examiner training, as addressed in this chapter, is to build upon basic clinical skills and knowledge and provide additional, task related knowledge and skills, and to foster those attitudes, that are required to achieve competency in the specialized tasks required of a medical examiner. The training and its assessment should therefore be focused on developing and verifying that such additional competencies have been achieved. Potential designated medical examiners have currency in medical knowledge and practice. States employ various means to ensure that examiners are receiving ongoing education and training and are maintaining currency in clinical practice. Verifying such currency is somewhat beyond the scope of the medical examiner training, although it may reveal deficiencies if present. Guiding Principles the following premises provide background to the rationale behind the formulation of the competency framework: a) Physical incapacitation is a rare cause of accidents in two pilot aircraft undertaking commercial flight operations. V 1 6 Manual of Civil Aviation Medicine b) Overall incidence of physical disease increases significantly with age. Safety context Since soon after the birth of aviation, medical standards have been applied to aviators with an overriding focus on maintaining the safety of flight. In the 100 years since the first fatal aircraft accident involving heavier than air aircraft in 1909 (DeJohn, 2004), the industry has evolved from aircraft carrying a few people to aircraft carrying several hundreds of passengers; consequently, a single aircraft accident today may have very severe consequences. Large aircraft are flown by professional pilots, a reason for this chapter being focused primarily on the professional pilot group, as mentioned above. When private pilots are involved in aircraft crashes, the number of individuals involved is much smaller since the aircraft typically flown carry only 1 3 passengers. Furthermore, the likelihood of causing harm to members of the public, either on the ground or in other aircraft, is minimal (although such accidents do very occasionally occur). It has been estimated that across the industry 3 per 1 000 aircraft accidents (15 per 1 000 fatal aircraft accidents) result from pilot incapacitation (Booze, 1989), although this does not include accidents in which medical factors may be a contributory, as opposed to primary, cause. Because of difficulties in identifying medical causes, there may also be situations in which a primary medical cause may have been present but which cannot be established through investigatory processes. In an analysis of fatal commercial (two pilot) crashes over a 20 year period (1980 2000) in which medical factors were identified as the cause(s), ten incidents were found. Of the ten, eight were ascribed to a psychiatric disorder with the majority (six) being related to alcohol and/or other drugs (Evans, 2007). The discussion which follows will therefore place particular emphasis on these conditions. Aims and limitations of the examination process the primary purpose of a medical examination is often considered to be the detection of conditions with a propensity to cause incapacitation (Evans, 2006). |