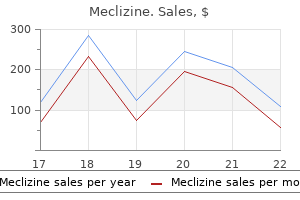
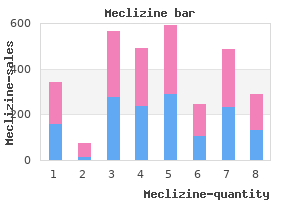
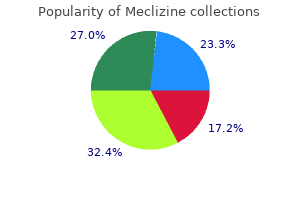
Karl S Mainprize
Palliative Care: A multidisciplinary approach to specialized medical and nursing care for people with life-limiting illnesses medicine 2015 25mg meclizine otc. It focuses on providing patients with relief from the symptoms medicine 319 pill buy meclizine line, pain treatment resistant depression best purchase for meclizine, physical stress schedule 8 medications victoria order cheap meclizine online, and mental stress of the terminal diagnosis. Palliative Care differs from Hospice Care in that the patient can continue with therapy for their disease while on Palliative Care. Pathology Report: A document that contains the diagnosis determined by examining cells and tissues under a microscope. This interaction tells the T cells to leave the other cells alone and not attack them. Perimenopause: Menopause is defined as the time when a woman has not had a menstrual period for 12 consecutive months, and the time that precedes preceding menopause has been referred to as the perimenopause, although there is no strict medical definition for this. Perimenopause usually begins for women in their 40s but may start as early as the late 30s. Perimenopausal women will have had one or more periods within 12 months, And typically begin experiencing menopausal symptoms such as mood swings, irregular periods, and/or hot flashes. Phenotype: the characteristics of a protein, cell, organ, or organism as determined by its genes. The placebo arm of a clinical trial is used as a control to compare how effective or safe the actual treatment drug is. Port: A small disc made of plastic or metal about the size of a quarter that sits just under the skin. The port is attached to a catheter (tube) that is threaded into a vein or specific area for purposes of extracting blood or delivering a drug(s) to a patient. Postmenopausal women: Women who have not had a menstrual period for 12 consecutive months. Premenopausal women: Women who have had one or more periods within a 12-month calendar year and who have not yet begun experiencing menopausal symptoms such as mood swings, irregular periods, and/or hot flashes. Prevalence: Prevalence refers to the number of existing cases of a disease in a population at a given point in time. Proliferation (as in cell proliferation): Cell proliferation is the process that results in an increase of the number of cells and is defined by the balance between cell divisions versus cell loss through cell death or differentiation. Promoter methylation: the promoter is a section of a gene that regulates expression of the gene. Addition or removal of a methyl group from a promoter is a common way for cells to temporarily turn genes on or off. Prospective: A term used to describe a trial or data in which the information will be collected in the future according to a specified plan. Proton Beam Therapy: A type of radiation treatment that uses protons to treat cancer. Proton therapy is a type of external-beam radiation therapy which painlessly delivers radiation through the skin from a machine outside the body. In contrast, with photon-based externalbeam radiation therapy, x-rays continue depositing radiation as they exit the body, which can damage healthy tissue. Randomized control studies: Randomized controlled studies are considered the gold standard for clinical research and testing new treatments, particularly when they are double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. In double-blind trials, both the trial participants and the research team are unaware of which treatment has been assigned to whom. Placebocontrolled trials test a treatment or intervention against a placebo (the same in appearance as the study drug but with no treatment effects). However, in cancer trials new treatments are tested against the standard treatment, and placebo would be given as part of a treatment combination. When such chemical signals bind to a receptor, they cause some form of cellular/tissue response such as a change in the activity of a cell. Recurrence: Cancer that has recurred (come back), usually after a period of time during which the cancer could not be detected. A reference product is approved based on, among other things, a full complement of safety and effectiveness data. Retrospective: When used to describe a trial or data, retrospective means that the information already exists, such as in electronic medical records or banked tumor samples and will be collected and analyzed as is. Risk Ratio: A term used when comparing the risk of a disease or outcome in one group in contrast to another group. These are measured against the absolute risk, which is the probability of a specified outcome/disease occurring in a specified population. Fulvestrant comes as a solution (liquid) to be injected slowly over 1 to 2 minutes into a muscle in the buttocks. Fulvestrant is administered by a doctor or nurse in a medical office and is usually given once every 2 weeks for the first 3 doses (days 1, 15, and 29) and then once a month thereafter. The classic example is the process by which a zygote [a fertilized egg] develops from a single cell into a multicellular embryo that further develops into a more complex fetus). Stroma: the supportive framework of an organ (or gland or other structure), usually composed of connective tissue. In this type of injection, a short needle is used to inject a drug into the tissue layer between the skin and the muscle. For example, the drug Fulvestrant (Faslodex) is administered subcutaneously into the buttocks. Subtype: A term describing the smaller groups that a type of cancer can be divided into based on certain characteristics of the cancer cells. Surgical Oncologist: General surgeons who have completed an additional three years of fellowship training in all cancers in order to diagnose, biopsy, and surgically treat cancer. Surrogate endpoint: A scientifically accepted sign of efficacy, such as a laboratory test, radiographic image, or physical sign. Systematic review: An overview of primary studies, such as randomized controlled trials in cases of therapy or treatment, or prospective cohort studies for prognosis-related factors that used explicit and reproducible methods. A systematic review is done by searching for published studies that measured the same variables and outcomes in the same way. Systemic therapy: Treatment using substances that travel through the bloodstream, reaching and affecting cells all over the body. This is required if the tissue sample contains a mixture of cell types as in a biopsy sample or if a mutation is rare. Targeted therapy: In cancer, a treatment that is aimed at a specific characteristic of a tumor. Telomere: the tip of a chromosome that functions to prevent deterioration of the chromosome. Toxicity: the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Translational Research/Medicine: Translational research is the process of applying knowledge from basic biology and clinical trials to approved techniques and tools that address critical medical needs and improve health outcomes. Trk Receptors: Trk receptors are a family of tyrosine kinases that regulates synaptic strength and plasticity in the mammalian nervous system. The common ligands of trk receptors are neurotrophins, a family of growth factors critical to the functioning of the nervous system. Tumor (or Tissue) Agnostic Therapies: Therapies that are based upon specific molecular signatures of the cancer, as opposed to where the cancer originated. In addition, tumor marker levels may initially rise after effective treatment when cancer cells die rapidly and release the marker into the bloodstream; hence the temporary increase may not necessarily mean treatment failure. Tyrosine kinase: An enzyme that acts as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions. Umbrella trials: Clinical trials that test the impact of different drugs on various mutations in a single type of cancer.
Gastrointestinal stoma Superficial necrosis; Severe symptoms; Life-threatening Death necrosis intervention not indicated hospitalization or elective consequences; urgent operative intervention intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of a necrotic process occurring in the gastrointestinal tract stoma medications used to treat bipolar disorder discount 25mg meclizine with mastercard. Intraoperative breast injury Primary repair of injured Partial resection of injured Complete resection or Life-threatening Death organ/structure indicated organ/structure indicated reconstruction of injured consequences; urgent organ/structure indicated; intervention indicated disabling Definition: A finding of damage to the breast parenchyma during a surgical procedure medicine 1900 cheap meclizine. Intraoperative gastrointestinal Primary repair of injured Partial resection of injured Complete resection or Life-threatening Death injury organ/structure indicated organ/structure indicated reconstruction of injured consequences; urgent organ/structure indicated; intervention indicated disabling Definition: A finding of damage to the gastrointestinal system during a surgical procedure medications list template meclizine 25 mg with mastercard. Intraoperative ocular injury Primary repair of injured Partial resection of injured Complete resection or Life-threatening Death organ/structure indicated organ/structure indicated reconstruction of injured consequences; urgent organ/structure indicated; intervention indicated disabling Definition: A finding of damage to the eye during a surgical procedure 6mp medications purchase cheap meclizine on line. Intraoperative skin injury Primary repair of injured Partial resection of injured Complete resection or Life-threatening Death organ/structure indicated organ/structure indicated reconstruction of injured consequences; urgent organ/structure indicated; intervention indicated disabling Definition: A finding of damage to the skin during a surgical procedure. Intraoperative venous injury Primary repair of injured Partial resection of injured Complete resection or Life-threatening Death organ/structure indicated organ/structure indicated reconstruction of injured consequences; urgent organ/structure indicated; intervention indicated disabling Definition: A finding of damage to a vein during a surgical procedure. Kidney anastomotic leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; radiologic, Life-threatening Death observations only; intervention intervention indicated endoscopic or elective consequences; urgent not indicated operative intervention operative intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of leakage of urine due to breakdown of a kidney anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Large intestinal anastomotic Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; radiologic, Life-threatening Death leak observations only; intervention intervention indicated endoscopic or elective consequences; urgent not indicated operative intervention operative intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of an anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures) in the large intestine. Pancreatic anastomotic leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; radiologic, Life-threatening Death observations only; intervention intervention indicated endoscopic or elective consequences; urgent not indicated operative intervention operative intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a pancreatic anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Radiation recall reaction Faint erythema or dry Moderate to brisk erythema; Moist desquamation in areas Life-threatening Death (dermatologic) desquamation patchy moist desquamation, other than skin folds and consequences; skin necrosis mostly confined to skin folds creases; bleeding induced by or ulceration of full thickness and creases; moderate minor trauma or abrasion dermis; spontaneous bleeding edema from involved site; skin graft indicated Definition: A finding of acute skin inflammatory reaction caused by drugs, especially chemotherapeutic agents, for weeks or months following radiotherapy. Rectal anastomotic leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; radiologic, Life-threatening Death observations only; intervention intervention indicated endoscopic or elective consequences; urgent not indicated operative intervention operative intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a rectal anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Seroma Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; simple Symptomatic, elective diagnostic observations only; aspiration indicated radiologic or operative intervention not indicated intervention indicated Definition: A finding of tumor-like collection of serum in the tissues. Spermatic cord anastomotic Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; radiologic, Life-threatening Death leak observations only; intervention intervention indicated endoscopic or elective consequences; urgent not indicated operative intervention operative intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a spermatic cord anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Tracheal hemorrhage Minimal bleeding identified on Moderate bleeding; medical Severe bleeding; transfusion Life-threatening Death clinical or diagnostic exam; intervention indicated indicated; radiologic or consequences; urgent intervention not indicated endoscopic intervention intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of bleeding from the trachea. Urethral anastomotic leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; radiologic, Life-threatening Death observations only; intervention intervention indicated endoscopic or elective consequences; urgent not indicated operative intervention operative intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a urethral anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Urostomy obstruction Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; dilation or Altered organ function. Uterine perforation Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic and intervention Severe symptoms; elective Life-threatening Death observations only; intervention not indicated operative intervention consequences; urgent not indicated indicated intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the uterine wall. Cardiac troponin I increased Levels above the upper limit Levels consistent with of normal and below the level myocardial infarction as of myocardial infarction as defined by the manufacturer defined by the manufacturer Definition: A laboratory test result which indicates increased levels of cardiac troponin I in a biological specimen. Lymphocyte count increased >4000/mm3 20,000/mm3 >20,000/mm3 Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an abnormal increase in the number of lymphocytes in the blood, effusions or bone marrow. Metabolism and nutrition disorders Metabolism and nutrition disorders Grade Adverse Event 1 2 3 4 5 Acidosis pH <normal, but >=7. Anorexia Loss of appetite without Oral intake altered without Associated with significant Life-threatening Death alteration in eating habits significant weight loss or weight loss or malnutrition consequences; urgent malnutrition; oral nutritional. Iron overload Moderate symptoms; Severe symptoms; Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated intervention indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by accumulation of iron in the tissues. Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Grade Adverse Event 1 2 3 4 5 Abdominal soft tissue necrosis Local wound care; medical Operative debridement or Life-threatening Death intervention indicated. Head soft tissue necrosis Local wound care; medical Operative debridement or Life-threatening Death intervention indicated. Joint range of motion Mild restriction of rotation or Rotation <60 degrees to right Ankylosed/fused over multiple decreased cervical spine flexion between 60 70 or left; <60 degrees of flexion segments with no C-spine degrees rotation Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in flexibility of a cervical spine joint. Soft tissue necrosis lower limb Local wound care; medical Operative debridement or Life-threatening Death intervention indicated. Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (incl cysts and polyps) Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (incl cysts and polyps) Grade Adverse Event 1 2 3 4 5 Leukemia secondary to Present Death oncology chemotherapy Definition: A disorder characterized by leukemia arising as a result of the mutagenic effect of chemotherapy agents. Myelodysplastic syndrome Life-threatening Death consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by insufficiently healthy hematapoietic cell production by the bone marrow. Treatment related secondary Non life-threatening Acute life-threatening Death malignancy secondary malignancy secondary malignancy; blast crisis in leukemia Definition: A disorder characterized by development of a malignancy most probably as a result of treatment for a previously existing malignancy. Central nervous system Asymptomatic; clinical or Moderate symptoms; Severe symptoms; medical Life-threatening Death necrosis diagnostic observations only; corticosteroids indicated intervention indicated consequences; urgent intervention not indicated intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the brain and/or spinal cord. Cerebrospinal fluid leakage Post-craniotomy: Post-craniotomy: moderate Severe symptoms; medical Life-threatening Death asymptomatic; Post-lumbar symptoms; medical intervention indicated consequences; urgent puncture: transient headache; intervention indicated; Postintervention indicated postural care indicated lumbar puncture: persistent moderate symptoms; blood patch indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by loss of cerebrospinal fluid into the surrounding tissues. Dysarthria Mild slurred speech Moderate impairment of Severe impairment of articulation or slurred speech articulation or slurred speech Definition: A disorder characterized by slow and slurred speech resulting from an inability to coordinate the muscles used in speech. Dysgeusia Altered taste but no change in Altered taste with change in diet diet. Dysphasia Awareness of receptive or Moderate receptive or Severe receptive or expressive characteristics; not expressive characteristics; expressive characteristics; impairing ability to impairing ability to impairing ability to read, write communicate communicate spontaneously or communicate intelligibly Definition: A disorder characterized by impairment of verbal communication skills, often resulting from brain damage. Edema cerebral Life-threatening consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by swelling due to an excessive accumulation of fluid in the brain. Ischemia cerebrovascular Asymptomatic; clinical or Moderate symptoms diagnostic observations only; intervention not indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease or absence of blood supply to the brain caused by obstruction (thrombosis or embolism) of an artery resulting in neurological damage. Symptoms include an increase in the muscle tone in the lower extremities, hyperreflexia, positive Babinski and a decrease in fine motor coordination. Patients experience marked discomfort radiating along a nerve path because of spinal pressure on the connecting nerve root. Seizure Brief partial seizure; no loss of Brief generalized seizure Multiple seizures despite Life-threatening; prolonged Death consciousness medical intervention repetitive seizures Definition: A disorder characterized by a sudden, involuntary skeletal muscular contractions of cerebral or brain stem origin. Syncope Fainting; orthostatic collapse Definition: A disorder characterized by spontaneous loss of consciousness caused by insufficient blood supply to the brain. Vasovagal reaction Present Life-threatening Death consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a sudden drop of the blood pressure, bradycardia, and peripheral vasodilation that may lead to loss of consciousness. Fetal growth retardation <10% percentile of weight for <5% percentile of weight for <1% percentile of weight for gestational age gestational age gestational age Definition: A disorder characterized by inhibition of fetal growth resulting in the inability of the fetus to achieve its potential weight. Premature delivery Delivery of a liveborn infant at Delivery of a liveborn infant at Delivery of a liveborn infant at Delivery of a liveborn infant at >34 to 37 weeks gestation >28 to 34 weeks gestation 24 to 28 weeks gestation 24 weeks of gestation or less Definition: A disorder characterized by delivery of a viable infant before the normal end of gestation. Typically, viability is achievable between the twentieth and thirty-seventh week of gestation. Psychiatric disorders Psychiatric disorders Grade Adverse Event 1 2 3 4 5 Agitation Mild mood alteration Moderate mood alteration Severe agitation; Life-threatening Death hospitalization not indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a state of restlessness associated with unpleasant feelings of irritability and tension. Anorgasmia Inability to achieve orgasm not Inability to achieve orgasm adversely affecting adversely affecting relationship relationship Definition: A disorder characterized by an inability to achieve orgasm. Delusions Moderate delusional Severe delusional symptoms; Life-threatening Death symptoms hospitalization not indicated consequences, threats of harm to self or others; hospitalization indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by false personal beliefs held contrary to reality, despite contradictory evidence and common sense. Insomnia Mild difficulty falling asleep, Moderate difficulty falling Severe difficulty in falling staying asleep or waking up asleep, staying asleep or asleep, staying asleep or early waking up early waking up early Definition: A disorder characterized by difficulty in falling asleep and/or remaining asleep. Libido decreased Decrease in sexual interest Decrease in sexual interest not adversely affecting adversely affecting relationship relationship Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in sexual desire. Libido increased Mild increase in sexual Moderate increase in sexual Severe increase in sexual interest not adversely interest adversely affecting interest leading to dangerous affecting relationship relationship behavior Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in sexual desire. Bladder perforation Extraperitoneal perforation, Intraperitoneal perforation; Life-threatening Death indwelling catheter indicated elective radiologic, consequences; organ failure; endoscopic or operative urgent operative intervention intervention indicated indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the bladder wall. Renal hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Analgesics and hematocrit Transfusion, radiation, or Life-threatening Death not indicated monitoring indicated hospitalization indicated; consequences; urgent elective radiologic, radiologic or operative endoscopic or operative intervention indicated intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the kidney. Urine discoloration Present Definition: A disorder characterized by a change in the color of the urine. Reproductive system and breast disorders Reproductive system and breast disorders Grade Adverse Event 1 2 3 4 5 Azoospermia Absence of sperm in ejaculate Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate complete absence of spermatozoa in the semen. Breast atrophy Minimal asymmetry; minimal Moderate asymmetry; Asymmetry >1/3 of breast atrophy moderate atrophy volume; severe atrophy Definition: A disorder characterized by underdevelopment of the breast. Fallopian tube stenosis Asymptomatic clinical or Symptomatic and intervention Severe symptoms; elective Life-threatening Death diagnostic observations only; not indicated operative intervention consequences; urgent intervention not indicated indicated operative intervention indicated. Feminization acquired Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; medical not indicated intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by the development of secondary female sex characteristics in males due to extrinsic factors. Hematosalpinx Minimal bleeding identified on Moderate bleeding; medical Severe bleeding; transfusion Life-threatening Death imaging study or laparoscopy; intervention indicated indicated; radiologic or consequences; urgent intervention not indicated endoscopic intervention operative intervention indicated indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of blood in a fallopian tube. Lactation disorder Mild changes in lactation, not Changes in lactation, significantly affecting significantly affecting breast production or expression of production or expression of breast milk breast milk Definition: A disorder characterized by disturbances of milk secretion. Menorrhagia Mild; iron supplements Moderate symptoms; medical Severe; transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death indicated intervention indicated. Buy generic meclizine line. SHINee - SCAR 샤이니 - 스카 Music Core 20090912.
A negative result does not rule out the presence of a mutation below the limits of detection of the assay medications given before surgery generic 25 mg meclizine free shipping. Learning Objectives As a result of this learning opportunity medicine effexor cheap meclizine 25mg online, you will be able to: 1 treatment conjunctivitis cheap meclizine. Explain the reasons for revision of our prior approaches to impairment assessment treatment zenker diverticulum buy cheap meclizine 25mg. Describe how to determine Diagnosis-Based Impairments, and make adjustments on the basis of the results of Functional History, Physical Examination, and Clinical Studies. Explain why methods used in previous editions (such as spinal range of motion assessment and strength determination) are no longer determinates. Demonstrate the ability to rate most commonly rated disorders, including spinal pain, upper limb disorders (hand, wrist, elbow, shoulders and entrapments), lower limb disorders (foot / ankle, knee and foot), nervous system disorders, and pain. Discuss challenges and opportunities associated with this evolution in impairment assessment. As a clinician with over thirty years experience, he has performed several thousand independent medical and impairment evaluations, providing him with excellent insight to the complexities of human potential, impairment, and disability. As a result of this experience, he has consulted for numerous organizations (including governmental jurisdictions). The Sixth Edition1, published in December 2007, introduces new approaches to rating impairment, using innovative methodology to enhance the relevancy of impairment ratings, improve internal consistency, promote greater precision and simplify the rating process. To appreciate the impact of the Sixth Edition, it is useful to understand the history and structure of the Guides, previous criticisms, and the new approaches used in the Sixth Edition. The Fourth Edition is still used for assessing workers compensation cases in Alabama, Arkansas, Kansas, Maine, Maryland, South Dakota, Texas, and West Virginia. The Fifth Edition is used in California, Delaware, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Iowa, Kentucky, Nevada, New Hampshire, North Dakota, Ohio, Vermont and Washington. The most recent edition is also expected to remain the standard for automobile casualty and personal injury cases, both domestically and internationally. Some of the countries abroad that use the Guides include Australia, Canada, Hong Kong, Korea, New Zealand, and South Africa. The Guides are often used to quantify the extent of injuries resulting from an automobile casualty or personal injury. Insurers may use an impairment rating as one of the factors in determining the reserve or settlement value of a claim. Insurers and attorneys may use this as factor considered in quantifying the impact of an injury and the associated case value. In some states, suits under no-fault automobile insurance are limited to cases where a specific defined impairment threshold has been met; in these states the Guides play an important role in providing numerical data to indicate that the threshold has indeed been met. The Guides impairment ratings are used in different ways, depending on the type of case and the jurisdiction. Although impairment is a different concept than disability, some jurisdictions use impairment as a proxy for the latter, while others use the impairment rating value in a formula that results in a disability rating. Still other jurisdictions are similar to motor vehicle insurers in using the impairment value as a threshold indicator for a more serious injury or illness. Challenges and Criticisms of Prior Editions There are many challenges associated with the use of the Guides, including criticisms of the Guides themselves, the use of impairment rating numbers, and a high error rate. Studies have demonstrated poor inter-rater reliability and revealed that many impairment ratings are incorrect, more often rated significantly higher than appropriate. Sixth Edition Approaches and Developmental Process the Guides defines the process for evaluating impairment. Clinical discussions among physician colleagues regarding potential severity of an illness or injury typically involve four basic points of consideration: 1) What is the problem (diagnosis)fi This framework, illustrated in Figure 2, is intended for describing and measuring health and disability at the individual and population levels. Functioning is an umbrella term encompassing all body functions, activities and participation; similarly, disability serves as an umbrella term for impairments, activity limitations or participation restrictions. Impairment, activity limitations and limitations in participation are not synonymous; an individual may have impairment and significant limitations in most activities but be able to participate in a specific life situation of relevance, have minor impairment and activity limitations with inability to participate in a specific life situation, or any permutation of these three factors. These grids use commonly accepted consensus-based criteria to classify most diagnoses relevant to a particular organ or body part into five classes of impairment severity ranging from Class 0, normal, to Class 5, very severe. The final impairment is determined by adjusting the initial impairment rating given by factors that may include physical findings, the results of clinical tests, and functional reports by the patient. The basic template of the diagnosis-based grid is common to each organ system and chapter; therefore although there is variation in the ancillary factors used to develop the impairment rating (depending on the body part), there is greater internal consistency between chapters than was seen formerly. This uniform diagnosis-based approach is a significant change from the anatomical approach that was the primary approach with many previous musculoskeletal assessments. However, there are similarities to other approaches used in the Fourth and Fifth Editions. For example, as mentioned previously, spinal impairment assessments have typically been based on the Diagnosis-Related Estimates Method, with specific findings or diagnoses used to assign the patient to a category. In the Fifth Edition the patient is assigned to one of five categories, with the first category having no ratable impairment and the other four categories having four possible impairment values. Likewise, although lower extremity impairments had been based on thirteen possible approaches in the Fifth Edition, the most commonly used approach is the Diagnosis-Based Estimates where specific impairment values are provided for diagnoses. For example, a patient with a partial medial meniscectomy is assigned 1% whole person permanent impairment. Rating systems previously used for the lower extremity likewise did not provide for adjustments based on functional difficulties, physical examination findings, or the results of clinical studies. The Preface to the Sixth Edition states that the features of the new edition include 22: fi A standardized approach across organ systems and chapters. The Sixth Edition reflects movement toward these features; however such change will not be immediately achieved. Thus it should be considered a step in the evolution of the Guides rather than as an end point in and of itself. The process was guided by an Editorial Panel and an Advisory Committee, and features an open, well-defined, and tiered, peer review process. The editorial process used an evidence-based foundation when possible, primarily as the basis for determining diagnostic criteria, and a Delphi panel approach to consensus building regarding the impairment ratings themselves. When there was not a compelling rationale to alter impairment ratings from what they had 7 The Section Editors led a group of 53 specialty-specific, expert contributors in developing the chapters and in conjunction with the Senior Contributing Editor wrote considerable portions of the revised chapters. The review process involved over 140 physicians, attorneys and other professionals. An Advisory Committee was developed to provide ongoing discussion of items of mutual concern and current issues in impairment and disability. Sixth Edition Structure the Sixth Edition is 634 pages in length and is comprised of 17 chapters; it is similar in length to the Fifth Edition (613 pages) and has one less chapter since the Cardiovascular System is now a single chapter. Chapter 1, Conceptual Foundations and Philosophy and Chapter 2, Practical Applications of the Guides define the overall approaches to assessing impairment.
If there is more than one pathology report for the same melanoma at initial diagnosis and different mitotic counts are documented medicine xanax generic meclizine 25 mg mastercard, code the highest mitotic count from any of the pathology reports medicine joint pain order meclizine in united states online. The Allred score combines the percentage of positive cells (proportion score) and the intensity score of the reaction product in most of the carcinoma medications knowledge buy cheap meclizine 25 mg on line. If there are no results prior to neoadjuvant treatment treatment receding gums buy discount meclizine 25mg on line, code the results from a post-treatment specimen. Code Description 0 Negative (Score 0) 1 Negative (Score 1+) 2 Equivocal (Score 2+) Stated as equivocal 3 Positive (Score 3+) Stated as positive 4 Stated as negative, but score not stated 7 Test ordered, results not in chart 8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case (If this item is required by your standard setter, use of code 8 will result in an edit error. Exception: If results from both an in situ specimen and an invasive component are given, record the results from the invasive specimen, even if the in situ is positive and the invasive specimen is negative. Note 8: If the test results are presented to the hundredth decimal, ignore the hundredth decimal. Note 7: If the test results are presented to the hundredth decimal, ignore the hundredth decimal. The Breast Cancer Index reports two scores: how likely the cancer is to recur 5 to 10 years after diagnosis and how likely a woman is to benefit from taking hormonal therapy for a total of 10 years. Coding Instructions and Codes Note 1: Physician statement of the Multigene Signature Method can be used to code this data item. Note 6: For Mammaprint, EndoPredict, and Breast Cancer Index, only record the risk level. The results may be used clinically to evaluate benefits of radiation therapy following surgery. Coding Instructions and Codes Note 1: Physician statement of Oncotype Dx Recurrence Score-Invasive score can be used to code this data item. Note 3: Record only the results of an Oncotype Dx-Invasive recurrence score in this data item. Coding Instructions and Codes Note 1: Physician statement of Oncotype Dx Risk Level-Invasive can be used to code this data item. Do not confuse intramammary nodes, which are within breast tissue and are included in level I, with internal mammary nodes, which are along the sternum. If no ipsilateral axillary nodes are examined, or if an ipsilateral axillary lymph node drainage area is removed but no lymph nodes are found, code X9. One data item collects the status (positive, negative, unknown) involvement of femoral-inguinal, para-aortic and pelvic lymph nodes. Note 2: Assign the highest applicable code (0-2) in the case of multiple assessments. Definition this data item records the appropriate description of involved regional lymph nodes, specifically whether they are unilateral or bilateral involvement. Code Description 0 Negative mediastinal and scalene lymph nodes 1 Positive mediastinal lymph nodes 2 Positive scalene lymph nodes 3 Positive mediastinal and scalene lymph nodes 8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case (If this item is required by your standard setter, use of code 8 will result in an edit error. Note 2: Record the number of positive para-aortic lymph nodes documented in the medical record. Note 2: Record the number of examined pelvic lymph nodes documented in the medical record. Note 3: Cytologic examination for malignant cells may be performed on ascites (fluid that has accumulated in the peritoneal cavity in excess amount) or the fluid (saline) that is introduced into the peritoneal cavity or pelvis, and then removed by suction. The introduction of fluid may be termed peritoneal or pelvic washing or peritoneal lavage. Code Description 0 Peritoneal cytology/washing negative for malignancy 1 Peritoneal cytology/washing atypical and/or suspicious 2 Peritoneal cytology/washing malignant (positive for malignancy) 3 Unsatisfactory/nondiagnostic 7 Test ordered, results not in chart 8 Not applicable: Information not collected for this case (If this item is required by your standard setter, use of code 8 will result in an edit error. The typical human reference ranges are 0 to less than or equal 35 units per milliliter (U/mL). Definition the amount of ovarian tumor and the location of tumor remaining in the patient after initial ovarian or peritoneal cancer surgery are the most important prognostic factors for advanced disease. The less tumor left behind, the more likely the patient will respond well to adjuvant chemotherapy. Information about residual tumor volume will be in the operative report; information about preoperative (neoadjuvant) chemotherapy will be elsewhere in the medical record or physician notes. Note 2: the surgery to remove as much cancer in the pelvis and/or abdomen as possible, reducing the "bulk" of the cancer, is called "debulking" or "cytoreductive" surgery. It is performed when there is widespread evidence of advanced stage of ovarian cancer with obvious spread to other organs outside the ovary, typically in the upper abdomen, intestines, the omentum (the fat pad suspended from the transverse colon like an apron), the diaphragm, or liver. Whether patients undergo neoadjuvant chemotherapy or primary cytoreduction, the best prognostic category after surgery includes those who are left with no gross residual tumor. This is mainly determined by physical examination and includes statements such as fixed or matted nodes. Although originally not intended to be a screening test, this relatively simple blood test has become a very common method of detecting new prostate cancer in its earliest stages. The pathologist assigns a grade to the most predominant pattern (largest surface area of involvement, more than 50% of tissue) and a grade for the secondary pattern (second most predominant) based on published Gleason criteria. When a patient undergoes radical prostatectomy, the pathologist may look for a third or tertiary pattern in the specimen. When Gleason pattern 5 is present as a tertiary pattern, its presence should be indicated in the pathology report, as a high Gleason pattern appears to be an indicator for worse outcome (shortened time to recurrence). A low Gleason score means the cancer tissue is similar to normal prostate tissue and the tumor is less likely to spread; a high Gleason score means the cancer tissue is very different from normal and the tumor is more likely to spread. Examples for Pathological Gleason Patterns and Score Examples Pattern Code Score Code Gleason 3+3 33 06 Gleason 4+3 43 07 Gleason 4 (Assume a number in the range 2-5 is a primary 49 X9 pattern and code unknown (9) in the second digit) Gleason 7 (Assume a number in the range 6-10 is a score) X6 07 Gleason 10 (only combination of values that equals 10 is 5+5) 55 10 No prostatectomy done X7 X7 Gleason not done, or unknown if done X9 X9 Tertiary Gleason Pattern Used to code information on the Gleason tertiary pattern from a prostatectomy. Note 3: Code the Gleason primary and secondary patterns prior to neoadjuvant treatment. Note 5: If different patterns are documented on multiple needle core biopsies, code the pattern that reflects the highest or most aggressive score regardless if the pathologist provides an overall pattern in a final summary. Coding Instructions and Codes Note 1: Physician statement of Gleason Score Clinical can be used to code this data item when there is no other information available. This data item represents the Gleason primary and secondary patterns from prostatectomy or autopsy. Note 2: Code the Gleason primary and secondary patterns from prostatectomy or autopsy only in this field. Gleason grading for prostate primaries is based on a 5-component system (5 histologic patterns). The primary pattern, the pattern occupying greater than 50% of the cancer, is usually indicated by the first number of the Gleason grade, and the secondary pattern is usually indicated by the second number. Note 5: Do not infer Gleason Primary and Secondary Pattern from Grade Group (Code X9). Note 2: Code the Gleason Score Pathological from prostatectomy or autopsy only in this field. These two numbers are added together to create a pattern score, ranging from 2 to 10. This data item represents the tertiary pattern value from prostatectomy or autopsy. A diagnostic procedure, such as a needle core biopsy, can take as many as 20 or more core biopsies to determine the extent of the cancer within the prostate. |