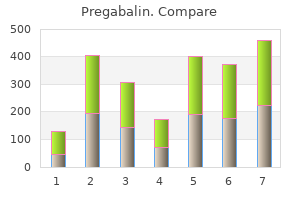
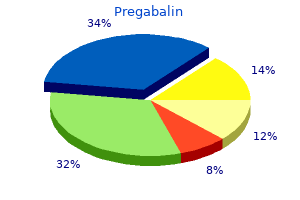
"Buy pregabalin 75mg mastercard, ". C. Rasul, M.A., M.D. Professor, George Washington University Medical School A high-flux membrane can be either high efficiency or low efficiency buy generic pregabalin 75mg online, depending on its surface area and discount 150mg pregabalin free shipping, to a lesser extent pregabalin 150 mg low price, its thickness buy pregabalin 150mg overnight delivery. In Greenberg A, editor: Primer on kidney diseases, ed 3, Philadelphia, 2001, National Kidney Foundation/Saunders, ch 47. In general, the relative contribution of convective transport to the overall clearance for small molecules, such as urea, is minor, but it is more substantial for larger molecules. Convection the simple equation for solute clearance does not take into account convective clearance of solutes. Convection refers to the mass transport of solutes along with the fluid it is dissolved in (plasma water) and is driven by the higher hydrostatic pressures in the blood compartment generated by the blood pump. The amount of solute removed by convection is not dependent on the concentration of the solute, but rather on the difference in hydrostatic pressure between the blood and dialysate compartment and the characteristic of the membrane, termed the "sieving coefficient. Because any solute removed from the blood compartment appears in the dialysate, another expression of solute clearance (K) that includes both convective and diffusive removal is based on the measurement of the concentration of that solute at the outlet of the dialysate; this is true for all solutes that are not already present in dialysate. The mass transfer coefficient is usually represented as KoA where A is the effective surface area of the specific dialyzer. B Glomerular capillary Basement membrane Bowman space Fluid reabsorption Renal tubule C Figure 58. Because of diffusive loss across the semipermeable hemodialysis membrane (dotted line), the plasma concentration in the blood outlet is much lower. The thin arrow across the dialysis membrane represents a small amount of fluid loss (which is not necessary for solute removal). A high dialysate flow rate is used to maintain the concentration gradient across the dialysis membrane for solute removal. Plasma concentrations of solutes in the blood compartment remain unchanged as blood travels the length of the fiber and are similar to their concentrations in the ultrafiltrate. The hemofiltration membrane (broken line) has relatively large pores, which allow the necessary removal of a large volume of fluid (heavy arrow). Replacement fluid is infused into the blood outlet to lower the plasma concentration of solutes and compensate for the fluid loss. Analogous to hemofiltration, plasma concentration of solutes remains unchanged throughout the length of the glomerular capillary and is similar to that in Bowman space. Fluid removal across the glomerular basement membrane (broken curve) is large (heavy arrow). Reabsorption of fluid from the renal tubules lowers the plasma concentration of the solutes. In Greenberg A, editor: Primer on kidney diseases, ed 4, Philadelphia, 2005, National Kidney Foundation, Saunders, ch 90. However, in the absence of fluid reabsorption mediated by the renal tubules in the native kidney, the hemofiltration technique relies on infusion of large amounts of fluids to replace the large convective fluid losses, generally middialyzer or at the outlet of the dialyzer. Because of the requirement of large volumes of sterile solutions to replace the ultrafiltrate, hemofiltration is not widely used for the treatment of chronic dialysis patients in the United States, and is commercially available only through one manufacturer in the United States. In this chapter, we will limit the detailed discussion to the hemodialysis procedure. Net Clearance solute (both diffusive and convective) and does not depend on the extent of partitioning of the solute between plasma water and red blood cells or on calculation of the sieving coefficient of the membrane, it is the more easily used and accurate measurement of solute clearance. Hemofiltration A technique that allows for the removal of solutes as well as plasma water primarily or solely by convection. In this technique, there is no dialysate flow, and the ultrafiltrate has the same composition as plasma water. This plateau is reached at different clearance values depending on the size of the solute and the specific membrane characteristics (porosity, thickness, surface charge, the chemical composition of the membrane, and so forth). The summative membrane characteristics are called the mass transfer coefficient (Ko). The mass transfer coefficient is specific for the membrane used and the solute being considered; for dialyzers, this is usually represented as KoA, where A is the effective surface area of the specific dialyzer. A 32-year-old man presents with a three-month history of arthralgias discount 75 mg pregabalin otc, weight loss buy discount pregabalin 75mg on line, diarrhea with fatty stools generic pregabalin 75mg on-line, and abdominal pain generic pregabalin 75mg with visa. After careful observation and testing, his physician obtains a biopsy of the lamina propria of the small intestine, which shows periodic acid-Schiff-positive material, particularly in macrophages. A pregnant woman comes to the physician for a check-up before the beginning of her third trimester. Fortunately, the infectious disease caused no morbidity to the fetus, and the resulting pregnancy is uncomplicated. A 75-year-old man comes to the physician because he recently began experiencing seizures. A 4-month-old girl who was born full-term presents to her pediatrician with an upper respiratory infection. Her mother notes that this is the fifth time her daughter has had an upper respiratory infection since birth. This child is presenting with a syndrome that is due to aberrant development of which of the following embryonic structures Full-length exams (A) Glioblastoma multiforme (B) Medulloblastoma (C) Meningioma (D) Neurilemmoma (E) Oligodendroglioma 45. A 19-year-old college student developed sore throat, palatal petechiae, splenomegaly, fever, and generalized lymphadenopathy after she began dating her first serious boyfriend. The symptoms were self-limiting and lasted approx- test Block 6 Test Block 6 Questions 681 47. A 91-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his daughter after being found unresponsive in his home. What is the expected hemodynamic pattern in this patient in terms of peripheral vascular resistance, cardiac output, and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure A 67-year-old man presents to the emergency department with diaphoresis and crushing chest pain that radiates down his left arm. He is taken to the cardiac catheterization unit, where he is diagnosed with an obstructive myocardial infarction due to occlusion of the right coronary artery. A duodenal ulcer can be caused by hypersecretion of stomach acid, Helicobacter pylori infection, or the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Initial treatment of a duodenal ulcer involves a trial of a histamine2 (H2)-blocker such as cimetidine or a proton pump inhibitor such as omeprazole. By inhibiting the H2-receptor, gastric acid secretion is decreased, allowing the ulcer to heal. If a biopsy of the ulcer is positive for H pylori, appropriate treatment involves "triple therapy," commonly involving clarithromycin 500 mg twice a day, amoxicillin 1 g twice a day, and a proton pump inhibitor twice a day for 10-14 days. Gastrin causes an increase in gastric acid secretion, and whereas blockade of gastrin receptors (cholecystokinin B) would decrease gastric acid production slightly, alternative receptors would continue to stimulate gastric acid secretion. Acetylcholine is released by cholinergic neurons in the enteric nervous system, resulting in contraction of smooth muscle, relaxation of sphincters, increase in gastric secretion, and increase in pancreatic secretion. Blockade of the muscarinic3receptor would not lead to a significant decrease in acid production, which is necessary for this patient. Norepinephrine is released from adrenergic neurons in the enteric nervous system, resulting in relaxation of smooth muscle, contraction of sphincters, and increase in salivary secretion. Secretin increases pancreatic and biliary bicarbonate secretion, and decreases gastric acid secretion. Blockade of secretin receptors potentially could increase the amount of acid produced as a result of loss of feedback inhibition. Left lateral gaze requires contraction of the left lateral rectus, not the left medial rectus. To assess the function of the left medial rectus, the examiner should instruct the patient to attempt right lateral gaze. Palsy of the left medial rectus with attempted right lateral gaze would result from a lesion affecting the left medial longitudinal fasciculus. Right lateral gaze requires contraction of the right lateral rectus, not the right medial rectus. To assess the function of the right medial rectus, the examiner should instruct the patient to attempt left lateral gaze. Based on the physical exam findings, the patient is likely experiencing congestive heart failure. Given his young age and lack of risk factors, a myocarditis should be high on the differential.
Congenital bronchiectasis Cystic fibrosis Hereditary immune deficiency diseases Immotile cilia syndrome Atopic bronchial asthma buy pregabalin 150mg lowest price. Obstruction Post-obstructive bronchiectasis pregabalin 150mg, unlike the congenitalhereditary forms buy pregabalin 150mg low price, is of the localised variety discount 75 mg pregabalin amex, usually confined to one part of the bronchial system. The causes of endobronchial obstruction include foreign bodies, endobronchial tumours, compression by enlarged hilar lymph nodes and post-inflammatory scarring. As secondary complication Necrotising pneumonias such as in staphylococcal suppurative pneumonia and tuberculosis may develop bronchiectasis as a complication. The dilated airways, depending upon their gross or bronchographic appearance, have been subclassified into the following different types: i) Cylindrical ii) Fusiform iii) Saccular iv) Varicose Cut surface of the affected lobes, generally the lower zones, shows characteristic honey-combed appearance. The bronchi are extensively dilated nearly to the pleura, their walls are thickened and the lumina are filled with mucus or mucopus. M/E Main findings are as under: i) the bronchial epithelium may be normal, ulcerated or may show squamous metaplasia. Late complications occurring in cases uncontrolled for years include development of clubbing of the fingers, metastatic abscesses (often to the brain), amyloidosis and cor pulmonale. These include viral infection (frequently adenovirus and respiratory syncytial virus), bacterial infection, fungal infection, inhalation of toxic gases. The bronchiolar walls are inflamed and are infiltrated by lymphocytes and plasma cells. There are changes of interstitial pneumonitis and fibrosis in the alveoli around the affected bronchioles. Restriction due to chest wall disorder Kyphoscoliosis Poliomyelitis Severe obesity Pleural diseases. Some dusts are inert and cause no reaction and no damage at all, while others cause immunologic damage and predispose to tuberculosis or to neoplasia. The factors which determine the extent of damage caused by inhaled dusts are as under: 1. The tissue response to inhaled dust may be one of the following three types: Fibrous nodules. A number of predisposing factors have been implicated in this transformation as follows: 1. Activation of alveolar macrophage plays the most significant role in the pathogenesis of progressive massive fibrosis by release of various mediators. There is some increase in the network of reticulin and collagen in the coal macules. They are usually bilateral and located more often in the upper parts of the lungs posteriorly. Sometimes, these masses break down centrally due to ischaemic necrosis or due to tuberculosis forming cavities filled with black semifluid resembling India ink. The fibrous lesions are composed almost entirely of dense collagen and carbon pigment. The wall of respiratory bronchioles and pulmonary vessels included in the massive scars are thickened and their lumina obliterated. There is scanty inflammatory infiltrate of lymphocytes and plasma cells around the areas of massive scars. G/A the lungs have rounded, firm nodules with central necrosis, cavitation or calcification. M/E the lung lesions are modified rheumatoid nodules with central zone of dust-laden fibrinoid necrosis enclosed by palisading fibroblasts and mononuclear cells. Progressive massive fibrosis is, however, a serious disabling condition manifested by progressive dyspnoea and chronic cough with jet-black sputum. More advanced cases develop pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular hypertrophy (cor pulmonale). Silicosis is caused by prolonged inhalation of silicon dioxide, commonly called silica. Therefore, a number of occupations engaged in silceous rocks or sand and products manufactured from them are at increased risk.
Emotional adjustment Adjusting to a diagnosis of epilepsy involves living with unpredictability buy generic pregabalin 75 mg online. Responses Establish good communication between health cheap pregabalin 150 mg mastercard, education cheap 150 mg pregabalin otc, and the family order pregabalin 75mg visa. In and around water A child with poorly controlled seizures should be accompanied at all times in and around water. They are currently very restrictive (arguably excessively so) and require an individual to have been seizure-free off medication for 5 yrs. Cycling A child with poorly controlled seizures should cycle away from traffic under supervision. Alcohol Excessive alcohol can cause seizures particularly in juvenile myoclonic and other primary generalized epilepsies. The at-risk period for the foetus is early, quite possibly before pregnancy will have been recognized. The effect may be dose dependent, so reducing dose, rather than discontinuing drug may be an option. Death in epilepsy Epilepsy-related death in a child may be due to: Complication of seizure. Risk factors for epilepsy related death: Epilepsy with onset in the first 12 mths of life. Tentative explanations include primary or secondary cardiac arrhythmias and/or a primary respiratory dysfunction. It is clear that the very large majority of paediatric epilepsy-related deaths are in children with significant associated neurodisability: in this group there is likely to be greater prior recognition of the presence of a life-limiting situation. Concise factual data to inform but not frighten families is a constructive approach. If appropriate comparative realistic rates of other causes of death in children and in the general population may bring things into perspective. Hazards of a false-positive diagnosis of epilepsy include exposure to unnecessary investigations, but more particularly treatment failure. It is important to be familiar with the wide range of non-epileptic processes that can give rise to paroxysmal or episodic signs or symptoms. Episodes without prominent alteration of awareness the following conditions are arranged in approximate order by the age at which they are most commonly seen. Benign neonatal sleep myoclonus A healthy infant presents at a few weeks of age with quite dramatic myoclonic movements confined entirely to sleep. The jerks, which can be quite violent, typically occur in flurries and migrate, involving first one limb and then another in clusters of a few per second. The child is not woken or distressed by the episodes and the abnormal movements do not involve the face. No treatment is required: the phenomenon stops automatically, usually within a few months and there are no long-term neurodevelopmental implications. Shuddering spells this is a common, under-recognized variant of normal infant behaviour. Presenting the child with an interesting or novel object such as a toy (or dinner! The child typically holds his or her arms out and shows an involuntary shiver or shudder sometimes involving most of the body. Hyperekplexia this is a rare differential of neonatal seizures in its severe form. Typically due to mutations in glycine receptor genes, with failure of inhibitory neurotransmission, it causes a marked susceptibility to startle. Sudden sounds, and particularly being touched or handled, precipitate episodes of severe total body stiffening. The spells (and apnoea) can be terminated by forcibly flexing the neck: a manoeuvre family and carers should be taught. Event severity tends to lessen with time and so long as hypoxic complications are prevented, prognosis is good. Paroxysmal tonic upgaze of infancy this involves prolonged episodes lasting hours at a time of sustained or intermittent upward tonic gaze deviation, with down-beating nystagmus on down gaze. |