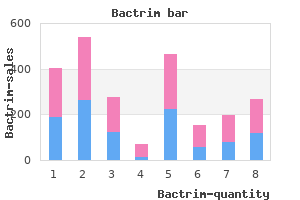
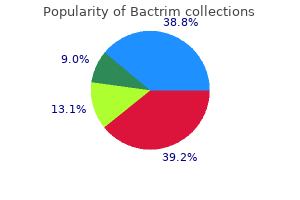
Anne L. S. Sullivan, MD
Successful multi-intervention treatment of severe obesity: a 7-year prospective study with 96% follow-up infection japanese horror order bactrim 960 mg. Bariatric Surgery and the Risk of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Swedish Obese Subjects antibiotic resistance powerpoint order bactrim on line amex. Long-term effects of gastric surgery for treating respiratory insufficiency of obesity antibiotic resistance case study purchase generic bactrim from india. Comparative long-term mortality after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding versus nonsurgical controls antibiotics for dogs diarrhea buy bactrim 480 mg with mastercard. Maryon Davis A & Press V on behalf of the Cardiovascular Health Working Group of the Faculty of Public Health. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: a systematic review and meta-analysis. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol as a predictor of coronary heart disease risk. Triglycerides and the risk of coronary heart disease: 10,158 incident cases among 262,525 participants in 29 Western prospective studies. Nonfasting triglycerides and risk of myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, and death in men and women. Safety of anacetrapib in patients with or at high risk for coronary heart disease. Gemfibrozil for the secondary prevention of coronary heart disease in men with low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Veterans Affairs High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Intervention Trial Study Group. Effect of intensive compared with moderate lipid-lowering therapy on progression of coronary atherosclerosis: a randomized controlled trial. Fasting is not routinely required for determination of a lipid profile: clinical and laboratory implications including flagging at desirable concentration cut-points-a joint consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society and European Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine. Prevalence of and Trends in Diabetes Among Adults in the United States, 1988-2012. Prevalence of Abnormal Glucose Tolerance and Risk Factors in Urban and Rural Malaysia. Relation between blood glucose and coronary mortality over 33 years in the Whitehall Study. Reduction in the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes with Lifestyle Intervention or Metformin. The long-term effect of lifestyle interventions to prevent diabetes in the China Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Study: a 20-year follow-up study. Effect of rosiglitazone on the frequency of diabetes in patients with impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose: a randomised controlled trial. DiabCare 2013: A cross-sectional study of hospital based diabetes care delivery and prevention of diabetes related complications in Malaysia. Mortality and morbidity during a five-year follow-up of diabetics with myocardial infarction. Acute myocardial infarction in the diabetic patient: pathophysiology, clinical course and prognosis. Low-dose aspirin for primary prevention of atherosclerotic events in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Association Between Severe Hypoglycemia, Adverse Macrovascular Events, and Inflammation in the Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study. Severe Hypoglycemia and Mortality After Cardiovascular Events for Type 1 Diabetic Patients in Sweden. Intensive Blood Glucose Control and Vascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Aspirin for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U. Aspirin in the primary and secondary prevention of vascular disease: collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. Analysis of risk of bleeding complications after different doses of aspirin in 192,036 patients enrolled in 31 randomized controlled trials. Clopidogrel and aspirin versus aspirin alone for the prevention of atherothrombotic events. Clopidogrel plus aspirin versus aspirin alone for preventing cardiovascular disease. Collaborative meta-analysis of randomised trials of antiplatelet therapy for prevention of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke in high risk patients. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Incidence of early left ventricular thrombus after acute anterior wall myocardial infarction in the primary coronary intervention era. Frequency of left ventricular thrombus in patients with anterior wall acute myocardial infarction treated with percutaneous coronary intervention and dual antiplatelet therapy. Embolic potential, prevention and management of mural thrombus complicating anterior myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis. Assessing the Impact of Medication Adherence on Long-Term Cardiovascular Outcomes. Interventions to enhance medication adherence in chronic medical conditions: a systematic review. Medication adherence among hypertensive patients of primary health clinics in Malaysia. Elevated Blood Pressure Among Patients with Hypertension in General Hospital or Penang, Malaysia: Does Poor Adherence Matter? Adherence to drugs that prevent cardiovascular disease: meta-analysis on 376,162 patients. Identifying psychosocial predictors of medication non-adherence following acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Interventions for improving adherence to treatment in patients with high blood pressure in ambulatory settings. Interventions used to improve control of blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Impact of pharmacist care in the management of cardiovascular disease risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Global action plan for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases: 2013-2020. Chronic disease prevention: health effects and financial costs of strategies to reduce salt intake and control tobacco use. Sodium intake among normotensive health staff assessed by 24-hour urinary excretion: a cross-sectional study. A handbook of Traditional and Complementary Medicine Programme in Malaysia [Internet]. The use of complementary and alternative medicine by people with cardiovascular disease: a systematic review. The gap between knowledge and perception on education in traditional and complementary medicine among medical staff in Malaysia. Acupuncture for Essential Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Sham-Controlled Clinical Trials. Complementary and Alternative Medicine and Cardiovascular Disease: An Evidence-Based Review. Mind-body practices for patients with cardiac disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. State of complementary and alternative medicine in cardiovascular, lung, and blood research: executive summary of a workshop. Herbal medicine for the treatment of cardiovascular disease: clinical considerations. Ginkgo biloba for preventing cognitive decline in older adults: a randomized trial. Reduction of Fasting Blood Glucose and Hemoglobin A1c Using Oral Aloe Vera: A Meta-Analysis. Urothelial carcinoma associated with the use of a Chinese herb (Aristolochia fangchi). Their presence is correlated with age but not with an iridodialysis antimicrobial prophylaxis discount bactrim american express, a dark crescent showing at the root of the the number of cafe-au-lait spots antibiotics for uti gonorrhea buy 480mg bactrim fast delivery, the number of neurof iris; that it is not an iridodialysis is shown by the fact that bromata or the severity of the disease bible black infection generic bactrim 960 mg otc. They are bilateral virus removal programs order bactrim paypal, no red refex can be obtained through it on illuminating multiple, well defned, dome-shaped gelatinous elevations with the ophthalmoscope and from the absence of a history protruding above the iris surface and ranging from clear to of a blow. They are pathognomonic of be yellowish, but vessels will usually be visible upon the neurofbromatosis. The patient had a slowly enlarging choroidal tumour, followed over a 9-year period. Occasionally it takes on a ring or annular distribu tion, extensively infltrating the ciliary region. Pathology Malignant melanoma of the ciliary body is less common this arises from the outer layers of the choroid. It forms at than that of the choroid; the treatment and prognosis are frst a lens-shaped mass, raising the retina over it. Rarely, opening and the retinal pigment epithelium to form a Chapter | 23 Intraocular Tumours 375 globular mass in the subretinal space, separated from the appearance; most tumours are mixed-celled. The neurosensory melanomas can be classifed by cell type as: retina remains in contact with the tumour at the summit, but 1. Spindle A?predominance of slender spindles with is detached from the choroid at the sides, the intervening flattened nucleus and no nucleolus space being flled with exudative fuid. Spindle B?predominance of larger spindles with round/ in any location, and the fuid may sink down to the lowest oval nucleus and prominent nucleolus part of the eye, forming a detachment isolated from that 3. Epithelioid?large cells with nuclei that are round and over the tumour, but with continuing growth the retina eccentric. There is a high mitotic figure count; and becomes more and more detached, until no part remains 4. The tumour may fll the globe before Silver staining reveals a variable amount of argyrophil perforating the sclera, or this may occur relatively early reticulin fbres, generally more numerous in spindle along the perivascular spaces of the vortex veins or ciliary celled sarcomata. Epithelioid tumours are lymph nodes are not commonly affected, but metastases the most malignant. Flat malignant melanoma of the choroid: In rare cases Clinical Features the choroid becomes widely infltrated so that a uniform In adults, choroidal melanoma is the commonest intraocular thickening results, with a shallow detachment of the retina. The tumour usually occurs in adults of the cells are usually spindle shaped; they may also between 40 and 60 years of age. It is less common in those be cylindrical or palisade-like, arranged in columns or of African or Asian origin as compared to Caucasians. It is around blood vessels, or even resemble endothelial cells in always primary, single and unilateral. B-scan ultrasonography demonstrating a nodular extrascleral extension along the base of a relatively flat intraocular tumour (a, arrows). The extrascleral extension of the tumour should be differentiated from the extraocular muscles, which have flat configuration and appear to separate from the sclera when traced posteriorly corresponding to the normal anatomic location of the muscle (b, arrows). The growth is usually pigmented but is occasionally growth, is also usually situated near the disc. The pigment is chiefy melanin, but haematogenous pig the differential diagnosis also includes posterior scleritis mentation occurs after haemorrhages. The surface may have which may be diffcult to distinguish from a malignant a mottled orange and black appearance (Fig. Peripherally located tumours usually attain a consider able size, and cause a retinal detachment before the patient Diagnosis becomes symptomatic. The patient may also seek relief from Investigations for the diagnosis of choroidal melanoma in the pain of glaucoma. It is of the utmost importance that the clude B-scan ultrasonography, radio-isotope uptake studies, cause of a detachment of the retina should be identifed in all especially when the media are opaque, and fuorescein cases. A simple detachment shows numerous folds and ing retinal detachment and provides details of any underly undulations can be seen to travel over the surface when the ing tumour mass. Patches of pigment upon the rounded part support the A-scan through the mass will show rapid attenuation and diagnosis of a tumour, but pigmentary disturbance, more a large angle k. Ultrasonographic measurements of the particularly at the periphery, is not uncommon in a simple dimensions of the tumour, particularly the height or thick detachment. Commonly an orange pigment, lipofuscin, is ness and maximum horizontal diameter, are helpful in deposited on the surface of the tumour. The range of b-rays is small, about 2?3 mm sels can be made out between the latter; this is the most on an average with a maximum of 7?8 mm, and this restric positive evidence of a growth, but it is only occasionally tion makes the technique of the measurement of 32P uptake seen. A solid-state detector is capable of distinguishing or upper part of the globe is almost certain to be due to a clearly between the majority of benign and malignant intra tumour of the choroid. Most malignant tumours show uptakes in lumination will afford assistance in diagnosis; a simple excess of 80% of controlled values, a level which is not detachment is transparent, a choroidal growth opaque. Gallium-67 cause of the glaucoma in some cases is the forward movement (67Ga) is another radio-active material that is injected into of the lens and iris due to posterior pressure, so that the angle the bloodstream and picked up by rapidly dividing cells, of the anterior chamber becomes blocked and a sudden rise in and is more sensitive in the diagnosis of these tumours. Alternatively, the trabecular meshwork Fluorescein angiography in choroidal malignant mela may be infltrated with neoplastic cells. In other cases, particu nomata in conjunction with the clinical examination may larly those of early onset, obstruction to the venous outfow provide suffcient evidence for a correct diagnosis. A double from the eye is a possible explanation, the tumour being, in circulation, with an increased fuorescence in the mass, is some instances, so situated as to press upon a vortex vein. Initially one can see In the differential diagnosis, two other tumours must be the flling of abnormal vessels in the tumour during the cho kept in mind, particularly in the early stages. Overlying this, the naevus appears as a bluish patch with somewhat feathered retinal vasculature can be visualized. The abnormal circula edges, usually about the size of the optic disc and situated tion is better delineated by indocyanine green angiography. It is congenital and symp the fuorescein angiographic fndings of lesions in the dif tomless but like naevi elsewhere, may occasionally assume ferential diagnosis may have certain distinguishing features. Metastatic tumours tend to produce poor no evidence of scleral involvement, conservative manage fuorescence in the early phase but are probably indistin ment is recommended. However, death usually occurs Treatment within a year of the detection of metastasis. The tumour is generally very slow grow ing and conservative management is advocated especially if Metastasis to the choroid occurs primarily in cases of carci the tumour is small less than 2 mm in size, or if no altera nomas, particularly of the breast and alimentary tract, but tion in size can be demonstrated. The patient may as an increase in size or occurrence of a retinal detachment complain of a diminution of vision, and ophthalmoscopic ensue, or if sight is threatened, therapy should be instituted. The disease is nearly tumour, with the goal of maintaining vision and ultimately, always bilateral, and as it is frequently only one of many if all else fails, a cosmetically acceptable globe. These metastases, however, are radiosensitive and palladium 103, gold, cobalt-60 (60Co) or iodine-125 (125I). The treatment by radiation often provides suffcient improve plaques are surgically placed externally on the sclera over the ment to maintain some vision and prevent the occurrence tumour and removed 3?7 days later, causing tumour regression of pain while the patient survives. External beam radiation, cryotherapy or dependent and respond to ovariectomy or cytotoxic drugs. Medium-sized Reticulum Cell Sarcoma tumours 10?15 mm in diameter and 3?5 mm in height can also be treated by plaque or external proton beam radiation. The malignant cell of reticulum cell sarcoma resembles a Enucleation is an option that is not frequently used today, but histiocyte. It originates usually within the reticuloendothelial must be considered in larger tumours. Orbital spread of the system, but less commonly in the central nervous system, malignant melanoma necessitates exenteration but metastasis where the neoplasm is referred to as a microglioma. Thus, deaths from second elsewhere, the site is usually the central nervous system. They complain of decreased visual If the patient can see well with the affected eye and there is acuity with foaters or photopsiae. There may be a mild the growth consists chiefy of small round cells with large anterior segment reaction resembling a non-granulomatous nuclei resembling the cells of the nuclear layers of the iritis with or without keratic precipitates. Many of these stain poorly, showing that they are In some cases, lesions of the fundus resemble retinal or undergoing necrosis (Fig. Cheap bactrim 960mg without prescription. Antimicrobial Resistance Final Lecture.
The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the develop and progression of long term complications in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus antibiotics that cover mrsa purchase bactrim without prescription. Progression of retinopathy with intensive versus conventional treatment in the Diabetes Control and Complication Trial spironolactone versus antibiotics for acne cheap generic bactrim uk. The effect of intensive diabetes treatment on the progression of diabetic retinopathy in insulindependent diabetes mellitus antibiotic quadrant buy 480 mg bactrim with amex. Approval: 2011 Monitor blood pressure antimicrobial quaternary ammonium salts generic bactrim 480 mg without prescription, serum potassium and symptoms of fuid retention at least monthly. If clinically indicated, perform appropriate tests to Hepatotoxicity confirm the diagnosis of adrenocortical insufficiency. For patients who hepatic toxicity, including fulminant hepatitis, acute liver failure and deaths [see resume treatment, monitor serum transaminases and bilirubin at a minimum of Adverse Reactions (6. In patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment elevation [see Warnings and Precautions (5. The study was unblinded early based on an Independent Data Monitoring Committee recommendation. Increased Fractures and Mortality in Combination with Radium Ra 223 Dichloride [see Warnings and Precautions (5. Placebos were administered to patients in the 3 Includes terms Muscle spasms, Musculoskeletal pain, Myalgia, Musculoskeletal control arm. Additionally, two other randomized, placebo-controlled trials were discomfort, and Musculoskeletal stiffness. The safety data pooled from 2230 4 Includes terms Edema, Edema peripheral, Pitting edema, and Generalized edema. Laboratory Abnormality (%) (%) (%) (%) Deaths associated with treatment-emergent adverse events were reported for 7. Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. Hepatobiliary Disorders: fulminant hepatitis, including acute hepatic failure and death. In patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh 1,000 mg daily and prednisone 5 mg twice daily. Findings included embryo-fetal lethality (increased post implantation loss and resorptions and decreased number of live fetuses), fetal developmental delay (skeletal effects) and urogenital effects (bilateral ureter dilation) at doses? Other reported clinical experience has not andro stenedione, respectively, by C17, 20 lyase activity. In clinical studies, abiraterone acetate plasma concentrations were Patients with Renal Impairment below detectable levels (<0. Systemic exposure to abiraterone after a single oral 1,000 mg dose did abiraterone acetate. No major deviation from dose proportionality was observed in the In vitro studies with human hepatic microsomes showed that abiraterone has the dose range of 250 mg to 1,000 mg. The tablets should be swallowed whole with water pioglitazone was increased by 46% when pioglitazone was given together with [see Dosage and Administration (2. There are no clinical data available to confirm Abiraterone is highly bound (>99%) to the human plasma proteins, albumin and transporter based interaction. A two-year carcinogenicity study was conducted in rats at oral abiraterone Metabolism acetate doses of 5, 15, and 50 mg/kg/day for males and 15, 50, and 150 mg/kg/day Following oral administration of 14C-abiraterone acetate as capsules, abiraterone for females. Abiraterone acetate increased the combined incidence of interstitial acetate is hydrolyzed to abiraterone (active metabolite). The conversion is likely cell adenomas and carcinomas in the testes at all dose levels tested. The two main circulating metabolites of abiraterone in human plasma are regarded as more sensitive than humans to developing interstitial cell tumors are abiraterone sulphate (inactive) and N-oxide abiraterone sulphate (inactive), in the testes. Abiraterone acetate was not carcinogenic in female rats at which account for about 43% of exposure each. Following oral administration of primary human lymphocytes or an in vivo rat micronucleus assay. These effects were observed in rats at systemic exposures similar to (N=797) (N=398) humans and in monkeys at exposures approximately 0. Primary Survival Analysis In a fertility study in male rats, reduced organ weights of the reproductive Deaths (%) 333 (42%) 219 (55%) system, sperm counts, sperm motility, altered sperm morphology and decreased fertility were observed in animals dosed for 4 weeks at? Updated Survival Analysis In a fertility study in female rats, animals dosed orally for 2 weeks until day 7 of Deaths (%) 501 (63%) 274 (69%) pregnancy at? In 13 and 26-week studies in rats and 13 and 39-week studies in monkeys, a 2 Hazard Ratio is derived from a stratifed proportional hazards model. The changes in the reproductive organs are consistent with the antiandrogenic pharmacological activity of abiraterone acetate. Patients with prior ketoconazole treatment for prostate cancer and a history of adrenal gland or pituitary disorders were excluded from these trials. Both arms were given concomitant prednisone 5 mg twice the following patient demographics and baseline disease characteristics were daily. Patients continued treatment until radiographic or clinical (cytotoxic balanced between the treatment arms. The median age was 69 years (range chemotherapy, radiation or surgical treatment for cancer, pain requiring chronic 39-95) and the racial distribution was 93% Caucasian, 3. Patients with moderate or severe pain, performance status score of 0-1 and 45% had a Brief Pain Inventory-Short Form opiate use for cancer pain, or visceral organ metastases were excluded. The median percent of patients had metastases in bone and 30% had visceral involvement. Seventy percent of patients had previously status was 0 for 76% of patients, and 1 for 24% of patients. Co-primary effcacy received one cytotoxic chemotherapy regimen and 30% received two regimens. An updated survival analysis was Radiographic progression-free survival was assessed with the use of sequential conducted when 775 deaths (97% of the planned number of deaths for fnal imaging studies and was defned by bone scan identifcation of 2 or more new analysis) were observed. Results from this analysis were consistent with those bone lesions with confrmation (Prostate Cancer Working Group 2 criteria) from the interim analysis (Table 7). High-risk disease was defned as having at least two of three risk factors at baseline: a total Gleason score of? Patients continued treatment until radiographic or clinical disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, withdrawal or death. Baseline pain assessment was 0-1 (asymptomatic) in 50% of groups was observed (Table 9 and Figure 3). Advise patients that Overall Survival1 their blood pressure, serum potassium and signs and symptoms of fluid retention will be monitored clinically at least monthly. Advise patients to adhere Deaths (%) 169 (28%) 237 (39%) to corticosteroids and to report symptoms of hypertension, hypokalemia, or Median survival (months) edema to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5. Advise patients to report symptoms of adrenocortical insufficiency to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5. Inform patients to speak with their healthcare provider 3 Hazard Ratio is derived from a stratifed proportional hazards model. Instruct patients to swallow tablets whole with water and not to crush or chew the tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2. If more than one daily dose is skipped, inform patients to contact their healthcare provider [see Dosage and Administration (2. The median time to initiation of chemotherapy was crushed, or damaged without protection. Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take or treatments you receive, including prescription and over-the counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Keep a list of them with you to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. Tell your healthcare provider if you get any of the following symptoms: dizziness confusion fast or irregular heartbeats muscle weakness feel faint or lightheaded pain in your legs headache swelling in your legs or feet. Adrenal problems may happen if you stop taking prednisone, get an infection, or are under stress.
Menck (Hunter syndrome): a clinical review and recommendations for treatment in the era of enzyme replacement therapy antibiotics rabbits generic bactrim 960 mg mastercard. Eur License information: this is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License antibiotics for dogs safe for humans purchase generic bactrim on line, which permits unrestricted use antibiotics sinus infection npr order bactrim 480 mg with amex, distribution virus yugioh cheap 480 mg bactrim overnight delivery, and J Pediatr 167:267-277. It was started with the express purpose of offering practical clinical solutions for therapists with an interest in neuromusculoskeletal problems. The emphasis is on clinical neurodynamics for neuromusculoskeletal problems in a way which clari? Objectives Offer practical clinical solutions for therapists who treat patients with musculoskeletal problems with a neural component Include the most up-to-date research and clinical information Offer a systematic method of application of neurodynamics Foster further development in clinical neurodynamics Resources Free registration Web site neurodynamicsolutions. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior permission of the author. All illustrations, except where acknowledged otherwise, are copyrighted to Elsevier Health, Oxford, United Kingdom. During his undergraduate training, he quickly developed an interest in manual therapy and has pursued this interest throughout his career. He worked in public hospitals and private practices for several years in New Zealand before traveling to Adelaide, South Australia in 1985, to take part in post-graduate study. In 1989, he completed a Graduate Diploma in Advanced Manipulative Therapy at the University of South Australia and converted this to a Master of Applied Science in 1993. He has taught internationally for over 20 years and has given numerous keynote and invited presentations around the world. His Masters thesis was on the effect of order of movement on the peroneal neurodynamic test, in which he discovered the concept of neurodynamic sequencing. Since then he has studied neural mechanics and pain physiology, performing research and writing a number of publications on the subject. Michael edited the book Moving in on Pain and has featured as an invited contributor for various journals such as Manual Therapy, New Zealand Journal of Physiotherapy and the Australian Journal of Physiotherapy. His most recent publication is the book, Biomechanics of the Nervous System: Breig revisited. Physiotherapy 81: 9-16 Shacklock M 1995 Moving in on Pain, Butterworth-Heinemann, Sydney Shacklock M 1996 Positive upper limb tension test is a case of surgically proven neuropathy: analysis and validity. Manual Therapy 1: 154-161 Shacklock M 1999a Central pain mechanisms; a new horizon in manual therapy. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy 45: 83-92 Shacklock M 1999b the clinical application of central pain mechanisms in manual therapy. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy 45: 215-221 Shacklock M 2000 Balanced on a tight rope between low back pain and evidence-based practice. New Zealand Journal of Physiotherapy 28 (3): 22-27 Shacklock M 2005a Clinical Neurodynamics: a new system of musculoskeletal treatment, Elsevier, Oxford Shacklock M 2007 Biomechanics of the Nervous System: Breig revisited. Neurodynamic Solutions, Adelaide Rade M, Kononen M, Vanninen R, Marttila J, Shacklock M, Kankaanpaa M, Airaksinen O 2014 young investigator award winner: In vivo magnetic resonance imaging measurement of spinal cord displacement in the thoracolumbar region of asymptomatic subjects: part 1: straight leg raise test. Spine 2014 39 (16): 1288-1293 2014 Young Investigator Award Winner: In vivo magnetic resonance imaging measurement of spinal cord displacement in the thoracolumbar region of asymptomatic subjects: part 2: comparison between unilateral and bilateral straight leg raise tests. Key problems with neural tension treatments in the past have been the risk of provocation of symptoms, the method of diagnosis and treatment has been unclear and there has not been a systematic and methodical approach to diagnosis and selection and progression of treatment techniques. It is recommended that participants decline to have any manoeuvres performed on them if the participant may react with undue pain or suffering, have a condition which might in? Participants are under no obligation to have a manoeuvre performed on them and may freely decline. Move the Innervated tissues Other nerves: ulnar median motor branch (median) digital axillary musculocutaneous 20 Ways to Load the Nervous System 3. Sliders the nerves slide toward the site where force (elongation) is initiated down the tension gradient * Distal slider Proximal slider 37 3. Section 3 Technique Selection 2 Planning Examination and Treatment How extensive should it be? General Points Confusion exists about how to select examination and treatment techniques? There is a spectrum of patient problems ranging from the very sensitive to the athletic which systematic treatment can take into account? Below is a three tier system of deciding on the extent of the examination in the planning of neurodynamic testing. Naturally, not all criteria will occur simultaneously in the same patient and it is the role of the practitioner to choose the most appropriate elements in deciding on the extent of the examination. Previously this has not been the case because, in the presence of risk factors, therapists have generally neglected the neural component. Indications When pain that is easily provoked and takes a long time to settle after movement. Severe pain is present, a complete neurodynamic assessment may not be appropriate for ethical and safety reasons. Latency carries risk because adequate warning of an imminent increase in symptoms does not occur at the time of testing. When a lasting increase in neurological symptoms is possible with neurodynamic testing. Uncertain that the nervous system will tolerate standard testing (level 2 examination). If performance of a level 1 examination is found to be safe and does not reveal suf? The therapist performs the usual neurodynamic tests and other mechanical tests for the musculoskeletal structures separately ie. This is instead of performing a differentiating movement that increases tension at the end of the neurodynamic test and so prevents further provocation of symptoms. Indications the problem is not particularly irritable Neurological symptoms are absent, or are only a minor part of the condition, and these neurological symptoms are not easily provoked the problem is reasonably stable and is certainly not deteriorating rapidly the pain is not severe at the time of examination, neither is there severe latency in terms of symptom provocation. Method the nervous system is effectively put through all its normal paces, but without combining neural tests with musculoskeletal ones. The test movements should not evoke excessive pain, neurological symptoms or go into a great deal of resistance. Standard neurodynamic tests are used Neural and musculoskeletal structures are examined separately Movement into some symptoms is acceptable, as long as they are not severe and settle down immediately after the test A degree of resistance may be encountered, however, it should not be strong Full range of movement may be reached but this is not essential. Level 3 Advanced General Description Testing of the nervous system is more extensive than the previous levels. Indications Level 2 (standard) examination tests are normal, or do not reveal suf? Only the sensitizing movements of the standard neurodynamic test are added to the standard test. Neurodynamic Sequencing (Localised) Description Local sequence movements start locally and become progressively more remote. Multistructural Description Neural structures are tested in combination with tests for musculoskeletal structures. Generally used in the person with high expectations in terms of human function in which minor mechanical problems will provoke symptoms more easily than in patients whose needs are less extensive. Often athletes, sports people and persons who work in occupational settings where high demands are a feature of their activities. Method the patient nominates their provoking symptomatic position/movement and performs that particular manoeuvre. Structural differentiation is used to make a distinction between neural and non neural structures and is an essential part of neurodynamic testing. As a reminder, it is when the nerves in the problem area are moved without moving the musculoskeletal tissues. Therefore, if the symptoms change with the differentiating manoeuvre, the symptoms are inferred to be neurogenic. In the non-neural response, the symptoms do not change with the differentiating movement. Change the tension in the nerves with side bending of the neck and, if the symptoms also change, the symptoms are likely to be neural. Therefore, we must now distinguish between normal neurogenic and abnormal neurogenic responses in our patients. Subthreshold micropulse diode laser photocoagulation for clinically significant diabetic macular oedema: a three-year follow up popular antibiotics for sinus infection purchase genuine bactrim. Prospective randomised controlled trial comparing sub-threshold micropulse diode laser photocoagulation and conventional green laser for clinically significant diabetic macular oedema antibiotics variceal bleed buy genuine bactrim on-line. Microperimetry and fundus autofluorescence in diabetic macular edema: Subthreshold micropulse diode laser versus modified early treatment diabetic retinopathy study laser photocoagulation antibiotic kill curve protocol order bactrim 960mg with amex. A randomized trial comparing intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide and focal/grid photocoagulation for diabetic macular edema taking antibiotics for acne while pregnant order discount bactrim line. Three-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing focal/grid photocoagulation and intravitreal triamcinolone for diabetic macular edema. Five-year results of a randomized trial with open-label extension of triamcinolone acetonide for refractory diabetic macular edema. Intravitreal triamcinolone plus sequential Grid laser versus triamcinolone or laser alone for treating diabetic macular edema: six-month outcomes. Pretreatment with intravitreal triamcinolone before laser for diabetic macular edema: 6-month results of a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Randomized trial of peribulbar triamcinolone acetonide with and without focal photocoagulation for mild diabetic macular edema: a pilot study. Safety of an intravitreal injection of triamcinolone: results from a randomized clinical trial. Severe steroid-induced glaucoma following intravitreal injection of triamcinolone acetonide. Randomized controlled trial of an intravitreous dexamethasone drug delivery system in patients with diabetic macular edema. Sustained ocular delivery of Fluocinolone acetonide by an intravitreal insert Ophthalmology 2010 Jul;117(7):1393-9. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the vitreous of eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Randomized Trial Evaluating Ranibizumab Plus Promptor Deferred Laser or Triamcinolone Plus Prompt Laser for Diabetic Macular Edema. Meta-analysis and review on the effect of bevacizumabin diabetic macular edema Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2011) 249:15?27 38. Systematic review of intravitreal bevacizumab injection for treatment of primary diabetic macular oedema. Primary Intravitreal Bevacizumab for Diffuse Diabetic Macular Edema: Pan American Collaborative Retinal Study Groupat 24 months. Intravitreal bevacizumab with or without triamcinolone for refractory diabetic macular edema; a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Randomized trial of intravitreal bevacizumab alone or combined with triamcinolone versus macular photocoagulation in diabetic macular edema. Intravitreal bevacizumab and/or macular photocoagulation as a primary treatment for diffuse diabetic macular edema. An exploratory study of the safety, tolerability and bioactivity of a single intravitreal injection of vascular endothelial growth factor Trap-Eye in patients with diabetic macular oedema. Effect of ruboxistaurin on the visual acuity decline associated with long-standing diabetic macular edema. Single-session vs multiple-session pattern scanning laser panretinal photocoagulation in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: the Manchester Pascal Study. Prevention of vision loss after cataract surgery in diabetic macular edema with intravitreal bevacizumab: a pilot study. Phacoemulsification with intravitreal bevacizumab and triamcinolone acetonide injection in diabetic patients with clinically significant macular edema and cataract. Prophylactic intravitreal bevacizumab for diabetic macular edema (thickening) after cataract surgery: prospective randomized study. Intravitreal steroid treatment (preservative-free) combined with post-treatment argon laser treatment may be considered particularly in pseudophakic patients, but bearing in mind the risk of raised intraocular pressure (Level B). For those patients who have been unresponsive to other treatment, the intravitreal fluocinolone implant may be considered but taking into consideration the side-effect profile (Level B). In the absence of robust evidence, intravitreal injections by non-medical staff should be limited to research. After year 1, the period of time between follow-up appointments may be gradually increased if the eyes are stable off treatment, to a maximum of 12-16 weeks in years 2-3. Vitrectomy surgery is used to achieve specific goals, which may limit or halt the progress of advanced diabetic eye disease. To remove vitreous opacity (commonly vitreous haemorrhage, intra-ocular fibrin, or cells) and/or fibrovascular proliferation (severe extensive proliferative retinopathy and/or anterior hyaloidal fibrovascular proliferation). To allow completion of panretinal laser photocoagulation (with the endolaser, introduced into the vitreous cavity or with the indirect laser ophthalmoscope), or direct ciliary body laser photocoagulation. Peripheral cryoptherapy may sometimes be used to ensure extensive peripheral retinal ablation. Simple vitreous haemorrhage occurs in the absence of other intravitreal pathology. The need for supplemental laser photocoagulation where indicated should also be considered. Mild vitreous haemorrhage -where ophthalmoscopic examination and confirmation of an attached retina is possible often clears within a matter of days to weeks. Patients with type 2 diabetes are less likely to have severe progressive proliferative retinopathy. Over the last few years the threshold for surgical intervention has progressively decreased. These patients should nonetheless have surgery within 3 months from onset of persistent non-clearing vitreous haemorrhage or earlier in the presence of multiple recurrent vitreous haemorrhages in spite of adequate laser treatment. Regular weekly ultrasonographic examinations are required to ensure early detection of retinal detachment, and clinical biomicroscopy and applanation tonometry to detect iris or irido-corneal angle neovascularisation, or haemolytic/ghost cell glaucoma, while awaiting spontaneous clearing of haemorrhage or vitrectomy surgery. Surgical Goals and Procedure For non-clearing or significant vitreous haemorrhage the surgical goal is to remove the vitreous opacity through a 3-port pars plana vitrectomy procedure. Usually it takes the form of a diffuse vitreous haze generated by widespread fibrin deposition. Clearance is associated with spontaneous fibrinolysis which is often delayed in patients with diabetes. In all cases where the retina cannot be adequately visualised, it is essential to confirm the absence of underlying retinal detachment with ultrasonography. If cavity haemorrhage does not start to clear within the first few post-operative weeks (3-4 120 weeks), revision surgery with vitreous cavity lavage and possible supplemental endolaser should be considered. Surgery normally requires a 3-port pars plana vitrectomy to allow an adequate internal search for the source of bleeding. In particular, examination of the previous entry sites is important to search for possible bleeding sources, and top up endolaser is indicated if previous laser treatment is found to be inadequate. Cryotherapy to areas immediately posterior to the entry sites may also be considered. Limitation of blood to this site indicates incomplete vitreous detachment, providing a ready surface for continued forward proliferation of the new vessels and risk of tractional retinal detachment. Indications for vitrectomy in this type of haemorrhage include severe visual loss (for example inmonocular only eye cases), failure of regression or resumption of haemorrhage after supplemental laser photocoagulation and the presence of significant subhyaloid pre-macular haemorrhage in eyes with good preexisting panretinal laser photocoagulation or the suspicion of underlying treatable macular oedema. Haemorrhage is removed, residual membrane dissected and supplemental panretinal endolaser photocoagulation is placed if needed. Long standing cases are more likely to require significant membrane dissection with its attendant risk of iatrogenic retinal break formation. Tissue-dyes are now used to highlight the presence and extent of gliotic epiretinal tissue thus facilitating its complete removal in a safer way while reducing the risk of intraoperative iatrogenic retinal breaks. After a vitrectomy for diabetic vitreous haemorrhage, ghost cell glaucoma should be suspected in patients with 121 12 elevated intraocular pressure in the early post-operative period (2-6 weeks). It is important to differentiate this condition from steroid induced glaucoma, since many of these patients may also be using topical steroid drops. The physical signs of fine pigmented cells and flare in the anterior chamber indicate ghost cell glaucoma, however this appearance may be subtle. Ghost cell glaucoma is particularly common if vitrectomy is performed for removal of dense vitreous haemorrhage (ochre membrane). If the intra-ocular pressure remains elevated despite medical therapy after one to three weeks, surgery should be considered. Traction retinal detachment involving the macula is a main indication for vitrectomy surgery and should be carried out at the earliest possible irrespective the duration of the macular involvement. Additional information: |