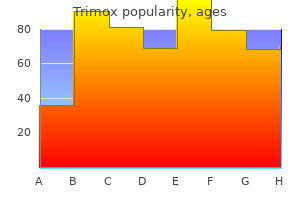
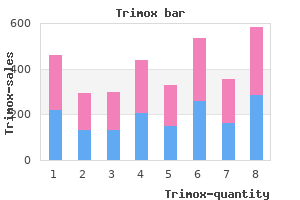
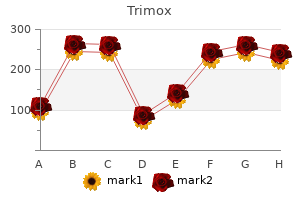
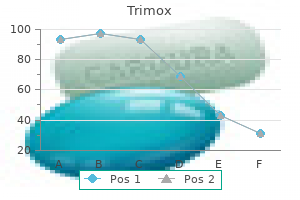
Louis Flancbaum, M.D., FACS, FCCM, FCCP
Most behavioural factors at the individual level are not found to be major determinants of the diarrhoeal diseases bacterial overgrowth discount trimox 500 mg without a prescription, when explored through a holistic epidemiology frame antibiotics used for diverticulitis buy generic trimox 250 mg on-line. A primary survey of 300 households was conducted and determinants at the household level were analysed antibiotics hives cheap trimox online mastercard. Storing of municipal water treatment for uti naturally buy trimox 250mg amex, considered among best storage practice did not prove to produce lower incidence of diarrhoeal diseases. Therefore it was found that major factors were external to the home, and beyond the immediate control of the household. The paper traces a study conducted in low-income localities in Delhi on the health damages incurred in urban households by adopting an approach involving health production function. The probability of illness in the household was calculated from a model for valuing damages from contaminated water supplies. Some of the conclusions of the study is that improvement in water quality lowers incidences of waterborne diseases. There are also traces of evidences to suggest that infrastructural variables such as garbage disposal and removal, water supply and sanitation play a key role in diarrhoea prevention. The data primarily answers the following question: (a) Whether the progress is time-bound? The data consists of quantitative information about outpatients and inpatients, of medical tests and malaria mortality, all between 2001 and 2006. Malaria is the eighth-highest contributor to the global disease burden, and the section dealing with the disease burden contains material on indirect and comorbid risks. Interventions that have been tried out so far are discussed along with their effectiveness. The Roll Back Malaria Campaign in 2005, has been chosen as a case study and explained. The chapter concludes that existing strategies need to be employed more effectively, and deployed more widely. Snow, Jo-Ann Mulligan, Christian Lengeler, Kamini Mendis, Brian Sharp, Chantal Morel, Paola Marchesini, Nicholas J. Water Supply, Sanitation, Hygiene and Health It is an established fact that public supply of water and public health are intrinsically linked to each other. Easy access to clean water can raise the public health standards of a certain area. In the developing water, water availability and sanitation patterns are different for urban and rural areas, which in turn has a huge bearing on the public health in these areas. This is especially in relevance to South Asia, where rural areas have different socio-economic dynamics from urban areas. Instead of policy attention given to rural areas, water and sanitation coverage is poor compared to urban areas. The paper goes into an in-depth discourse on water supply, sanitation and hygiene promotion in the following areas: levels of service and costs, policy implications and its direct health effects. Evans, Prabhat Jha, Anne Mills and Philip Musgrove (eds), Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries, pp. The case studies are documentations of model projects and their innovative approaches to the age old issues of rural sanitation. The document also seeks to analyse the successes and failures, and how these can be integrated in upcoming projects. The case studies deal with behavioural change, health campaigns, sewerage schemes, low cost toilet installation etc. Though difficult to operate and maintain, piped systems are important sources of water, and enable us to provide treatment facilities in ensuring safe supply of drinking water. Drinking water distributing systems are breeding grounds for microorganisms, however these are not major threats to public health. While there are no long-term health effects from the survival of pathogens, there is potential for the organisms to accumulate and persist within biofilms. Coli must be routinely monitored, and a holistic approach should be adopted in designing, operating and maintaining procedures. The publication is meant to reach out to a wider audience, than just water experts, planners and researchers. This publication looks at four key areas that impact all water and sanitation programmes around the world and particularly in India, viz, coverage, technology, behavioural change and partnerships. This report reviews priorities in national goals in drinking water and sanitation by analysing data and information to put together a report for assessment at the global level. It will also clarify any discrepancies in data and information and to provide information on national issues. The report also attempts to support reform and provide technical guidance to specific research and development and to draw more attention from investors to this sector. The study has been conducted in major cities in India, and the paper includes basic health issues due to improper water and sanitation, as well as an international perspective. Diseases have also been classified on the basis of transmission route and disease groups. The report concludes by describing key problem areas and basic maladies and includes recommendations for a future course of action to strengthen collaboration, training, legislations and information systems. There is quite a debate around what constitute appropriate and effective interventions in developing countries. Communication campaigns can go a long way in straightening weak links between health and water. Youngblood (eds), Water Stories: Expanding Opportunities in Small-Scale Water and Sanitation Projects, pp. The social investment is found to positively affect people in terms of poverty, health, longevity, education and environment quality. Taking up two factors; poverty and health, for valuation by case study method, the researcher uses two villages from Kerala. The study found that the averted annual public expenditure per household because of no waterborne and sanitation illness is Rs. Therefore the study proves that there are numerous benefits from water supply, sanitation and hygiene education. It also describes why these linkages are important and how they can be better managed. The publication also dwells into associated risks and benefits of the linkages between wetlands and water, sanitation and hygiene. Disasters, Water and Health Disasters are a recent addition to the study of natural resources management. One of the consequences of climate change has been the increase in the incidence of natural disasters. Disasters result in death, displacement, loss of livelihood, widespread destructions, but also have alarming and far reaching effects on human health. Disasters may result in different types of injury, communicable diseases (that have a greater chance of spreading, because of abnormal living conditions), acute illnesses, chronic illnesses and psychological effects. It describes priority measures to prevent and reduce disease impact in the post disaster time zone. The prevention is classified under the following headings: safe water, sanitation and site planning; Primary health-care services, Surveillance/ early warning system, immunization and prevention of malaria and dengue. It has sections on its institutional and policy framework and how it will prevent or mitigate disasters, and finally, how it will manage a disaster, if it has happened. The document provides guidelines for future emergency preparations, to other development agencies. The document covers the following aspects: staff safety, programme readiness, operations readiness, collaborative arrangements and capacity building. It also indicates its qualitative and quantitative needs in terms of human resources, funds and equipment, in order to achieve this vision. The strategies proposed are structured along the following themes: Policy, Institutional Mandates and Institutional Development; Hazard, Vulnerability & Risk Assessment, Multi-hazard Early Warning Systems; Disaster Preparedness Planning and Response; Disaster Mitigation and Integration into Development Planning; Community based Disaster Management; and Training, Education and PublicAwareness. Water Resource Management and Health Increasing rates urbanisation, deforestation and dam construction cause ecological changes leading to increase in vector density, and in turn transmission of vector-borne diseases.
Most patients require some form of non invasive testing for coronary artery disease virus taxonomy purchase trimox 500mg on line. Those 50 years should be screened for bowel neoplasia by stool occult blood or colonoscopy infection 2 cheap 250mg trimox mastercard. The evaluation of renal trans plantation candidates: clinical practice guidelines bacteria that causes pneumonia order cheap trimox on line. Transplantation across previously incompatible immunological Contraindications to renal transplantation include any barriers 51 antimicrobial effectiveness testing order trimox 500 mg free shipping. Deceased-donor characteristics major morbidity that would be worsened by transplant and the survival bene? The most effective means for diagnosing early when breast cancer is obviously present. Thus a nega breast cancer is screening mammography in combina tive mammogram does not replace the need for bi tion with physical examination. If needle biopsies are performed in the United States annually; biopsy shows a breast mass to be benign, conservative 11%?36% of biopsies performed for mammographically follow-up with physical examination and mammogra identi? This has led to the recommendation for performed with an 18 to 22-gauge needle with local clinical and mammographic observation rather than anesthesia. A preoperative bone scan is indi skin or nipple retraction, nipple eczema), (2) before cated only if the patient has symptoms that are suspi breast surgery (biopsy, augmentation, reduction), cious for bony metastasis. Clinical staging includes careful inspection tive mammography is performed (1) to characterize a and palpation of the skin, breast, and lymph nodes lesion as obviously benign (lipoma, oil cyst, calci? Pathologic staging lesion for adequate excision and treatment selection includes data used for clinical staging, surgical resec (especially important in a patient for whom conserva tion, and a pathologic examination of the primary car tive surgery and irradiation are being considered be cinoma. Pathologic staging can now be performed if cause multicentric disease in the affected breast is a the primary tumor is removed with no growth tumor in contraindication to this procedure), (3) to detect ad the margins and, in addition, if at least the lowest level ditional lesions in the ipsilateral or contralateral (1) of axillary lymph nodes is resected, rather than all breast, and (4) to obtain a baseline for comparison three levels. One struation report premenstrual symptoms, ranging from way is to ask the patient to list the symptoms that affect negligible in many women to disabling in up to 15%. It is the cyclic occurrence of symptoms begin Review of treatment research fails to demonstrate ning near or after ovulation and resolving soon after consistently effective therapy, and the rate of re the onset of menses that is of diagnostic signi? Initial interventions cant enough to interfere with work, school, or usual are education and support, stress reduction, healthy social activities or relationships with others. Many women are re ovarian steroids, prolactin, prostaglandins, mineralo assured by chart review and can plan their schedules corticoids, neurotransmitters, endogenous opiates, vi according to symptom severity, use relaxation exer tamin and mineral de? Neither history to rule out cardiac, renal, or thyroid disease, natural progesterone (in suppository or micronized collagen vascular disease, and diabetes. Consider further changes in hormone levels, prolactin, aldosterone, en evaluation or referral when the diagnosis is uncertain, dorphins, and glucose tolerance. Hyphema, 28 Infections, Hypertension Hypoactive sexual desire, 16 multiple pulmonary nodules, 498 High fever, 166 Hypoalbuminemia, 132 neutrophilia, 240 High index of suspicion, 656 Hypocalcemia, 132 postobstructive, 636 High urinary uric acid, 542 Hypochondriacal concern, 668 postoperative, 700 High-amplitude esophageal contractions, 178 Hypochondriacal reaction, 666 prophylaxis against, 319 High-density lipoprotein, 4 Hypochondriasis, 668 rhinitis, 32 High-dose prednisone, 402 Hypocitraturia, 364 sexually transmitted diseases, 314?317, High-dose statins, 68 Hypogeusia, 458 566, 584, 620 High-? Get superb visual guidance with exceptionally clear illustrations, Getting started diagnostic images, and step-by-step To start browsing, use the table of contents on the surgical photographs. Clicking the chapter or section title itself Website Features will take you to that section. Alternatively, search Consult the book from any computer the book using the search function above, or look at home, in your office, or at any up a term in the complete index. For further information on Expert Consult, view a Instantly locate the answers to your demo of the site. First edition 1997 Second edition 2005 No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. This book and the individual contributions contained in it are protected under copyright by the Publisher. Practitioners and researchers must always rely on their own experience and knowledge in evaluating and using any information, methods, compounds, or experiments described herein. To the fullest extent of the law, neither the Publisher nor the authors, contributors, or editors, assume any liability for any injury and/or damage to persons or property as a matter of products liability, negligence or otherwise, or from any use or operation of any methods, products, instructions, or ideas contained in the material herein. Close Print Page Krachmer > /Preface/ Close Print Page Preface In the age of instantaneous electronic information, a bound textbook may seem to some, perhaps, anachronistic. We, and even more so, our residents and fellows are accustomed to finding quick facts and lengthy lists of citations with but a few key strokes at the computer. Indeed, there are some advantages to modern day electronic texts universal access in spite of time of day or location, portability, rapidity of information access, and the ability to do complex Boolean searches in moments. For these very reasons, this edition is made available in an electronic format as well as the print version. At the same time, a multi-authored text which has been forged through the process of gathering the best minds in the field, written and rewritten through a laborious and meticulous editing process, and presented as a comprehensive and authoritative source that can be turned to repeatedly is highly desirable as a bound document codifying the current state of our knowledge in one place. The practice of our subspecialty in ophthalmology is more diversified than ever before. The proliferation of new surgical procedures targeted to specific corneal abnormalities, a variety of new diagnostic testing capabilities, and a dramatic broadening of our understanding of the pathophysiology of the cornea and ocular surface have revolutionized what we know about the remarkable structure through which we view the world. We hope that this book will continue to serve as a useful tool to all students and practitioners in our field, both in print and electronic forms. Close Print Page Krachmer > /Acknowledgments/ Close Print Page Acknowledgments these volumes are the result of the very hard work and thoughtful contributions of many people. First and foremost, we thank the contributing authors who provided extensive updates of previous work and a wealth of new material in this edition and who were so responsive to the demands of the editorial process. In addition, we cannot adequately thank Sharon Nash and Russell Gabbedy at Elsevier for their guidance, efficiency, responsiveness, resilience and good humor in the process of birthing this text. And as always, we thank our families who gave up so much time with us so that this book could be written. Close Print Page Krachmer > /Dedication/ Close Print Page Dedication To my wife, Kathryn our children, Edward, Kara, and Jill our parents, Paul and Rebecca Krachmer and Louis and Gertrude Maraist with great love and appreciation Jay H Krachmer To my sister, Libby, and in memory of my brother, Norman Mark J Mannis To my wife, Lynette who is a great partner and always supportive and our children, Colson, Kelsey and Natalie who keep me entertained, challenged and grounded Edward J Holland Copyright 2011 Elsevier Inc. Boyden, Endowed Chair Health Science Clinical Professor of Ophthalmology Research Associate, Francis I. Close Print Page Krachmer > Volume 1 Fundamentals and Medical Aspects of Cornea and External Disease > Part I Basic Science: Cornea, Sclera, Ocular Adnexa Anatomy, Physiology and Pathophysiologic Responses > Chapter 1 Cornea and Sclera: Anatomy and Physiology > /Fundamentals and Medical Aspects of Cornea and External Disease/Introduction Close Print Page Volume 1 Fundamentals and Medical Aspects of Cornea and External Disease Part I Basic Science: Cornea, Sclera, Ocular Adnexa Anatomy, Physiology and Pathophysiologic Responses Chapter 1 Cornea and Sclera : Anatomy and Physiology Teruo Nishida, Shizuya Saika Introduction the avascular cornea is not an isolated tissue. It forms, together with the sclera, the outer shell of the eyeball, occupying one-third of the ocular tunic. Although most of both the cornea and sclera consist of dense connective tissue, the physiological roles of these two components of the eye shell differ. The cornea serves as the transparent window? of the eye that allows the entry of light, whereas the sclera provides a darkbox? that allows the formation of an image on the retina. The cornea is exposed to the outer environment, whereas the opaque sclera is covered with the semitransparent conjunctiva and has no direct exposure to the outside. The differences in the functions of the cornea and sclera reflect those in their microscopic structures and biochemical components. Interwoven fibrous collagen is responsible for the mechanical strength of both the cornea and sclera, protecting the inner components of the eye from physical injury and maintaining the ocular contour. Together with the cellular and chemical components of the conjunctiva and tear film, the corneal surface protects against potential pathological agents and microorganisms. The regular arrangement of collagen fibers in the corneal stroma accounts for the transparency of this tissue. A functionally intact corneal endothelium is important for maintenance of stromal transparency as a result of regulation by the endothelium of corneal hydration. Close Print Page Krachmer > Volume 1 Fundamentals and Medical Aspects of Cornea and External Disease > Part I Basic Science: Cornea, Sclera, Ocular Adnexa Anatomy, Physiology and Pathophysiologic Responses > Chapter 1 Cornea and Sclera: Anatomy and Physiology > //Anatomy and Physiology Close Print Page Anatomy and Physiology Structure of the cornea and sclera the anterior corneal surface is covered by the tear film, whereas the posterior surface is bathed directly by the aqueous humor. The highly vascularized limbus, which is thought to contain a reservoir of pluripotent stem cells, constitutes the transition zone between the cornea and sclera. The adult human cornea measures 11 to 12 mm horizontally and 9 to 11 mm vertically. The refractive power of the cornea is 40 to 44 diopters, constituting about two-thirds of the total refractive power of the eye. The sclera, a tough and nontransparent tissue, shapes the eye shell, which is approximately 24 mm in diameter in the emmetropic eye. The nontransparency of the sclera prevents light from reaching the retina other than through the cornea, and, together with the pigmentation of the choroid and retinal pigment epithelium, the sclera provides a dark box for image formation. The scleral spur is a projection of the anterior scleral stroma toward the angle of the anterior chamber and is the site of insertion for the anterior ciliary muscle. At the posterior pole of the eyeball, where the optic nerve fibers enter the eye, the scleral stroma is separated into outer and inner layers.
However infection 17 quality trimox 250 mg, the clinician has an important role in facilitating initial investigations and management of the acutely jaundiced patient antibiotic resistance animation ks4 purchase 250 mg trimox with amex. Simultaneous bacteriologic assessment of bile from gall bladder and common bile duct in control subjects and patients with gallstones and common duct stones antibiotic resistance controversy purchase trimox 500 mg mastercard. Clinical evaluation of jaundice: a guideline of the Patient Care Committee of the Ameri can Gastroenterological Association antibiotics for dogs after teeth cleaning buy 500mg trimox with mastercard. Malignant perihilar biliary obstruction: magnetic resonance cholan giopancreatographic? Bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract is approxi mately four times more common than bleeding from the lower gastrointestinal tract (Fallah et al. Haemoglobin (Hb) value and blood type and cross-match of 2?6 units of blood should be ordered immediately. A platelet count of less than 50 with active bleeding requires platelet transfusion and fresh frozen plasma in an attempt to replete the lost clotting factors. Endoscopy Endoscopy should be performed within 24 h to discover whether the bleeding is variceal (from an oesophageal or gastric varix) or not. A total score of less than 3 is associated with an excellent prognosis, while a score above 8 is associated with a high risk of death. Resuscitation Resuscitation should precede further diagnostic and therapeutic measures. Management of patients with non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding 155 Endoscopic haemostasis Endoscopic haemostasis has been shown to signi? Injection of 1 : 10 000 adrenaline solution in normal saline in quadrants around the bleeding point, and then into the bleeding vessel, using a total of 4?16 mL: this approach achieves primary haemostasis in up to 95 per cent of patients, although bleeding will recur in 15?20 per cent of these patients. However, there is no consensus regarding the recommended dose or frequency of these substances. The combination of injection and ther mal coagulation is superior to either treatment alone (Barkun et al. Laser therapy is no longer used because of its high cost and the poor portability of equipment. Management following endoscopy Although routine second-look endoscopy is not recommended (Barkun et al. There are no convincing data to support the use of H2 receptor antagonists (Palmer, 2002). Surgery Patients who continue to actively bleed after endoscopy require urgent surgery. Early surgical consultation in patients at high risk of rebleeding and for those who rebleed after endoscopic therapy is indicated. Timing of an operation should, if possible, avoid the hours between mid night and 7 a. Vagotomy with antrectomy is reserved for patients who rebleed after simple under-running of the duodenal ulcer and for those with other ulcer complications such as gas tric outlet obstruction. Highly selective vagotomy with anatomical closure of the duodeno stomy or the pyloroduodenostomy in order to preserve the normal pyloric sphincter muscle is an operation reserved for young, stable, low-risk patients with a low risk of recurrent ulcer rate (< 10% at a mean follow-up of 3. The surgical management of bleeding gastric ulcer is slightly different and should exclude malignancy as well as control and prevent recurrent bleeding or ulceration. Alternative options include wedge resection of the ulcer with or without truncal vagotomy and drainage procedure. The type of operative approach relies on the location of the ulcer and the patient?s? Ulcer biopsy and oversewing, thus leaving the ulcer in situ, carries a high risk of rebleeding (20?40%) (Corson and Williamson, 2001) but may be jus ti? Arterial embolisation this is an effective option to control massive bleeding from peptic ulcers in patients with failed endoscopic therapy and in poor surgical candidates. Management of other causes of non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding 157 Follow-up? Test for and eradicate Helicobacter pylori in order to prevent rebleeding (Barkun et al. It is critical to distinguish Mallory?Weiss tear from Boerhaave syndrome, which represents a full-thickness laceration with perforation of the oesophagus. If bleeding from a Mallory?Weiss tear is visualised at endoscopy, then electrocoagulation, heater-probe application and sclerotherapy are viable options. The overall mortality rate of patients who require emergency surgery is 15? 25 per cent, in contrast to less than 3 per cent in those whose bleeding stops by the time of ini tial endoscopy. Endoscopi cally, the lesion appears as a large submucosal vessel that has become ulcerated; the bleeding can be massive and brisk. Endoscopic management options include contact thermal ablation with heater probe (with or without prior injection with adrenaline) as? Rebleeding after endoscopic therapy occurs in 15 per cent of patients and can be managed in most cases by repeated endoscopy with suture ligation or, more preferably, surgical excision of the lesion reserved for endoscopic failures. Histologically, angiodysplasias are dilated, thin-walled vascular channels that appear macroscopically as a cluster of cherry spots. Angiodysplasia can be acquired or con genital, as in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia and Rendu?Osler?Weber syndrome (an autosomal dominant disorder typically identi? Most lesions are smaller than 1 cm in diameter; they are multiple in two-thirds of patients. These lesions may be readily eradicated endoscopically with contact heater probes, argon plasma coagulation, or band ligation with surgery reserved for endoscopic failure. When the diagnosis is unknown and a vascular lesion is suggested, combined hormonal ther apy with oestrogen and progesterone may be bene? Patients usually present with self-limiting sentinel bleeding followed by exsanguinating massive gastrointestinal bleed. Emergency surgery to remove the aortic graft and debride and close the duodenum and the aorta, followed by bilateral extra-anatomic vascular bypass. All bleeding episodes regardless of severity should be counted in evaluating rebleeding. Failure to control bleeding within 6 h: this is represented by a transfusion requirement of 4 units of blood or more and inability to achieve an increase in systolic blood pressure by 20 mmHg or to 70 mmHg or more, and/or inability to achieve a pulse rate reduction to less than 100 beats/min or a reduction of 20 beats/min from baseline pulse rate. Development of varices the rise in portal pressure is associated with the development of collateral circulation that allows the portal blood to be diverted into the systemic circulation. The two factors that appear to determine the development of varices are continued hepatic injury and the degree of portosystemic shunting. The factors that predispose to and precipitate variceal haemorrhage are still not clear. The literature varies in its scoring of the rel evance of this point, due largely to the lack of clear de? These features represent changes in variceal wall structure and tension associated with the development of micro-telangiectasias. The two most important factors that determine the risk of variceal bleeding are the severity of liver disease and the size of the varices. The average mortality from a subsequent variceal haemorrhage is 5 per cent in Child class A patients, 25 per cent in Child class B patients and 50 per cent in Child class C patients. Control of active variceal bleeding the following summarises the management recommendations for control of active variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis: ? Treatment should ideally be undertaken by a dedicated appropriately equipped and staffed unit. Intravenous octreotide, a synthetic analogue of somatostatin, is often begun as soon as the diagnosis is certain. The potential side effects of vasopressin are primarily cardiovascular and increase with higher doses. The control of bleeding with this com bination therapy is superior to that achieved with vasopressin alone. An alternative to vasopressin for control of variceal haemorrhage is the synthetic analogue terlipressin (1?2 mg, depending on body weight, given by bolus every 4 h for 2?5 days); this is more effective than vasopressin. The most commonly used drug for treating variceal bleeding is somatostatin (an ini tial bolus of 250?
Cardiopulmonary monitoring and/or polysomnography: Continuous assessment of oxygenation and ventilation (especially for recurrent events or unusual apnea) infection 2 months after surgery discount trimox 500mg visa, rule out obstructive apnea c antibiotics for acne on back order trimox overnight delivery. Barium swallow pH probe: dysfunctional swallow antibiotic 30s ribosomal subunit buy cheap trimox, upper airway obstruction can antibiotics for acne delay your period buy cheap trimox 500mg line, gastroesophageal refux d. These episodes are usually associated with lower airway airfow obstruction, reversible either spontaneously or with therapy. The infammation also causes increased airway hyperreactivity to a variety of stimuli (viral infections, cold air, exercise, emotions, as well as environmental allergens and pollutants). Cough, increased work of breathing (tachypnea, retractions, or accessory muscle use), wheezing, hypoxia, and hypoventilation 2. No audible wheezing may indicate very poor air movement and severe bronchospasm 3. Chest radiographs often show peribronchial thickening, hyperinfation, and patchy atelectasis a. Attempt to minimize asthma triggers and environmental exposures, including tobacco smoke 4. Assess symptom control, inhaler technique, and medication adherence with regular clinical evaluations 5. Recommended Step 3 and consider step for initiating Step 1 Step 2 short course of oral therapy systemic corticosteroids In 2?6 weeks, depending on severity, evaluate level of (See Fig. Risk requiring oral Frequency and severity may fluctuate over time systemic for patients in any severity category. Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 or 5 Recommended step for and consider short initiating treatment course of oral systemic corticosteroids (See Fig. Consider short course of oral systemic corticosteroids if exacerbation is severe or patient has history of previous severe exacerbations. All other recommendations are based on expert opinion and extrapolation from studies in older children. Steps 2?4: Consider subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy for patients who have allergic asthma (see notes). Key: Alphabetical order is used when more than one treatment option is listed within either preferred or alternative therapy. Clinicians who administer immunotherapy should be prepared and equipped to identify and treat anaphylaxis that may occur. Intensity of treatment depends on severity of symptoms: up to 3 treatments at 20-minute intervals as needed. Key: Alphabetical order is used when more than one treatment option is listed within either preferred or alternative therapy. Step 6 preferred therapy is based on Expert Panel Report 2 (1997) and Evidence B for omalizumab. Variable and dynamic course ranging from transient apnea and mucus plugging to progressive lower airway disease a. Should be strongly considered for patients <12 weeks, history of prematurity, underlying cardiopulmonary disease, or immunodefciency 2. Supplemental oxygen therapy for oxyhemoglobin saturation (SpO2) consistently low a. Consider maintaining higher SpO2 for those with fever, acidosis or hemoglobinopathies due to oxyhemoglobin desaturation curve or for increased work of breathing 3. A trial of bronchodilators is an option, but should be continued only if there is documented improved clinical response 4. Corticosteroids and antibiotics (unless signs of bacterial co-infection) should not be used routinely in bronchiolitis 5. Fluid support is often needed due to increased loses from tachypnea, fever, and poor oral intake a. Hold oral feedings in hospitalized tachypneic infants to minimize risk of aspiration C. Infants hospitalized for bronchiolitis are more likely to have recurrent wheezing 3. Thought to be a result of airway infammation, damage from hyperoxia, hypoxia, or mechanical ventilation, resulting in interference with normal lung alveolar and vascular development. Severity based on oxygen requirement at time of assessment and characterized as mild if on room air, moderate if requiring <30% oxygen, or severe if requiring >30% oxygen and/or positive pressure a. If gestational age at birth was <32 weeks: Assess infant at 36 weeks postmenstrual age or at discharge to home, whichever comes frst b. If gestational age at birth >32 weeks: Assess infant at 28?56 days postnatal age or at discharge to home, whichever comes frst B. Persistent respiratory symptoms, airway hyperreactivity, and supplemental oxygen requirements, especially during intercurrent illness 2. Often require interventions such as bronchodilators, anti-infammatory agents, supplemental oxygen therapy, and diuretics. Most patients have chronic progressive obstructive pulmonary disease, pancreatic exocrine insuffciency with protein and fat malabsorption, and abnormally high sweat electrolyte concentrations. Diagnosis Over half of patients are diagnosed by 6 months old and three-fourths by 2 years old. Quantitative pilocarpine ionoelectrophoresis (sweat chloride) test: Gold standard for diagnosis a. Indeterminant: (1) Infants <6 months: Indeterminant if 30?60 mEq/L (2) Children >6 months: Indeterminant if 40?60 mEq/L c. Clinical pearl: Elevated sweat chloride levels can be from other disorders including untreated adrenal insuffciency, glycogen storage disease type 1, fucosidosis, hypothyroidism, nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, ectodermal dysplasia, malnutrition, mucopolysaccharidosis, panhypopituitarism, or poor testing technique C. Nearly all males have absence of the vas deferens; however, assisted fertilization is possible using aspiration of viable sperm from the testes b. Women may have trouble becoming pregnant due to mucus associated obstruction of the cervix 4. Decreased life expectancy: Survival continues to improve and the median predicted survival age is over 37 years X. Alternate names include obstructive hypoventilation, upper airway resistance syndrome. Snoring sometimes accompanied by intermittent pauses in breathing, snorts, or gasps 2. Increased respiratory effort during sleep, disturbed or restless sleep with increased arousals and awakenings 3. Long-term complications include neurocognitive impairment, behavioral problems, poor growth, and systemic and pulmonary hypertension 5. Risk factors include adenotonsillar hypertrophy, obesity, craniofacial or laryngeal anomalies, central nervous system disease (including brainstem dysfunction or compression), cerebral palsy, and neuromuscular disease B. Refer to specialists for nocturnal polysomnography (sleep study) for patients with history of nightly or near nightly snoring, risk factors, and/ or daytime symptoms a. Thought to be caused when a genetically vulnerable infant is exposed to an exogenous stressor during a critical developmental period when there is immaturity of the cardiorespiratory system, autonomic nervous system, immune system, and arousal pathways together with a failure of arousal responsiveness from sleep. Examination of pulse oximetry in sickle cell anemia patients presenting to the emergency department in acute vasoocclusive crisis. Pulse oximetry is a poor predictor of hypoxemia in stable children with sickle cell disease. The pathophysiology of respiratory impairment in pediatric neuromuscular diseases. Statement on the care of the child with chronic lung disease of infancy and childhood. Guidelines for diagnosis of cystic fbrosis in newborns through older adults: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Report. Cystic fbrosis pulmonary guidelines: chronic medicines for maintenance of lung health. Obstructive sleep-disordered breathing in children: new controversies, new directions. Considerations unique to the pediatric population include an increased radiosensitivity of the thyroid gland, breast tissue and gonads. They also have a longer lifespan in which to manifest radiation-related cancer compared with adults. If signs of shunt malfunction are noted, radiographs of the length of the shunt (a shunt series) should follow to look for kinks or disconnections. Craniosynostosis Suture examination is best done initially with radiographs of the skull. Order trimox australia. Caya Costa ZipFront Sun Hoodie with UV Protection. |